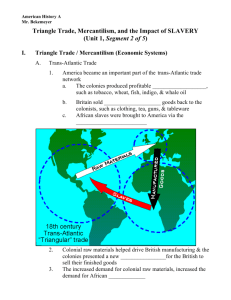
ghsgt review - Bibb County Schools
advertisement

GHSGT REVIEW Renaissance (1350-1600) ► “rebirth” of interest in learning and achievements of ancient Greece and Rome ► “classical learning” ► Ancient Greece and Rome Caesar; Mythology; Religion as a whole ► Development of in urban centers Urban City Rural Country Suburban Outside the city Renaissance ►begins Europe (Italy) Main city Florence, Italy ►spreads to northern Europe (England, France, Netherlands, Germany) Florence, Italy ► Politics ruled by wealthy merchant families Merchant trader ► Economy shipping trade ► Socially recovering from Black Plague and political instability Start of “individual thinking” Ideas of humanism Material comforts; positive human qualities Florence Renaissance ►Leads to Reformation Scientific Revolution Exploration and Discovery People of the Renaissance ►A “Renaissance Man” Term well-educated person who excels in multiple fields and has many talents ► Leonardo da Vinci ► Machiavelli ► Michelangelo Machiavelli Father of Political Science Political Science = Government The book – The Prince Force + shrewd decision making by leader in order to maintain power and order Leonardo da Vinci Original “The Renaissance Man” Painter; sculptor; engineer; physicist; studied anatomy Mona Lisa The Last Supper Michelangelo Painter & Sculptor Human images to reflect the divine beauty of God Humanists ► Studied the history, philosophy, and poetry of the ancient Greeks and Romans ► Petrarch ► Dante ► Erasmus Petrarch Petrarch ► Argued religious achievements and a person’s relationship with God had no relationship ► God gave certain people intelligence and talents that should be used in all aspects of life Dante Dante ► Common language of Italians ► Used common language of the city of Florence ► At the time, everything was Latin Father of Vernacular (Common Language) Italian Father of Italian Language Erasmus Erasmus ► Church was corrupt – so its needs reforming ► Believed in free will rather than predestination Free will a person’s ability to decide for themselves Predestination before you were born, God had already decided whether you were going to Heaven or Hell (later John Calvin) ► Wrote new testaments in Greek and Latin Protestant Reformation The Reformation ►Before Reformation, only ONE church existed in western Europe: The Roman Catholic Church. Martin Luther Martin Luther ► Europe (Germany) ► Posted 95 Theses on the Church door ► Attacked Church for indulgences Indulgences paying the church for forgiveness ► Believed doing good deeds did not get you into heaven Luther starts Protestantism ► Started the Lutheran Church ► Those who protested the Roman Catholic Church were called Protestants. ► Protestant – someone who believes in Jesus Christ as the Son of God but is not Catholic Today – Baptists, Methodists, Presbyterians, etc. John Calvin -Idea of Predestination - God is all powerful and has already decided who will receive salvation King Henry VIII of England Wives of Henry VIII Divorced, Beheaded, Died, Beheaded, Divorced, Survived Summary: ► In England (not mainland Europe) ► Wanted a divorce ► Catholic Church wouldn’t allow ► “Broke away” and formed his own church ► Church of England = Anglican Church Created Church of England (Anglican Church) Had a daughter Elizabeth I Elizabeth I “Virgin Queen” ?? Elizabethan Time Period Elizabeth I ► Her dad (King Henry VIII) had VERY Catholic beliefs (except divorce) ► Elizabeth I believed: ‘moderate’ form of Protestantism She didn’t force Religion into every day lives of her people Johannes Gutenberg ► Printed the 1st Bible in Europe made with movable type ► Allowed the ideas of the Protestant Reformation to expand quickly ► Promoted reading and thinking Catholics didn’t want to be outdone by Protestants Started the Counter Reformation (Catholic Reformation) Jesuits ► Group of Catholics ► Wanted to restore Catholicism ► Traveled throughout Europe ► Missionaries who wanted to turn Protestants back to Catholics ► Succeeded in many areas of Europe ► Still around today (Notre Dame is a Jesuit school) Council of Trent ► Body of Catholic Bishops ► Met over a period of 18 years ► Tried to reform Catholic practices” ► Believed: Good works were required to reach heaven Indulgences were okay ►However, were not allowed to be sold European Exploration Why are they exploring? Reasons for Exploring?? 1. 2. 