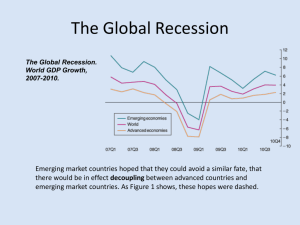
Factors Causing Financial Crises
advertisement

Factors Causing Financial Crises Asset Markets Effects on Balance Sheets – – – – Stock market decline Decreases net worth of corporations. Unanticipated deflation Debt burdens up/net worth down Unanticipated depreciation $ debts up/net worth down Asset write-downs (bad debts) Net worth down • Deterioration in Financial Institutions’ Balance Sheets Decline in lending. Increases in Interest Rates – Worsens adverse selection (who would pay the high rates?) – Increases need for external funds worsens adverse selection and moral hazard problems. Government Fiscal Imbalances – Fears of default on government debt Capital flight Banking Crises – Loss of information production / disintermediation. • Increases in Uncertainty Decline in lending. Stage One •Mismanagement of financial liberalization and innovations •Asset price boom & bust •Spikes in interest rates •Increase in uncertainty Stage two: Banking Crisis Stage three: Debt Deflation U.S. Financial Crises Financial Crisis of 2007 - 2009 • Financial innovations in mortgage markets: – Subprime and Alt-A mortgages – Mortgage-backed securities – Collateralized debt obligations (CDOs) • Housing price bubble forms – World savings glut Increase in liquidity from cash flows surging to the US – Subprime mortgage market housing demand and prices up. • Agency problems arise – “Originate to distribute” principal (investor) agent (mortgage broker) problem. – Commercial and investment banks/rating agencies …weak incentives to assess quality of securities • Information problems surface Housing price bubble bursts/Crisis spreads globally http://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2009/04/29/business/2009-wide-housing-graphic.html A “Global Saving Glut” The best of times Capital Inflows Escalating House Prices Easy Money Policy Ambitious Mortgage Brokers Eager Home Buyers Developer Clout Innovative Banks Bank Regulators Gov’t Sponsored Securitization MBSs Rating Agencies The best of times Capital Inflows Escalating House Prices Easy Money Policy Ambitious Mortgage Brokers Eager Home Buyers Developer Clout Innovative Banks Bank Regulators Gov’t Sponsored Securitization MBSs Rating Agencies Vicious Spirals Unleashed House Price – Foreclosure Spiral Deleveraging – Debt Deflation Spiral Demand – Jobs – Wages – Income – Spiral Government Revenue – Cutback Spiral Global Repercussion Spiral Macroeconomic Linkages and Feedbacks Financial Crisis of 2007 - 2009 (cont’d) • Banks’ balance sheets deteriorate – Write downs – Sale of assets and credit restriction • High-profile firms fail – Bear Stearns (March 2008) – Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (July 2008) – Lehman Brothers, Merrill Lynch, AIG, Reserve Primary Fund (MMMF) and Washington Mutual (September 2008). • Fed pumps up bank reserves: TARP/TALF,etc. – Lend and lend freely • Bailout package enacted – House votes down the $700 billion bailout package (9/29/08) Stock market slumps Bailout passes on October 3. – Congress approves a $787 billion economic stimulus plan on February 13, 2009. • Recession deepens Responses Lender of Last Resort / Spender of Last Resort • Tax Rebate $124 bil. • Fed Fund Rate Cuts • Fannie/Freddie $200 bil. • Bear-Stearns $29 bil. • AIG $174 bil. Fed “Facilities” • Primary Dealer Credit Facility (PDCF) $58 bil. • Treasury Security Loan Facility (TSLF) $133 bil. • Term Auction Facility (TAF) $416 bil. • Asset- Backed Commercial Paper Funding Facility (CPFF) $1,777 bil. • Money Market Investor Funding Facility (MMIFF) $540 bil. • More Fed Fund Rate Cuts … Hold At ~0% • Fed Purchases of Long-Term Securities: GSEs & MBSs $600 bil. • Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility (TALF) $200 bil. • Emergency Economic Stabilization Act/TARP $700 bil. Government Loans Government Equity • Stimulus Package $787 bil. aka The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act • TARP II • Stress Tests Vicious Spirals Unleashed Vicious Spirals Reversed? Tackle them all together! Refinance House Price – Mortgages Stimulus Demand – Program Jobs – •Infrastructure Spending Wages – •Tax Cuts Foreclosure Spiral Deleveraging Debt Deflation Revive dual–banking system Cash for Trash Spiral Income – Spiral •Recapitalize banks •Revive securitization Federal Aid Government To States Revenue – Cutback Spiral GGlobal – 20 Repercussion •Coordinated Spiral Stimulus Macroeconomic Linkages Macroeconomic Linkages and and Feedbacks Feedbacks Dynamics of Financial Crises in Emerging Market Economies • Stage one: Initiation of Financial Crisis. • Path one: mismanagement of financial liberalization • • • • Weak supervision and lack of expertise lending boom. Domestic banks borrow from foreign banks. Fixed exchange rates give a sense of lower risk. Securities markets not well-developed Banks important • Path two: severe fiscal imbalances: • Governments force banks to buy government debt. • When government debt loses value, bank net worth down . – Additional factors: • Increase in interest rates (from abroad) • Asset price decrease • Uncertainty linked to unstable political systems Dynamics of Financial Crises in Emerging Market Economies • Stage two: currency crisis – Bank losses currency crises: • Government cannot raise interest rates (doing so forces banks into insolvency)… • … and speculators expect a devaluation. • Foreign and domestic investors sell the domestic currency. • Stage three: Full-Fledged Financial Crisis: – The debt burden in terms of domestic currency increases – Banks are more likely to fail: • Individuals are less able to pay off their debts (value of assets fall). • Debt denominated in foreign currency increases (value of liabilities increase). Financial Crises: Mexico 1994-1995 • Financial liberalization in the early 1990s: – Lending boom, coupled with weak supervision and lack of expertise. – Banks accumulated losses and their net worth declined. • Rise in interest rates abroad. • Uncertainty increased (political instability). • Domestic currency devaluated on December 20, 1994. • Rise in actual and expected inflation. Financial Crises: East Asia 1997-1998 • Financial liberalization in the early 1990s: – Lending boom, coupled with weak supervision and lack of expertise. – Banks accumulated losses and their net worth declined. • Uncertainty increased (stock market declines and failure of prominent firms). • Domestic currencies devaluated by 1997. • Rise in actual and expected inflation. Financial Crises: Argentina 2001-2002 • Government coerced banks to absorb large amounts of debt due to fiscal imbalances. • Rise in interest rates abroad. • Uncertainty increased (ongoing recession). • Domestic currency devaluated on January 6, 2002 • Rise in actual and expected inflation. FIGURE 3 Sequence of Events in Emerging Market Financial Crises FIGURE 2 Treasury Bill–to– Eurodollar Rate (TED) Spread Source: www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/data.htm