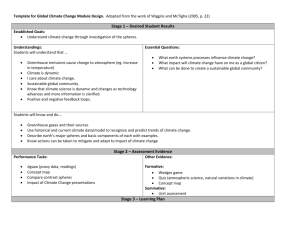
Sustainability-Human Impact

+
Human Lifestyles, Environmental Systems, and Sustainability
Think Critically and Become an Environmental Steward;
Awareness is the First Step. Jo A. Combs
+
Sustainability is the improvement of life without compromising the needs of future generations.
The Environmental
Foundations of Sustainability are: biotic systems and abiotic systems are interrelated; humans are absolutely dependent on the resources of the Earth, many of which are nonrenewable; as the human population grows, impact on the environment increases.
+
Learning Goal for: SC.912.L.17.20
Predict the impact of individuals on environmental systems, and examine how human lifestyles affect sustainability.
http://www.myfootprint.org/
http://www.nature.org/greenliving/carboncalculator/index.htm
+
Learning Goal for: SC.912.L.17.11
Evaluate the costs and benefits of renewable and nonrenewable resources, such as water, energy, fossil fuels, wildlife, and forests.
Students will evaluate possible environmental impacts resulting from the use of renewable and/or nonrenewable resources .
Renewable resources
Alternative energy sources
Wildlife and forests
Agricultural products
+
Learning Goal for : SC.912.N.1.3 Recognize that the strength or usefulness of a scientific claim is evaluated through scientific argumentation, which depends on critical and logical thinking, and the active consideration of alternative scientific explanations to explain the data presented.
Students will identify ways in which a scientific claim is evaluated (e.g., through scientific argumentation, critical and logical thinking, and/or consideration of alternative explanations). ( See resource articles addressing the global warming controversy where data was altered from original data to falsely represent an argument.) http://www.aos.wisc.edu/~aalopez/aos101/wk7.html
and http://www.durangobill.com/Swindle_Swindle.html
See the slide for test results on a North Florida Lake Apopka’s wildlife. Critical thinking was necessary to explain what was happening.
Tar sands vs ‘ethical oil’ http://greenpolicyprof.org/wordpress/?p=562
Natural gas and fracking https://www.magnetmail.net/Actions/email_web_version.cfm?publish=newsle tter&user_id=NSTA&message_id=2544527
+
(SC.912.L.17.13 Discuss the need for adequate monitoring of environmental parameters when making policy decisions.)
( Not mentioned in clarifications.)
Examples of Attitudes and Methods for maintaining Environmental Sustainability
FPL consumers pay higher prices for low sulfur fuel oil used to generate electricity,
Clean Air Act
Safe removal of BCSB chemical lab waste, Clean Water Act
Monitoring of Everglades fish for evidence of biomagnification of mercury
Establishment of conservation area for juvenile sawfish in SW Florida
Lead free gasoline
Specific labeling and disposal of biohazard and nuclear medical waste,
Toxic Substances Control Act and Nuclear Waste Policy
Specific locations for “drop days” for electronics, batteries, used oil,
VOC’s, fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, poisons
+
Content
Limitations
(What you do not need to worry about):
Items referring to renewable and nonrenewable resources will focus on the environmental costs and benefits of using those resources and not on identifying examples of renewable and nonrenewable resources.
Items will not require knowledge of specific energy technologies, environmental regulations, pollution prevention technologies or devices, or other mechanisms used to prevent pollution.
Items assessing a scientific claim are limited to impacts on the environment and renewable and nonrenewable resources.
*Items referring to monitoring of environmental parameters will focus on why monitoring is needed and not on how the monitoring is used. (Note that this benchmark is addressed here but was not mentioned in the clarifications (learning goals) for the specification????)
