Genetics Homework - s3.amazonaws.com
advertisement

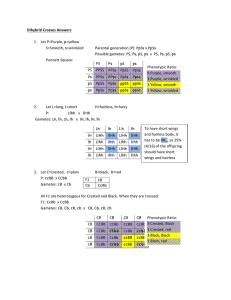
eScience Lab 14 – modified – Genetics Problems - Fall 2013, 20 pts. Assignment Instructions I will be posting an answer key online soon after this assignment is due. Due to the posting of the answers I will not accept this assignment after the key has been posted for any reason! No credit for late assignments after the key is posted! You may write or type your final answers on this sheet or on another page. Clearly mark each answer. I will not take the time to search through your work for an answer. You MUST show ALL work! (if you do not show or attach your work I won’t grade it). □ If you are submitting this online you can scan in your work, type up your work, take pictures of your work, or submit it to the instructor in person! Before you start you might want to look at the “practice genetics problems” or the videos of how to work through genetics problems, all posted with chapter 10 on D2L. If you are struggling with these problems this means you need a bit more practice first and the practice problems in D2L or the PowerPoint Lecture will help. **Don’t forget to underline your lowercase letters if you are writing this by hand!!** 1. (3pts) In a flower, yellow petals (Y) are dominant to blue petals (y). a. Complete a Punnett Square of the following cross (fill in the edges and the insides of the square. Yy x Yy Y y YY Yy Yy yy Y y 1 b. What is the resulting genotype ratio of this cross? 1 (YY) : 2 (Yy) : 1 (yy) c. What is the resulting phenotype ratio of this cross? 3 (yellow) : 1 (blue) 2. (4pts) In corn plants having a green color (G) is dominant to being albino (white) (g). Examine the picture and answer the following questions. a) Approximately how many green plants do you count? (I know it is hard to see them all, do your best) 25 b) Approximately how many albino (white) plants do you count? 8 c) Which ratio would you say most closely approximates these observed results? ¼ green: ¾ white, ¾ green : ¼ white, ½ green : ½ white. d) Using the ratio you determined and the information given at the beginning of this problem, determine the genotypes of the parents of your corn kernels. Support your answer with a Punnett square showing the correct offspring ratio! . Hint: start with a guess – do the Punnett square for your guess and then go from there. Only one combination of parent genotypes will result in the correct offspring ratio. Parents genotypes Gg Punnett square: x Gg 2 G g GG (green) Gg (green) Gg (green) gg (white) G g 3. (4pts) Dihybrid Cross. You will now look at 2 traits at once. On a cob of corn, each kernel (seed) that you see is ONE offspring. The picture you see below is of corn kernals that all resulted from the cross of the same 2 parent corn plants. Purple kernals (P) are dominant over yellow kernals (p), and Smooth seeds (S) are dominant over wrinkled seeds (s). There are four grain phenotypes in the picture of the ear of corn for this activity. Purple and smooth (A), Purple and wrinkled (B), Yellow and Smooth (C), Yellow and wrinkled (D). Take a minute to find these four phenotypes. a) Using the picture below, count the number of kernels in each of these categories and record your results below the picture. 3 Purple & smooth 85 Purple & wrinkled 28 Yellow & smooth 30 Yellow & wrinkled 10 b) Now determine the ratio of seeds in each category. To do this take your smallest number above (should be the Yellow and wrinkled) and divide each larger number by this smallest number. Purple & smooth 8.5 Purple & wrinkled 2.8 Yellow & smooth 3 Yellow & wrinkled __1____ c) I will also tell you that the above results were obtained from crossing 2 plants that were heterozygous for both traits. Write the genotype for a parent corn plant that is heterozygous for both traits. PpSs d) Now set up a Punnett square showing the cross of the 2 heterozygous parents that resulted in the offspring you see on your ear of corn. You will FIRST have to figure out the gametes produced by each parent plant (4 different ones each) and write these along each side of the square. See PowerPoint for help on this! PS PS pS Ps ps PpSS PPSs PpSs ppSS PpSs ppSs PpSs PPss Ppss ppSs Ppss ppss PPSS pS Ps ps PpSS PPSs PpSs 4. (3pts) Inheritance of a trait that results in a heterozygous phenotype that is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes is called incomplete dominance. The Allele for curly hair (H1) has incomplete dominance with the allele for straight hair (H2). Wavy haired people do not actually have a gene for “wavy hair”. Instead they are heterozygous and carry one copy of the allele for straight hair and one copy of the allele for curly hair. A). If a wavy haired woman has children with a wavy haired male, what is the expected genotype ratio and expected phenotype ratio of their offspring in regards to hair texture? Support your answer with a Punnett square. 4 H1 H1 H2 H2 H1H1 (straight) H1H2 (wavy) H1H2 (wavy) H2H2 (curly) Expected genotype ratio: 1 (H1H1) : 2 (H1H2) : 1 (H2H2) Expected phenotype ratio: 1 (straight) : 2 (wavy) : 1 (curly) 5. (3 pts) Hemophilia is an X-linked condition. A person with the disease hemophilia has blood that does not clot normally. Normal blood clotting is dominant and Hemophilia is recessive. Ahmed is a male who has hemophilia. Ahmed is worried about what would happen if he marries a woman who has normal blood clotting also but who is a carrier of the Hemophilia allele. A) What is Ahmed’s genotype? (use proper X-linked notation!) XhY B) What would be the genotype of a woman who is a carrier for hemophilia? (use proper X-linked notation!) XHXh C) Show a Punnet square for the possible offspring from the genotypes in parts A and B. XH Xh Xh Y XHXh (female, carrier) XHY (male, normal) XhXh (female, affected) XhY (male, affected) D) What proportion of boys would you expect to have hemophilia from parents of these two genotypes? 1/2 E) What proportion of girls would you expect to have hemophilia from parents of these two genotypes? 1/2 6 (3 pts) Susan has TYPE AB blood and Max has Type A blood. Max’s mother has type O blood. If Susan and Max have children together, what is the probability that they will have 5 a child with have the following blood phenotypes (give the probability for each one)? Show the Punnett square for this cross as well! Probability of Type O? 0 Probability of Type A? 1/2 Probability of Type B? 1/4 Probability of Type AB? 1/4 A B AA AB AO BO A O 6