3. Gold (money) God Glory New Inventions (1400) ► improved maps and compass ► Astrolabe Allowed sailors to locate and predict the position of the moon, sun, and stars making navigation easier and efficient (accurate) Vasco da Gama ► Established Portuguese dominance in the Indian Ocean ► Enabled the Portuguese to control the trade routes ► (He sailed around Africa) Christopher Columbus ► Italian who sailed for Spain ► Set out to find a westward route (water) from Spain to India ► Established a permanent settlement on the island of Hispaniola Ferdinand Magellan ► 1st European to lead an expedition that circumnavigated (sailed around) the world ► Proved that the world was spherical (round) Samuel de Champlain ► Established the 1st French Colony (Quebec City) Explorer From Found Da Gama 1497-99 Portugal India Columbus 1492-1493 Spain New World (West Indies) Magellan 1519-1522 Spain World is Round (Circumnavigated) Champlain 1608 France Settled in Canada Columbian Exchange ► The large-scale exchange of plants, diseases, animals, and people between the eastern and western hemispheres following Columbus’ first voyage to what would become known as the Americas Horse from Europe Potato from America Tobacco from America Scientific Revolution Explain things with Science instead of Religion Scientific Revolution ► Before the Scientific Revolution – Religion was used to explain EVERYTHING ► People started wondering WHY things happened…. Church believed Earth was center of universe Going against the Church was UNHEARD of… Copernicus ► Believed in heliocentric solar system (the Earth revolved around the sun) rather than the geocentric (Earth being the center) solar system ► Challenged the teachings of the Catholic Church Galileo Proved Copernicus Right! telescope Kepler Believed planets moved in an elliptical (oval or egg shaped) orbit around the sun Newton “Father of Calculus” Laws of gravity and motion Writings of John Locke Locke’s ideas ► Natural Rights “life, liberty, and property” Liberty = freedom ► Thomas Jefferson used his ideas in Declaration of Independence “life, liberty, and pursuit of happiness” Writings of Rousseau Rousseau’s Ideas… ►Social Contract theory “allowing government to exist and rule only by consent of the people being governed” People are willing to give up some rights so that the majority of their rights will be protected GEOGRAPHICAL TERMINOLOGY concept of place ► integrates the physical and human characteristics that make a part of the world what it is landforms ► Continent North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia) ► Cliff ► Plateau ► Mountain ► Plain ► Valley ► Canyon ► Peninsula (like Italy!) bodies of water ► Oceans Atlantic Pacific Indian Antarctic Arctic ► Rivers Mississippi ► Lakes ► Seas ► Gulf climate ► This is the temperature, rainfall, humidity, and wind that affect a region ► The type of climate decides what plants and animals live in a region Example- rocky land in New England made their economies not based on agriculture while the South had a climate that made growing crops easier soils refers to the type of dirt ► Different types of soils are better able to grow different crops ► natural vegetation ► Plants that grow in a region without being introduced by humans animal life ► Animals that live in a region Bison lived in the Great Plains region population ► Collection of people settlement patterns ► The order where people decide to live and settle Colonists began settling on the coast and moved inward, staying close to water agriculture ► The growing of food and crops The Native Americans grew beans and corn prior to the arrival of the Europeans Identify a map of Europe. Discuss how the climate of Europe affected the agricultural production of different regions. Trade routes of the major explorers Identify a map of North America. Find the four main colonial areas on a map geographic reasons-why settlements were established in these locations. They should include Virginia the Mid-Atlantic Colonies New England Colonies Virginia ► First permanent English colony in North America. ► Business venture of the Virginia Company ► Planned to make money by sending people to America to find gold and other valuable natural resources and then ship them back to England. ► They discovered no gold but learned how to cultivate tobacco. House of Burgesses ► Virginia Company established a legislative assembly that was similar to England‘s Parliament ► The House of Burgesses was the first Europeantype legislative body in the New World. Tobacco and VA ► Quickly became a major cash crop ► Important source of wealth ► Lead to major social and economic divisions between those who owned land and those who did not ► tobacco cultivation was labor-intensive caused the Virginia colony‘s economy to become highly dependent on slavery Native Americans ► Lived for centuries on the land the English settlers called Virginia. ► Powhatan- A notable Native American chieftain in the region was ► Forced off their own land by the settlers so it could be used by