+
Topic Misconceptions
A misconception is that the greenhouse effect and global warming are one and the same. Correctly, the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon involving the insulating properties of certain gases, the greenhouse gases, in the atmosphere. This blanket of gases traps energy from the sun and maintains an atmospheric temperature supporting life as we know it. Global warming is an increase in the temperature of the atmosphere resulting in far reaching effects including polar and oceanic changes. Fossil fuels, industry, and large herds of mammals are blamed for increased greenhouse gases concentrations.
A misconception is that industry is the largest source of water pollution.
Correctly, silt, pesticides, and fertilizer runoff from agricultural areas are the major water pollution sources in nonurban areas. Storm drains filled with urban runoff are also major pollution sources.
A misconception is that replanting trees after a clear-cutting or strip mining restores the ecosystem. Correctly, the ecosystem must “start from scratch” as the diversity of the flora and fauna, sometimes soil microflora/fauna, has been destroyed or is no longer present in the ecosystem. A forest is the product of a long succession; replanting is just an initial step in restoration.
+
Prior Knowledge:
Human IMPACT on the Environment
As with all topics (benchmarks) included in the Biology course
(culminating in an end-of–course exam), the scope of the course is built on a foundation of prior knowledge. Specific benchmarks included in 6 th , 7 th , and 8 th grade curriculum are noted. The topics from the middle school science courses include: the impact of human activities on Earth, the limiting factors within ecosystems, the difference between science and pseudoscience, and the scope of scientific debate at the community, national, and international levels.
+
7 Crosscutting Concepts from the Next Generation Standards
Look for:
1. Patterns- exotics disrupting normal ecosystem food webs
2. Cause and Effect- greenhouse gases and global warming
3. Scale, Proportion, and Quantity- examine graphic data revealing trends in human population growth, carrying capacity, global temperatures
4. Systems and System Models- examination of food/energy webs, (see slide for the Earth System )
5. Energy and Matter in Systems- basic concepts when discussing fossil fuels, alternative energy sources, basic cycles of water and atmospheric gases
6. Structure and Function- ecosystem structure (biotic and abiotic components) and function (energy flow and cycling of matter)
7. Stability and Change of Systems- changes from human impact (increased population, deforestation/reforestation with loss of original system, and study of indicator and umbrella species)
+
Human Impact Terminology
Can you differentiate between or relate these terms to each other?
You’ll be surprised at what you already know!
Indicator species, umbrella species, keystone species
Natural resources, renewable, nonrenewable
Biodegradable, non-biodegradable
Recyclable, non-recyclable
Fossil fuels, alternative energy sources, renewable energy, nonrenewable energy
High altitude ozone, low altitude ozone
Human population, carrying capacity
Habitat destruction, habitat fragmentation
(think- Alligator Alley corridors)
+
More
Terminology
Sustainability, human impact, technology, human population growth, Earth’s carrying capacity
Air quality, air pollution, acid rain, global warming, ozone depletion, smog, greenhouse gases, greenhouse effect
Bioaccumulation, biomagnification, toxins, fat soluble toxins, food pyramids and webs
Biodiversity, habitat destruction, habitat fragmentation, native species, introduced species, non-native species, exotic species
Water pollution, ground water, water cycle, aquifer
Ecological footprint, carbon footprint
Apathy, environmental awareness
+
Human overpopulation leads to exploitation of the environment beyond the Earth’s carrying capacity.
There are about 6.6 billion people in the world and over 95 million babies are born per year – that is an average of three
Has the rate of population growth always been the same? How do technology and the explosion of knowledge/techniques from Science figure into the picture?
+
Projected Outcome of Carrying Capacity* with Increase in Human Population
Red Line-Human Population
Black Line-Carrying Capacity
*Carrying Capacity here refers to available Fossil Fuels as major energy source.
+
The Challenge to Sustainability is
Human Impact from the Interaction of
Technology and Population Growth
Why have life expectancies extended and population numbers increased exponentially? Some predict downward changes, why?
