RETI climate Unit
advertisement
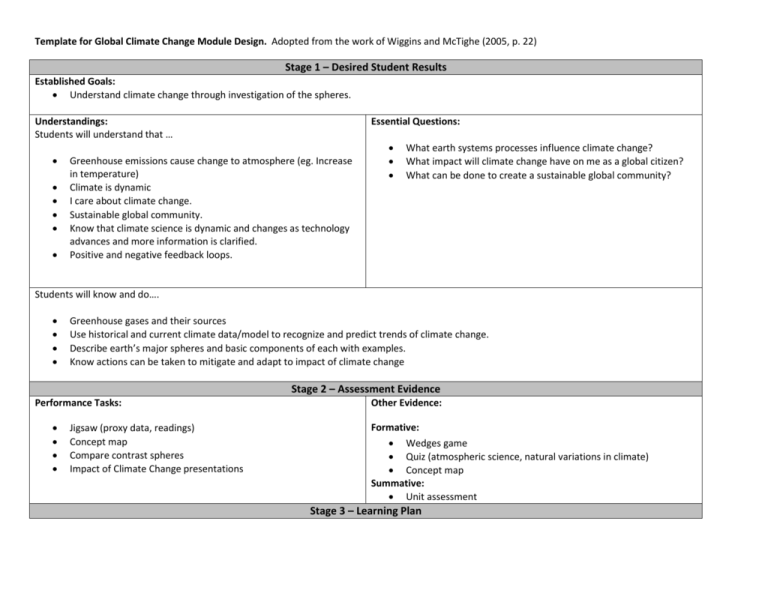
Template for Global Climate Change Module Design. Adopted from the work of Wiggins and McTighe (2005, p. 22) Stage 1 – Desired Student Results Established Goals: Understand climate change through investigation of the spheres. Understandings: Students will understand that … Essential Questions: Greenhouse emissions cause change to atmosphere (eg. Increase in temperature) Climate is dynamic I care about climate change. Sustainable global community. Know that climate science is dynamic and changes as technology advances and more information is clarified. Positive and negative feedback loops. What earth systems processes influence climate change? What impact will climate change have on me as a global citizen? What can be done to create a sustainable global community? Students will know and do…. Greenhouse gases and their sources Use historical and current climate data/model to recognize and predict trends of climate change. Describe earth’s major spheres and basic components of each with examples. Know actions can be taken to mitigate and adapt to impact of climate change Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Tasks: Jigsaw (proxy data, readings) Concept map Compare contrast spheres Impact of Climate Change presentations Other Evidence: Formative: Wedges game Quiz (atmospheric science, natural variations in climate) Concept map Summative: Unit assessment Stage 3 – Learning Plan Learning Activities: What learning experiences and instruction will enable students to achieve the desired results? Be able to effectively discuss climate change with scientific evidence to support their claims. What is the sequence of activities for this learning plan? See calendar What resources and materials are needed for students to participate in the learning activities? o NCAR o Earth observatory o “climate power point” w/ linked documents o “What’s up with the weather” o IPCC (4th ed) summary o HIAPER-HIPPO o Windows to the Universe o Supplemental Reading on Paleoclimate as part of assignment o Internet/Computers Advanced Placement Environmental Science –> 10-12 grades 2-3 weeks What background information is needed for teachers about the scientific concepts? Atmospheric composition, greenhouse effect, paleoclimaolgy, policies….. What are the web links to related resources or downloadable forms, data sets, etc? see calendar and activities(they are all linked/cited) What are the instructions for implementing the activity? (see calendar) What is the assessment process? (mentioned in stage 2 of this document) Colorado State High School Standards addressed: Life Science: 1. Matter tends to be cycled within an ecosystem, while energy is transformed and eventually exits an ecosystem Earth Systems Science: 1. The history of the universe, solar system and Earth can be inferred from evidence left from past events 2. As part of the solar system, Earth interacts with various extraterrestrial forces and energies such as gravity, solar phenomena, electromagnetic radiation, and impact events that influence the planet’s geosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere in a variety of ways 3. Climate is the result of energy transfer among interactions of the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, and biosphere 4. The interaction of Earth's surface with water, air, gravity, and biological activity causes physical and chemical changes AP Standards Addressed: I. Earth Systems and Resources A. Earth Science Concepts (Geologic Time Scale; Plate Tectonics, Earthquakes, Volcanism; Seasons; Solar Intensity and Latitude) B. The Atmosphere (Composition; Structure; Weather and Climate; Atmospheric Circulation and the Corolis Effect; Atmosphere- Ocean Interactions; ENSO) C. Global Water Resources and Use (Freshwater/Saltwater; Ocean Circulation; Agricultural, Industrial and Domestic Use; Surface and Groundwater Issues; Global Problems; Conservation) II. The Living World D. Natural Ecosystem Change (Climate Shifts, Species Movement; Ecological Succession) E. Natural Biogeochemical Cycles (Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, Water, Conservation of Matter) III. Population B. Human Population 2. Population Size (Strategies for Sustainability; Case Studies; National Policies) 3. Impacts of Population Growth (Hunger; Disease; Economic Effects; Resource Use; Habitat Destruction) IV. Land and Water Use B. Forestry (Tree Plantations; Old Growth Forests ; Forest Fires; Forest Management; National Forests) C. Rangelands (Overgrazing; Deforestation; Desertification; Rangeland Management; Federal Rangelands) 4. Land Conservation Options (Preservation; Remediation; Mitigation; Restoration; Adaptation) 5. Sustainable Land-Use Strategies G. GlobaI Economics (Globalization; World Bank; Tragedy of the Commons; Relevant Laws and Treaties) V. Energy Resources and Consumption C. Fossil Fuel Resources and Use (Formation of Coal, Oil, and Natural Gas; Extraction/Purification Methods; World Reserves and Global Demand; Synfuels; Environmental Advantages/Disadvantages of Sources) VI. Pollution A. Pollution Types 1. Air Pollution (Sources - Primary and Secondary; Major air pollutants; Measurement Units; Smog; Acid Deposition - Causes, Effects, Heat Islands and Temperature Inversions; Indoor Air Pollution; Remediation and Reduction Strategies; Clean Air Act and Other Relevant Laws) VII. Global Change A. Stratospheric Ozone (Formation of Stratospheric Ozone; Ultraviolet Radiation; Causes of Ozone Depletion; Effects of Ozone Depletion; Strategies for Reducing Ozone Depletion; Relevant Laws and Treaties) B. Global Warming (Greenhouse Gases and the Greenhouse Effect; Impacts and Consequences of Global Warming; Reducing Climate Change; Relevant Laws and Treaties) C. Loss of Biodiversity 1. Habitat Loss; Overuse; Pollution; Introduced Species; Endangered and Extinct Species 2. Maintenance through Conservation 3. Relevant Laws and Treaties Wiggins, G., & McTighe, J. (2005). Understanding by design (2 ed.). Alexandria: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.7/8/2011