the settlers for agricultural purposes especially to grow tobacco. ► Fled live. the region and sought new places to Bacon’s Rebellion ► Poor English and slave colonists staged an uprising against the governor ► Landless rebels wanted harsher action against the Native Americans Wanted more land available to colonists ► The rebellion was put down ► Virginia House of Burgesses passed laws to regulate slavery This way poor white colonists wouldn’t with slaves anymore Puritans ► Established New England colonies ► Immigrated with their entire families better life practice religion freely ► Puritans were not tolerant of religious beliefs that differed from their own Rhode Island ► Founded by religious dissenters from Massachusetts who were more tolerant of different religious beliefs Colonial Government ► Town Meetings Ran New England colonies ► King Controlled there was often an appointed royal governor partially elected legislature. Voting rights were limited to men who belonged to the church ► church membership was tightly controlled by each minister and congregation ►Many born in America grew up to be adults who lacked a personal covenant (relationship) with God (this was the )central feature of Puritanism Half-Way Covenant ► Developed in response to the declining church membership ► Allowed partial church membership for the children and grandchildren of the original Puritans ► Hoped that this partial church membership would encourage second and third generation children to become full members included full life of the church ► Example voting privileges. Massachusetts ► 1686 ► King canceled Massachusetts charter that made it an independent colony ► Combined British colonies throughout New England into a single territory governed from England ► The colonists in this territory greatly disliked this centralized authority. ► 1691- Massachusetts Bay became a royal colony. Salem witch trials ► ► ► 1690s Series of court hearings Over 150 Massachusetts colonists accused of witchcraft were tried 29 of whom were convicted 19 hanged. 6 more people died in prison. ► Causes of the Salem witch trials extreme religious faith stress from a growing population bad relations with Native Americans narrow opportunities for women and girls to participate in Puritan society. Pennsylvania ► Located in the territory between New England and Virginia ► Founded by the religiously tolerant Quakers ► Led by William Penn. New York ► Settled by the Dutch called it New Amsterdam ► 1664 British conquered the colony Renamed it New York. ►A diverse population ► Center of trade and commerce ► Many Dutch remained ► With members of various British and Dutch churches New York tolerated different religions Mercantilism ► Parliament controlled trans-Atlantic trade with its American colonies All goods shipped to or from British North America had to travel in British ships Any goods exported to Europe had to land first in Britain to pay British taxes Some goods could be exported to Britain only. These restrictions were designed to keep the colonies from competing against Britain Americans responded by becoming smugglers. Slavery in the Colonies The African population in North America increased as tobacco and other cash-crop farming grew. ► Land owners greatly expanded the size of their farms. ► There were never enough workers available to plant, grow, and harvest the crops. ► Farmers turned to African slaves to do this work. When the Virginia Company founded Jamestown in 1607, there were no African slaves in British North America. ► By 1700, however, there were thousands of African slaves throughout the British colonies. ► The vast majority of these slaves were located in the Southern colonies where they supplied the labor required to support the region‘s agriculturally based economy. Middle Passage ► The sea voyage that carried Africans to North America was called the Middle Passage because it was the middle portion of a three-way voyage made by the slave ships. 1. 2. 3. ► ► ► British ships loaded with rum, cloth, and other English goods sailed to Africa, where they were traded for Africans. Then, in the Middle Passage, the slaves would be transported to the New World. The crew would buy tobacco and other American goods from profits they made by selling the slaves in the colonies and ship the tobacco and goods back to Britain. It was said that people in the colonial port cities could smell the slave ships arriving before they could see them. The slaves were packed like bundles of firewood. About two of every ten slaves died during the passage. African American culture ► Grew in America as slaves lived their lives under the worst of circumstances ► Slave communities were rich with music, dance, basket-weaving, and