+
Atmospheric Pollution
Global Warming
Excess greenhouse gases water vapor methane carbon dioxide + others*
Smog (low altitude)
Particulate matter+ O
3
+* soot soil
Ozone Depletion (high altitude)
Chlorofluorocarbons refrigerants propellants
Acid Rain
Fossil fuel combustion byproducts* nitrogen oxides sulfur oxides water vapor
+
The Greenhouse
Effect and
Global Warming
The burning of fossil fuels and forests increases CO atmosphere.
2 in the
Increases in CO
2
, H
2
O, and CH cause more heat to be trapped in the earth’s atmosphere.
As a result , global temperatures are rising.
Warmer temperatures raise sea levels (by melting more ice) and decrease agriculture output (by affecting weather patterns).
+
What will be the results of
Global Warming?
Melting of the polar ice caps
Coastal floods as ocean rise
Reduced salinity levels in the oceans
Displacement of wildlife from sensitive ecosystems
Violent weather patterns
Changes in climate for biomes
Drought, desertification
Crop failure
+
Acid Rain
The burning of fossil fuels
(such as coal) and other industrial processes release into the air pollutants that contain sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide.
When these substances react with water vapor, they produce sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
When these acids return to the surface of the earth
(with rain or snow), they kill plants and animals in lakes and rivers and on land.
+
Effects of Acid Rain
Forests in Europe near industrial centers were near destruction.
Buildings and statuary composed of limestone or marble were susceptible to decomposition by acid rain.
Shock to lakes after heavy acid snow melts can drive pH very low, very acidic.
(Here in S Florida, coral bedrock buffers effects of acid rain.)
+
Origin of Smog:
Emissions + O
2
= O
3
+ Particulates
+
The ozone layer forms in the upper atmosphere when UV radiation reacts with oxygen (O
2
) to form ozone (O
3
).
The ozone absorbs UV radiation and thus prevents it from reaching the surface of the earth where it would damage the DNA of plants and animals.
Various air pollutants, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), enter the upper atmosphere and break down ozone molecules.
CFCs have been used as refrigerants, as propellants in aerosol sprays, and in the manufacture of plastic foams.
When ozone breaks down, the ozone layer thins, allowing UV radiation to penetrate and reach the surface of the earth.
UV, strong ionizing radiation is dangerous.
Ozone
Depletion
+
Ozone Hole
•
Areas of major ozone thinning, called ozone holes, appear regularly over Antarctica, the
Arctic, and northern Eurasia.
•
These images of the ozone hole were taken by NASA between September 1981 and
September 1999.
+
Upper Atmosphere and Lower Atmosphere Ozone:
The Good, The Bad, and the Ugly-
Extreme UV Protection and Respiratory Distress
+
The Good News Concerning
Ozone Depletion
+
Water Pollution
Two methods of water pollutants exist; point source and nonpoint source.
Point Source
The technology exists for point sources of pollution to be monitored and regulated, although political factors may complicate matters.
The Gulf BP oil rig and the
Exxon Valdez oil tanker oil spills best illustrate a point source water pollution.
The drain pipes are classified as?
Nonpoint Source
A nonpoint source delivers pollutants indirectly through environmental changes. An example of this type of water pollution is when fertilizer from a field is carried into a stream by rain, in the form of run-off which in turn affects aquatic life.
Nonpoint sources are much more difficult to control. Pollution arising from nonpoint sources accounts for a majority of the contaminants in streams and lakes.
+
Water Pollution
Urban runoff
Sewage
Light industry waste
Household chemicals
Oil and gasoline
Agricultural runoff
Fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides
Soil
Animal waste
Infectious organisms
Caustic, corrosive solutions
Petroleum residues
Nitrates, phosphates, organophosphates
Infectious agents
+
Water Pollution…more
Industry
Paper mills
Food processing
Mining waste
Ocean dumping and outfall pipes
Garbage barges, tankers, drilling rigs
In port bilge flushing
Cruise liners
Increased biomass promotes bacterial growth, odor
Oxygen demand
Slag, Hydrofluoric acid, Cu, Se,
Pb, Hg
Sewage, infectious agents
Plastic trash entangling turtles, reefs, even whales
Oil spills
Invasion of exotic species like the zebra mussels
+
Water Pollution-
Agricultural Runoff
Fertilizers enable farmers to grow more food as they are replacing the nutrients removed from the soil by plants.
