Chapter 1 An Introduction to Money and the Financial System
advertisement

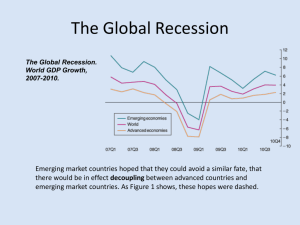
ECON 304 Money and Banking Instructor: Bernard Malamud –Office: BEH 502 Phone (702) 895 –3294 Fax: 895 – 1354 »Email: bernard.malamud@unlv.edu Website: www.unlv.edu/faculty/bmalamud Office hours: MW 11:30 - 12:30 pm; 2:30 – 3:30 pm; and by appointment Money, Banking, Financial Markets and Crisis • The role of money and monetary policy in the economy TRUST • How financial markets such as bond, stock and foreign exchange markets work TRUST • How financial institutions such as banks and insurance companies work TRUST Course Objectives • Roles played by banks and other intermediaries • Determination of asset prices in financial markets • How financial institutions operate – Asymmetric information • Adverse selection/Moral hazard/Principal – Agent Problems – Innovations – Regulation • The conduct and impacts of monetary policy. – How policies can promote macroeconomic stability • Understand and explain the roots, responses and consequences of the subprime-triggered financial crisis. Texts • Frederic S. Mishkin, The Economics of Money, Banking and Financial Markets, 9th edition. Earlier editions work…but read Chapter 9 of 9th edition • Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission Report Supplemental Books and Articles (see course outline): • • • • • • • • Frank Partnoy. Infectious Greed: How Deceit and Risk Corrupted the Financial Market, Times Books, 2003. Gillian Tett, Fool’s Gold: How the Bold Dream of a Small Tribe at J.P. Morgan Was Corrupted by Wall Street Greed and Unleashed a Catastrophe, Free Press, 2009. David Wessel, In Fed We Trust: Ben Bernanke’s War on the Great Panic, Random House, 2009. Michael Lewis, The Big Short: Inside the Doomsday Machine. W.W. Norton, 2010 Andrew Ross Sorkin, Too Big to Fail. Viking, 2009 Simon Johnson and James Kwak, 13 Bankers : The Wall Street Takeover and the Next Financial Meltdown. Random House, 2010 Raghuram G. Rajan, Fault Lines: How Hidden Fractures Still Threaten the World Economy. Princeton, 2010. Articles in Journal of Economic Perspectives (JEP) and Federal Reserve System publications cited in this outline and as added as the semester proceeds. These can be accessed from the JEP and Federal Reserve Bank websites. M & B Talk Some Terms Liquidity/solvency Shadow banking system Structured Investment Vehicles (SIVs) “This time is different” … Irrational exuberance “Too Big to Fail” … Too Big to Bail Discount window stigma Term Auction Facility (TAF)/Term Security Lending Program (TSLP) Primary Dealer Credit Facility (PDCF)/Money Market Investor Funding Facility (MMIFF) Asset Backed Securities (ABS/MBS)/Credit Default Swaps (CDS) Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) Lender of Last Resort Stress test “Large negative tail” Black swan Some Basics of Money, Banking and Financial Markets • A security (financial instrument) is a claim on the issuer’s future income or assets • A bond is a debt security that promises to make specified payments over time – An interest rate is the cost of borrowing or the price paid for the rental of funds • Common stock represents a share of ownership in a corporation – A share of stock is a claim on the earnings and assets of the corporation Interest Rates on Selected Bonds, 1953–2011 Sources: Federal Reserve Bulletin; www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H15/data.htm. Understanding Financial Distress I … credit routinely turned over … but in crunch … Background Concepts • Flavors of liquidity Funding liquidity “haircut” on collateral Market liquidity fire sale in crisis • Lending channel (turn to banks) – Moral hazard monitoring cost When borrower net worth down … don’t lend – Precautionary hoarding by intermediary • Network effects: everyone a borrower & lender/no netting When counterparty credit risk up … GRIDLOCK • Silent run … loans not renewed Connectivity and Amplification Reduced Positions Fire Sale Initial Initial Losses Losses Funding Problems Falling Prices Higher Margins Losses on Existing Assets A “Global Saving Glut” The best of times Capital Inflows Easy Money Policy Escalating House Prices Ambitious Mortgage Brokers Eager Home Buyers Developer Clout Innovative Banks Bank Regulators Gov’t Sponsored Enterprises Securitization MBSs Rating Agencies The best of times Capital Inflows Escalating House Prices Easy Money Policy Ambitious Mortgage Brokers Eager Home Buyers Developer Clout Innovative Banks Bank Regulators Gov’t Sponsored Enterprises Securitization MBSs Rating Agencies Underlying Innovations • • • • Securitization SIVs Ratings bias ARMs, teaser rates, no-doc loans, NINJA loans Episodes • American Home Loan, PNB Paribus hedge fund failures TED rate jump ECB, Fed Injections (TAF) • Monoline insurers (of MBSs) downgrade Impact on money market funds • Carlyle failure run on Bear Fed backed JP Morgan takeover/TSLF for investmt banks • Lehman, Merrill, AIG TARP Responses Lender of Last Resort / Spender of Last Resort • • • • • Tax Rebate $124 bil. Fed Fund Rate Cuts Fannie/Freddie $200 bil. Bear-Stearns $29 bil. AIG $174 bil. Fed “Facilities” • • • • • • • • • • • Primary Dealer Credit Facility (PDCF) $58 bil. Treasury Security Loan Facility (TSLF) $133 bil. Term Auction Facility (TAF) $416 bil. Asset- Backed Commercial Paper Funding Facility (CPFF) $1,777 bil. Money Market Investor Funding Facility (MMIFF) $540 bil. More Fed Fund Rate Cuts … Hold At ~0% Fed Purchases of Long-Term Securities: GSEs & MBSs $600 bil. Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility (TALF) $200 bil. Emergency Economic Stabilization Act/TARP $700 bil. Government Loans Government Equity Stimulus Package $787 bil. aka The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act TARP II • Stress Tests Money and Business Cycles • Recessions (unemployment) and booms (inflation) affect all of us • Monetary Theory ties changes in the money supply to changes in aggregate economic activity and the price level Money Growth (M2 Annual Rate) and Interest Rates (Long-Term U.S. Treasury Bonds), 1950–2008 Sources: Federal Reserve Bulletin, p. A4, Table 1.10; www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h6/hist/h6hist1.txt. Money and Inflation • The aggregate price level is an average price of goods and services in an economy • A continual rise in the price level (inflation) affects all economic players Monetary and Fiscal Policies • Monetary policy is the management of the money supply and interest rates – Conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank (Fed) • Fiscal policy is government spending and taxation – Any deficit must be financed by borrowing … government borrowing affects interest rates Macro Facts: Bank Excess Reserves M1/Monetary Base=M1/(Currency + Reserves) Core Principles of Money and Banking • Time has Value Interest rate • Risk Requires Compensation • Financial decisions are based on Information and TRUST • Markets set prices and allocate resources • Stability reduces risk and spurs enterprise • Uncertainty Fear Enterprise Function of Financial Markets • Channel funds from economic players that have saved surplus funds to those that have a shortage of funds • Promotes economic efficiency by producing an efficient allocation of capital – increases production • Improves consumer well-being – allows them to time purchases better Structure of Financial Markets • Debt and Equity Markets • Primary and Secondary Markets – Investment Banks underwrite securities in primary markets – Brokers and dealers work in secondary markets • Exchanges and Over-the-Counter (OTC) Markets • Money and Capital Markets – Money markets deal in short-term debt instruments – Capital markets deal in longer-term debt and equity instruments Principal Money Market Instruments Principal Capital Market Instruments Internationalization of Financial Markets • Foreign Bonds—sold in a foreign country and denominated in that country’s currency • Eurobond—bond denominated in a currency other than that of the country in which it is sold – Perhaps in the future a bond backed by all eurozone countries • Eurocurrencies—foreign currencies deposited in banks outside the home country – Eurodollars—U.S. dollars deposited in foreign banks outside the U.S. or in foreign branches of U.S. banks • World Stock Markets Function of Financial Intermediaries: Indirect Finance • Lower transaction costs – Economies of scale – Liquidity services • Reduce Risk – Risk Sharing (Asset Transformation) – Diversification • Asymmetric Information – Adverse Selection (before the transaction)—more likely to select risky borrower – Moral Hazard (after the transaction)—less likely borrower will repay loan Banking and Financial Institutions • Financial Intermediaries—institutions that borrow funds from people who have saved and make loans to other people and businesses • Banks—accept deposits and make loans • Other Financial Institutions—insurance companies, finance companies, pension funds, mutual funds and investment banks • Financial Innovation – The information age and e-finance – Derivatives … bubbles and crisis – Securitization … bubbles and crisis Principal Financial Intermediaries and Value of Their Assets Regulation of the Financial System • To increase the information available to investors: – Reduce adverse selection and moral hazard problems – Reduce insider trading • To ensure the soundness of financial intermediaries: – Restrictions on entry – Disclosure – Restrictions on Assets and Activities – Deposit Insurance – Limits on Competition – Restrictions on Interest Rates M & B Talk Some Terms Liquidity/solvency Shadow banking system Structured Investment Vehicles (SIVs) “This time is different” … Irrational exuberance “Too Big to Fail” … Too Big to Bail Discount window stigma Term Auction Facility (TAF)/Term Security Lending Program (TSLP) Primary Dealer Credit Facility (PDCF)/Money Market Investor Funding Facility (MMIFF) Asset Backed Securities (ABS/MBS)/Credit Default Swaps (CDS) Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) Lender of Last Resort Stress test “Large negative tail” Black swan