pottery-making ► Brought with them the arts and crafts skills of their various cultures as well as advanced farming techniques. ► A hundred slaves working on one farm and each slave might come from a different culture and a different part of Africa European and British Influence on the American Colonial Independence Movement John Locke ► Natural Rights Life Liberty Property ► His work heavily influenced the writers of the Declaration of Independence Jean-Jacques Rousseau ► Argued in favor of a social contractgovernment exists and rules by the consent of the governed England 1689 ► English Monarchy was stripped of its unlimited authority ► Governmental control was placed in the hands of the Parliament (representative assembly) ► English Bill of Rights- forms the basis for the American Bill of Rights Proclamation of 1763 ► English colonists were not allowed to live west of the Appalachian Mountains ► Convinced the colonists that the English did not understand life in the New World ► Led to the American Revolution Treaty of Paris or Treaty of 1763 ► Signed by Great Britain, France, and Spain ► Ended the French and Indian War (Seven Years’ War) ► Marked the beginning of a period of British dominance outside Europe ► England received control of all French possessions as well as most territory East of the Mississippi River Crisis in the Colonies ► Stamp Act- 1st direct tax on the colonists; all printed materials had to be stamp to show that the tax had been paid ► Sons and Daughters of Liberty- secret organization that was formed to protest British actions ► Committees of Correspondence- first organization linking the colonies in their opposition to British Rule; urged people to send representatives to the Stamp Act Congress Crisis in the Colonies ► Intolerable Acts Passed by the British to punish the Massachusetts colonists for the Boston Tea Party Closed Boston Harbor until the tea was paid for Required colonists to feed and house British soldiers in their homes Reduced the colonists’ right of self-government Convinced the 13 colonies to form a union of resistance against the British COLONIAL ACTIONS AND DOCUMENTS LEADING TO THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION Thomas Paine ► Common Sense Rejected prejudice and tyranny, while appealing to reason, natural laws, and the promise of freedom Promoted independence for economic, social, and moral reasons Declaration of Independence (1776) ► Based on the ideas of John Locke ► Social Contract Theory- government derives its power from the consent of the governed (people); this gave people the right to abolish any government that threatened to unalienable rights ► “Committee of Five” was appointed to draft a statement for Independence ► Thomas Jefferson is the primary author Declaration of Independence (1776) ► Divided into 5 parts Introduction The Preamble The Body (divided into two sections) The Conclusion KEY EVENTS AND PEOPLE OF THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION Benjamin Franklin ► American Ambassador to France ► French began to publicly support the Americans after the victory at Saratoga ► French agreed not to make peace with Britain unless Britain recognized American Independence Marquis de Lafayette ► French soldier who joined the war against the British ► Was assigned to George Washington’s staff ► Was a key strategist in the Yorktown campaign that led to the British surrender Lord Charles Cornwallis ► Commander of the British forces during the American Revolution ► Surrendered at Yorktown George Washington ► Commander-in- Chief of the Continental Army ► Reorganized the army, secured additional equipment and supplies Valley Forge ► Where Washington led his men in December 1777 ► The men were lacking clothing, shoes, food, and many supplies necessary for survival ► The Continental Army emerged after the long hard winter as a more unified fighting force capable of defeating the British Crossing the Delaware River ► Washington led his soldiers on a surprise attack on a fort occupied by Hessian mercenaries fighting for the British ► This victory proved Washington’s army could fight as well an experienced army Battle of Yorktown ► Victory won by a combination of American and French forces ► Last major battle of the American Revolution ► Treaty of Paris (1783)- officially ended the American Revolution and announced American Independence French Revolution (1789-1799) ►3 Phases Moderate Phase- Constitutional Monarchy Radical Phase- Reign of Terror Final Moderate Phase- Republic ► Cause- lack of voice in the Estates General (legislature) and influenced by the American Revolution Three estates ►1st►2nd Clergy Nobility French Revolution ► Tennis Court Oath- 3rd Estate