However, if too much fertilizer is added, and it rains, the fertilizer finds its way into rivers and lakes.
This causes algae and water plants to grow, and as there is competition for light, some will die.
Bacteria decay the dead plants; this increases the rate that oxygen is used up from the water.
The result is that fish suffocate and die.
This process is called Eutrophication.
Raw sewage pumped into rivers has the same effect
Both may contain infectious agents
+
Pollution with Toxins
Some toxins, such as the pesticide DDT, concentrate in plants and animals.
As one organism eats another, the toxin becomes more and more concentrated, a process called Biological
Magnification.
+
Land Abuse
Mining, drilling and pipelines
Overdevelopment
Land Fills
Accumulation
Runoff
Toxic pollution
Unusable land
Draining wetlands = uncharged aquifers
Habitat Destruction
Loss of diversity
Great heaps of non-biodegradeable garbage
Toxins can runoff in local water
Some energy can be produced
+
Land Abuse…more
“Rainforests are the lungs of the Earth.”
Desertification
misuse or climate changes
Poor farming methods, overgrazing
Overdevelopment of coast
Loss of arable land
Coastal erosion
Deforestation
Clear cutting
strip mining
Slash and burn
Overuse by population
Loss of soil
Increase in
Greenhouse gases
Habitat Destruction
Loss of Diversity
+
Diversity: Benchmarks for the Sustainability of an
Ecosystem
Indicator Species- Study this species- range, population, health-to assess the ‘health’ of an ecosystem.
Umbrella Species- Identify this species and protect as required. Keeping its population strong will reflect on keeping many organisms in the ecosystem protected.
Non-native, Exotic Species- Melaleuca introduced to South
Florida, kudzu vine proliferating in the entire South, shrubbery-destroying spiraling white flies reproduce at amazing rates, large iguanas in my back yard- these aliens can crowd out the native diversity of an area.
+
Keystone Species…hidden among the rest, but the importance, oh so overlooked!
Keystone species are necessary to the structure of their communities.
Examples are: the sea otter of the coastal
California kelp forests; they keep the urchins from consuming all the kelp;
(Go to Classzone.com , chap 16, animated Biology to explore interactions in a kelp forest.
Remember: students must predict what are consequences to changes in ecosystems.)
A hummingbird is a chief pollinator in many ecosystems, keeping the plants of the producers’ trophic level in supply for all other levels.
http://education.national
geographic.com/education/encyclopedia/keystonespecies/?ar a=1
+
Harmful Effects to
Biodiversity and Health
Exotic plants, animals, and insect vectors released by man present unforeseen problems.
An Introduced Species, this lionfish, released illegally, outcompetes, lacks predators on South Florida’s reefs.
Foolishly released into the Everglades, the Burmese python challenges the bird, fish, small and large mammal populations…even taking on the alligator.
Sentinel chickens penned in the Everglades alert health officials to non-native disease-carrying vector mosquitoes.
+
A beautiful creature in a beautiful reef setting, but it is more than meets the eye.
The sea turtle is an Umbrella Species …since it is protected as an
Endangered Species, many commercial fish are protected from longline fishing.
The reef ecosystem is fragile with a complex food web.
The sensitive corals are reservoirs for carbon (CaCO
3
) in the Carbon Cycle.
The food web is sensitive to exotic species that may outcompete or lack predators.
The reef is sensitive to temperature fluctuations as CaCO
3 dissolves in cooler water.
Outfall and dumping of sewage, garbage, and toxins foul the water.
+
What do you already know about..?
