Vertebrates Biology Reading Guide Chapter 34
advertisement

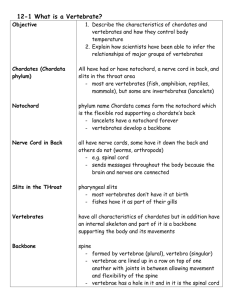
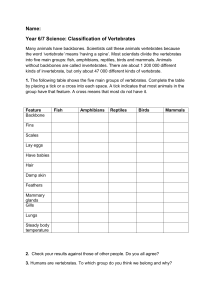
Name _______________________ Biology Reading Guide Chapter 34: Vertebrates Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Copyright © 2010 Chapter 34: Vertebrates Concept 34.1 Chordates have a notochord and a dorsal, hollow nerve cord 1. We are vertebrates. What phylum do we belong to? 2. Here is a figure showing the four key chordate characteristics. Label and explain each one. 3. One of the important characteristics is a notochord. What is a notochord? For us, as vertebrates, what remains of the notochord? 4. Pharyngeal gill slits develop into what structures in the fishes? Concept 34.2 Vertebrates are craniates that have a backbone 5. What is the oldest lineage of vertebrates? ___________________ They are jawless parasitic fish with a skeleton made of ___________________________. Concept 34.3 Gnathostomes are vertebrates that have jaws 6. What animals are in the clade Chondrichthyes? 7. What does the name Chondrichthyes mean? What material makes up their skeleton? 8. The “fishes” with a bone skeleton are aquatic Osteichthyes. 9. What is the function of a swim bladder? Concept 34.4 Tetrapods are gnathostomes that have limbs 10. What does tetrapod mean? 11. What animals are in the class Amphibia? What does the class name Amphibia mean? 12. What factors tie amphibians to a life near water? Concept 34.5 Amniotes are tetrapods that have a terrestrially adapted egg 13. What is an amniotic egg? How has it enabled animals to occupy a wider range of terrestrial habitats than amphibians can? 14. What groups have an amniote egg? 15. Label the four extraembryonic membranes seen in an amniotic egg, and explain the role of each one. 16. What is the body covering of a reptile? How does this enable it to live a more terrestrial life? 17. What is internal fertilization? How does this enable reptiles to reproduce on land? 18. Fishes, amphibians, and reptiles are ectothermic. What does this mean? 19. What are four avian adaptations for flight? Concept 34.6 Mammals are amniotes that have hair and produce milk 36. There are three groups of mammals. Contrast the groups based on how they bear young, and give an example. Mammalian Group Reproduction Example Monotremes Marsupials Eutherians 20. As a human, you are in the class Mammalia and the order Primates. What features are unique to primates only? Word Roots arch- = ancient (archosaurs: the reptilian group which includes crocodiles, alligators, dinosaurs, and birds) cephalo- = head (cephalochordates: a chordate without a backbone, represented by lancelets, tiny marine animals) crani- = the skull (craniata: the chordate clade that possess a cranium) dino- terrible; -saur = lizard (dinosaurs: an extremely diverse group of ancient reptiles varying in body shape, size, and habitat) endo- = inner; -therm = heat (endotherm: an animal that uses metabolic energy to maintain a constant body temperature, such as a bird or mammal) eu- = good (eutherians: placental mammals; those whose young complete their embryonic development within the uterus, joined to the mother by the placenta) gnantho- = the jaw; -stoma = the mouth (gnathostomes: the vertebrate clade that possesses jaws) homin- = man (hominid: a term that refers to mammals that are more closely related to humans than to any other living species) lepido- = a scale (lepidosaurs: the reptilian group which includes lizards, snakes, and tuatara) marsupi- = a bag, pouch (marsupial: a mammal, such as a koala, kangaroo, or opossum, whose young complete their embryonic development inside a maternal pouch called the marsupium) mono- = one (monotremes: an egglaying mammal, represented by the platypus and echidna) neuro- = nerve (neural crest: a band of cells along the border where the neural tube pinches off from the ectoderm) noto- = the back; -chord = a string (notochord: a longitudinal, flexible rod formed from dorsal mesoderm and located between the gut and the nerve cord in all chordate embryos) osteo- = bone; -ichthy = fish (Osteichthyans: the vertebrate clade that includes the rayfinned fishes and lobefins) ovi- = an egg; -parous = bearing (oviparous: referring to a type of development in which young hatch from eggs laid outside the mother’s body) paleo- = ancient; -anthrop = man; -ology = the science of (paleoanthropology: the study of human origins and evolution) pro- = before; -simi = an ape (prosimians: a suborder of primates that probably resemble early arboreal primates) soma- = body (somites: blocks of mesoderm that give rise to muscle segments in chordates) tetra- = four; -podi = foot (tetrapod: a terrestrial lobefin, possessing two pairs of limbs, such as amphibians, reptiles, and mammals) vivi- = alive (ovoviviparous: referring to a type of development in which young hatch from eggs that are retained in the mother's uterus)