refused to adjourn until they had equal rights ► Storming of the Bastille Symbol of the revolution Bastille was a French jail ► Result- power Napoleon takes Haiti (1791-1804) ► French colony of Saint Dominique ► France imposed strict mercantilistic policies on them and denied them a voice in government ► Leader: Toussaint L’Ouverture ► Slave rebellion drove out the French ► Jean-Jacques Dessalines declared Haiti independent 1804 ► US buys Louisiana from the French Haiti Latin America (1808-1825) ► Revolutions in the early part of the 19th Century led to the following independent countries: Mexico, Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Argentina, Chile, Brazil, and Bolivia ► Revolutions in Latin America were spawned after the American and French Revolutions ► Inspired by the efforts of Simon Bolivar who believed in self-government for the Spanish colonies Latin America THE PRINCIPLES AND HISTORICAL CONTEXT OF THE U.S. CONSTITUTION Articles of Confederation ► First Constitution of the United States ► Lacked provisions for executive and judicial powers ► Had no power to tax, regulate commerce, or establish one national currency ► Individual states had more power than the national government Shays’ Rebellion ► An attempt by a group of indebted farmers to secure weapons fro a Federal Armory ► Caused the United States to recognize the need for a new constitution Federalists ► Focused their arguments on the inadequacies of the national government under the Articles of Confederation and on the benefits of a national government as formed by the Constitution ► Argued that a strong central government would foster the commercial growth of the nation Anti-Federalists ► Feared the power of a strong central government ► Worried that the rights of the common people, like farmers, would be suppressed The Federalist Papers ► Written by Alexander Hamilton and James Madison ► Communicate the central ideas of the Federalists Benefits of a union between the states The problem with the confederation The importance of an energetic and effective federal government The Great Compromise ► Settled the dispute between states with large populations and states with small populations ► Combined parts of the Virginia and New Jersey plans ► Called for the creation of a legislature with two chambers House of Representatives- representation based on population Senate- equal representation for all states Three-Fifths Compromise ► Compromise on slavery ► 3/5 of a state’s slave population was counted when determining population ► Slave trade was allowed to continue for 20 years ► Northern states were required to return runaway slaves to their owners Separation of Powers ► Designed to prevent the government from becoming too powerful ► Power was divided between the national and state governments (Federalism) ► Power of the national government was divided among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches Checks and Balances ► Included to ensure none of the three branches would become too powerful ► Example- President has the power to veto laws passed by Congress Bill of Rights ► Added to the Constitution after it was ratified ► 1st 10 Amendments to the Constitution ► The promise of a Bill of Rights helped convince a majority of the voters to support the Constitution HISTORICAL ISSUES, EVENTS, & PEOPLE CONNECTED TO THE U.S. CONSTITUTION George Washington ► 1st President of the United States ► Favored non-intervention in Europe and avoided siding with France against Great Britain ► Warned of the dangers of political parties as people followed the views of Alexander Hamilton or Thomas Jefferson Whiskey Rebellion ► Congress passed taxes on liquor t help pay states’ debts from the Revolutionary War ► Armed violence broke out as farmers frightened and attacked federal tax collectors ► President Washington sent the militia to put down the rebellion; showed Washington’s constitutional authority to enforce the law NAPOLEON, JEFFERSON, THE LOUISIANA PURCHASE, & EXPLORATION BY LEWIS & CLARK Napoleon Bonaparte ► Rose to power in France through a coup that overthrew the Constitutional Government ► Developed higher education and a system of civil law known as the Napoleonic Code ► Development of modern warfare Louisiana Purchase ► The French sale of New Orleans and a large amount of land west of the Mississippi River to the U.S. ► Purchased for $15 million ► U.S. nearly doubled in geographic area Lewis and Clark Expedition ► Explored Louisiana and the western lands all the way to the Pacific Ocean ► Charted trails west, mapped rivers and mountain ranges, wrote descriptions and collected samples of unfamiliar animals and plants, and recorded facts and figures about the various native American tribes and customs Lewis and Clark EARLY 19TH CENTURY ECONOMIC AND TERRITORIAL GROWTH War of 1812 Britain vs. America Causes of the War of 1812 1. 