Do you know a country that depends on geothermal energy?
What fuel is made from biomass?
What are common household uses for solar power? (calculators……)
Of what significance is Lake Mead?
In South Florida, where would you position wind turbines?
Natural gas is described as clean burning, but do you know about fracking?
+
Nonrenewable
Resources
Fossil fuels (oil, natural gas, coal)
Uranium, metals, minerals
Water, soil
Ecosystems damaged by:
Draining, deforestation, desertification
Extinct species
+
Costs and Benefits:
Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources
+
Assessing
Nonrenewable Energy:
Costs/Disadvantages
& Benefits/Advantages
Coal – ready-made fuel cheap to mine, more supply than oil or gas
Oil – ready-made fuel cheap to mine
Natural gas – ready-made fuel, cheap, cleaner than oil or coal
When burned gives off greenhouse gases
Limited supply, when burned gives off greenhouse gases
Limited supply, gives off greenhouse gases, controversy concerning fracking (extraction)
Nuclear –small amount / large amount of energy, no pollutants
Reactors are expensive to run, waste is very toxic, any leakage toxic
+
More Assessment of Nonrenewable Energy:
Costs/Disadvantages & Benefits/Advantages
Biomass – cheap and readily available from crops, easy to process (ferment) into fuel, can be sustainable
Wood – cheap and readily available, can be sustainable
Solar – unlimited supply, no pollution
Wind – never runs out, no pollution
When burned, greenhouse gases given off
When burned, greenhouse gases given off
Not always available, costly to obtain and install equipment
Costly initially, not always available
+
Futures Wheel
http://www2.gsu.edu/~mstnrhx/5news.htm
http://www.landlearn.net.au/newsletter/
2007term4/page3.htm
Ex.
Control of an
Invasive
Pest
+
+
Predict the
Environmental
Impact
A temperature inversion holds particulates from local industry close to the ground. What does a city full of automobiles add to this recipe? Consequences?
A family in a boat at Holiday Park is seen emptying a bag of animals into the water; when asked, a young boy says it was an ugly frog from South America.
Home yards bordering the canals in Coral Springs are observed to be pea green with dead fish on the banks.
+
How can this situation become an
Enemy of Diversity?
Field of GMO( resistant to specific pests) growing near traditional farms
Clear cutting of a pine forest in North Florida
Legislature disproves funding to build wildlife corridors with new I-95
Lanes
Removal of regulations on imports of produce and flowers from South
America
Can you think of more situations?
+
Everyday Earth Friendly Solutions to Ecological Dilemmas
Safeguard water resources; carefully discard waste of all types;
Limit the use of vehicles by walking, biking, carpooling;
Use alternative energies like solar, wind, water; buy local (shipping wastes gas and produces air pollution);
Be a wildlife advocate- support reserves and breeding programs; eliminate non-native species from your property; plant trees;;
Avoid plastic bags, recycle garbage, avoid the use of fertilizers and pesticides;
Eat locally produced food; avoid processed foods;
Support and adhere to environmental regulations
+
There are 3 components central to the idea of
Sustainability. It is from these components that the costs and benefits of practicing environmental stewardship are estimated.
+
An important connection between environmental pollutants and life is more than the obvious threats to health.
There is much more; read about epigenomics.
http://www.genome.gov/27532724
+
Lab-Inquiry
+
Demonstration
+
Studies of the Contamination of Lake
Apopka
The alligator population at Lake Apopka in central Florida declined dramatically between 1980 and 1987. Endocrinedisrupting chemicals and DDT metabolites have been implicated in the alligators' reproductive failure. The DDT metabolite hypothesis is based largely on the observation of elevated concentrations of p,p-DDE and p,p-DDD in alligator eggs obtained from Lake Apopka in 1984 and 1985.
Lake Apopka is significantly contaminated with a variety of chemicals including anthropogenic nutrients, organochlorine pesticides, and multiple congeners of polychlorinated biphenyls(PCBs).
According to Thea M. Edwards, Gunnar Toft, and Louis J. Guillette of the Department of Biology in Florida, "Our laboratory has previously documented a number of reproductive abnormalities in alligators from Lake Apopka, compared with alligators captured from Lake Woodruff, a nearby reference lake. We conducted the present study to investigate if another native vertebrate, Gambusia holbrooki (eastern mosquitofish), is similarly affected." So for these researchers to conduct this study, first adult female mosquitofish were collected from Lake Apopka and Lake
Woodruff monthly for 16 months in order to document seasonal and lake-associated variation in reproductive patterns. What was found during this study was that in contrast to fish from Lake Woodruff, females from Lake
Apopka exhibited earlier and more synchronized spring ovarian recrudescence, increased body size, increased fecundity, increased adjusted hepatic weight, and more extreme fluctuations in muscle estradiol concentrations in most months. Endocrine disruption, consistent with other studies and Lake Apopka's pollution profile, is one explanation for these findings. Other environmental and physiological factors are also addressed. However, the higher fecundity among Apopka females suggests that, unlike Apopka alligators, Apopka mosquitofish are not impacted at the population level.
A case study related to this topic of water polluted with estrogen mimics can be found at: http://sciencecases.lib.buffalo.edu/cs/files/kermit.pdf
+
Representation of the Earth System
+
Sample question 1
+
Sample question 2
Which human activity would most likely deplete finite resources?
A. use of natural enemies to eliminate insect pests
B. development of wildlife refuges
C. governmental restriction of industrial pollution
D. uncontrolled population growth
+
Sample question 3
The increasing demands for fossil fuels has led government and businesses to consider several possibilities to solve the energy crisis. Which solution will reduce the impact of this crisis on the environment and future generations?
A. increase the number of drilling sites for crude oil in North
America
B. build more power plants away from population centers
C. limit the number of people in each vehicle
D. develop alternative fuel sources that can be produced from renewable resources
+
Sample Question 4
One reason why people should be aware of the impact of their actions on the environment is that
A. ecosystems are never able to recover once they have been adversely affected
B. the depletion of finite resources cannot be reversed
C. there is a decreased need for new technology
D. there is a decreased need for substances produced by natural processes
+
Sample Question 5
Humans often have not given much thought to the long-term impacts of technological change. As the 21st century begins, most scientists would agree that humans should
A. develop the uninhabited parts of Earth for the human population increase
B. learn how to control every aspect of the environment so that damage due to technology will be spread evenly
C. use new technology to expand human influence on all natural communities
D. use knowledge of ecology to consider the needs of future generations of humans and other species
+
Sample Question 6
Many governments are limiting the use of toxic pesticides and enforcing stricter hunting and fishing laws. These efforts are attempts to
A. increase importation of organisms
B. produce nonbiodegradable pollutants
C. develop new farming techniques
D. prevent species extinction
+
Sample Question 7
Researchers have recently determined that children scored better in intelligence tests after the amount of lead in their blood was reduced This study offers hope that the effects of lead poisoning can be reversed. Lead poisoning can cause mental retardation, learning disabilities, stunted growth, hearing loss, and behavior problems Scientists estimate that at least 3 million children in the United
States have lead concentrations above the danger level of 10 micrograms per deciliter blood.
Researchers found an average increase of one point on an index scale for intelligence for every decrease of 3 micrograms per deciliter blood concentration. A common source of lead poisoning is peeling or chipping paint in buildings constructed before 1960. Soil near heavily traveled roads may have been contaminated by the exhaust from older cars burning leaded gasoline. In a recent
related study, another group of researchers concluded that removing lead contaminated soil does not reduce blood lead levels enough to justify its cost. The children in the study began with blood levels 7 to 24 micrograms per deciliter. Replacing the lead contaminated soil resulted in a reduction in blood lead levels of 0.8 to 1.6 micrograms per deciliter in 152 children under the age of 4. These studies are not conclusive. Results indicate that further studies are needed to determine if reducing environmental lead levels will significantly reduce lead levels in the blood.