2. 3. 4. The British were trying to prevent U.S. merchants fro trading with the French The British forced captured American sailors to serve in the British navy. The British were suspected of giving military aid to Native Americans fighting to keep Americans from settling on land in the west The Americans wanted to drive the British out of North America completely. Results of the War of 1812 1. 2. 3. End of all American/British hostilities. Establishment of America as a military force equal to those of Europe Americans became more nationalistic after the success in the War of 1812. War of 1812 Monroe Doctrine ►A warning issued by President James Monroe to the nations of Europe not to meddle in the politics of North and South America ► The U.S. intended to stay neutral in the politics and conflicts of Europe ► The U.S. would consider any military action in the Americas to be a hostile act against the U.S. Eli Whitney ► Developed the cotton gin which greatly reduced the cost of processing cotton and increased profits ► Interchangeable Parts- could be replaced without disposing of an entire machine REFORM MOVEMENTS OF THE EARLY 19TH CENTURY Women’s Suffrage ► Movement in the early 1800s was led by Elizabeth Cady Stanton Outspoken advocate for women’s full rights of citizenship, including voting rights and parental and custody rights Seneca Falls Conference (1848)- America’s 1st women’s rights convention ►Adopted a declaration of women’s independence, including women’s suffrage (the right to vote) Jacksonian Democracy ►A period when the office of the presidency and the executive branch became stronger in relation to the Congress ► Greater emphasis on the rights of the common man ► Suffrage was granted to all adult white males ► Politicians should be allowed to appoint their followers to government jobs ► Favored Manifest Destiny- expand the U.S. and its culture all the way to the Pacific Ocean Other Reform Movements Movement Issue Impact Temperance People should drink less alcohol or alcohol should be outlawed altogether Increased the size of Protestant religious organizations and their influence in western and rural sections of the country. Women played an important role, which laid the foundation for the women’s movement Abolition Slavery should be abolished and it should not be allowed in new states Made slavery and its expansion an important political issue. Women played an important role, which laid the foundation for the women’s movement. Public School All children should be required to attend free schools supported by taxpayers and staffed by trained teachers Established education as a right for all children and as a state and local issue. Improved the quality of schools by requiring trained teachers. GROWING NORTH/SOUTH DIVISIONS LEADING TO THE CIVIL WAR The Abolition Movement ► William Lloyd Garrison White abolitionist who was a writer and an editor Founded regional and national abolitionist societies Published an antislavery newspaper Frederick Douglass ► Former slave who escaped ► Worked for Garrison ► Gave eloquent speeches on behalf of equality for African Americans Missouri Compromise of 1820 ► Maine was admitted as a free state and Missouri was admitted as a slave state ► Slavery would be prohibited in the northern part of the Louisiana Purchase except for Missouri Nullification Crisis ► Resulted when southern states sought to nullify (cancel) a high tariff Congress had passed on manufactured goods imported from Europe ► The tariff helped protect northern manufacturers, but hurt southern plantation owners ► South Carolina nullified the tariff States Rights ► The idea that states have certain rights and political powers separate from those held by the federal government that the federal government may not violate Mexican-American War ► Occurred when the United States declared the annexation of Texas ► United States occupied much of northern Mexico ► Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo- ceded portions of Northern Mexico to the United States ► Wilmot Proviso- New Mexico and California territories acquired from Mexico would be a free state with no slavery; did not pass the House of Representatives Compromise of 1850 ► New Mexico would be established by carving its borders from the state of Texas ► All citizens would be required to apprehend runaway slaves and return them to their owners ► The slave trade would be abolished in the District of Columbia ► New Mexico voters would determine whether the state would permit or prohibit the practice of slavery KEY EVENTS, ISSUES, & PEOPLE