.
One effect of lead poisoning is
A. decrease in learning problems
B. decrease in platelet numbers
C. increase in behavior problems
D. increase in growth
+
Sample Question 8
A decrease of 9 micrograms per deciliter in blood lead level would most likely lead to an average
A. decrease of six points on an index scale for intelligence
B. increase of three points on an index scale for intelligence
C. increase of one point on an index scale for intelligence
D. decrease of three points on an index scale for intelligence
+
Sample Question 9
The most serious consequences of cutting down forests and overgrazing land is
A. the prevention of flooding
B. an increase in the chance of fire
C. the loss of topsoil
D. an increase in the number of predators
+
Sample questions’ answers
1. B
2. D
3. D
4. B
5. D
6. D
7. C
8. B
9. C
+
Resources
A resource of information on Environmental Issues specific to
Florida
http://www.floridiannature.com/FloridaEnvironmentalIssues.
htm
***Prompt students re environmental remedies by visiting this site; see the DON’T MISS on left side
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/lists-of-environmentalproblems.html#land
Fracking: a STEM lesson
https://www.magnetmail.net/Actions/email_web_version.cf
m?publish=newsletter&user_id=NSTA&message_id=254452
7
+
Resources
Population Growth and Regulation academics.tctc.edu/dehay/ch54.ppt
Getting started with bottle biology:
http://www.learner.org/courses/essential/life/bottlebio/
Bottle Biology
www.bottlebiology.org/
+
Resources
Tar sands
http://greenpolicyprof.org/wordpress/?p=562
Global warming controversy
http://www.aos.wisc.edu/~aalopez/aos101/wk7.html
and
http://www.durangobill.com/Swindle_Swindle.html
General, all purpose Ecology ppt reference for teachers
Ecology Review - Biology4Teachers Home biology4teachers.com/Ecology/Ecology%20Earth%20Cycles%2
0Pyr…
Principles of Ecology - 2.ca.us
teachers.sduhsd.k12.ca.us/
+
Resources
Carbon footprint calculator
http://www.nature.org/greenliving/carboncalculator/index.htm
Ecological footprint calculator
http://www.myfootprint.org/
Problem based learning activity:
Project Based Learning Assignment: Human Impact on the ... - CPalms
www.cpalms.org/Resources/PublicPreviewResource20939.aspx
Water Pollution notes and slide shows for urban and agricultural waste.
http://www.sccdistrict.com/resubwt.htm
Good source for Human Impact on biodiversity
http://redpath-museum.mcgill.ca/Qbp/3.Conservation/impacts.htm
+
Resources
An excellent case study on the Everglades making a case for population growth and many problems faced by the National Park
http://www.aaas.org/international/ehn/biod/banc.htm
National Geographic site: see the coal/natural gas interactive fact quiz
http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/coal-vs-natural-gas-quiz/
South Florida Water Management resource on the Everglades
http://www.sfwmd.gov/portal/page/portal/xrepository/sfwmd_repository_ pdf/everglades_american_treasure.pdf
Greenhouse Gas emissions footprint calculator
http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/ghgemissions/ind-calculator.html
+
Resources
http://www.ecsd-fl.schoolloop.com/biologyeocreview
Review from Escambia Co for EOC Bio.
Flashcards- Human Impact on the Environment
http://quizlet.com/5518772/human-impact-on-the-environment-final-flashcards/
Virtual Lab- Assessing Water Quality by Examining an Indicator Species
Ecology Virtual Lab
Teaching Controversial Environmental Topics
http://serc.carleton.edu/NAGTWorkshops/affective/environment.html
An encyclopedic collection of informational blogs (quite good) on a wide assortment of environmental topics
www.earthtimes.org/