OF THE CIVIL WAR Kansas-Nebraska Act ► Repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820 ► Popular sovereignty (rule by the people) would be used to determine whether a territory would be slave or free ► Both pro- and anti- slavery groups hurried to Kansas to create voting majorities; violence erupted between the two groups Dred Scott Decision ► The Court state that no African Americaneven free- could ever by a U.S. citizen ► Congress could not prohibit slavery in federal territories ► The Missouri Compromise of 1820 was unconstitutional John Brown ► Famous abolitionist who decided to fight slavery with violence and killing ► Believed he was chosen by God to end slavery ► Commanded family members and other abolitionists to attack proslavery settlers in Kansas ► Led a raid on the federal armory at Harpers Ferry, VA and killed 7 people; convicted of treason and hung Abraham Lincoln ► Elected president in 1860 ► South Carolina voted to secede (separate from) the U.S. & were followed by other southern states and formed the Confederate States of American ► CSA attacked the U.S. Army base at Fort Sumter, SC Emergency Powers Used by Lincoln ► Suspended habeas corpus (the legal rule that anyone imprisoned must be taken before a judge to determine if they are being held legally) ► Issued the Emancipation Proclamation (freed all slaves held in the Confederate States) Antietam (Sept. 1862) ► Antietam Creek, Maryland ► 1st major battle on northern soil ► Deadliest one-day battle in American history ► Neither side won a victory ► Less’ failure to win encouraged Lincoln to issue the Emancipation Proclamation Gettysburg (April 1863) ► Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee march north to Pennsylvania ► Battle lasted for 3 days ► Deadliest battle of the Civil War ► Lee failed to show Britain and France they should assist the Confederacy ► Lee gave up attempts to invade the Union ► Nov. 1863- Lincoln gave the Gettysburg Address to dedicate a military cemetery at the site of the battle Vicksburg (May-July 1863) ► Union Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant laid siege to Vicksburg, MS because the army that controlled its high ground over a bend in the Miss. River controlled the river ► Union won and gained control of the river Atlanta (July-September 1864) ► An important center of Confederate manufacturing and railway traffic that was captured by the Union Gen. William T. Sherman ► Sherman burned Atlanta to the ground and marched to the Atlantic Ocean LEGAL, POLITICAL, & SOCIAL ASPECTS OF RECONSTRUCTION Presidential Reconstruction ► Refers to the plans laid out by President Lincoln and carried out by President Andrew Jackson ► Urged no revenge on former Confederate supporters ► Purpose was to readmit the southern states to the Union as quickly as possible Radical Republican Reconstruction ► The more laborious process of rejoining the union that Congress required of the former confederate states ► Southern states had to reapply for admission to the Union ► Passage of 3 Amendments 13th- abolished slavery and involuntary servitude 14th- defined U.S. citizenship as including all persons born in the U.S.; no citizen could be deprived of his rights without due process 15th- removed restrictions on voting based on race, color, or ever having been a slave Progress of African Americans ► Morehouse College- university established for African Americans in 1867 ► Freedmen’s Bureau- helped former slaves solve everyday problems by providing food, clothing, jobs, medicine, and medical-care facilities Impeachment of Andrew Johnson ► Occurred because President Johnson ignored laws passed by congress to limit presidential powers ► Johnson missed being convicted by one vote, therefore he was not removed from office Resistance to Racial Equality ► Black Codes laws written to control the lives of freed slaves Deprived voting rights to freed slaves Allowed plantation owners to advantage of black workers ► Ku Klux Klan (KKK) Founded by veterans of the Confederate Army to fight against Reconstruction LATE 19TH AND EARLY 20TH CENTURY INDUSTRIAL GROWTH, BIG BUSINESS, & THE PROGRESSIVE ERA Railroad and Chinese Labor ► The federal government gave vast areas of western land to railroad owners to lay tracks to connect the eastern and western states ► Chinese Laborers did much of the work because they were willing to accept lower pay than others John D. Rockefeller ► Founded Standard Oil Company ► Created a trust (owned more than 90% of America’s oil industry) Monopoly- a single company that controlled virtually all the U.S. oil production and distribution American Federation of Labor & Samuel Gompers ► American Federation of Labor (AFL) was a labor union Led by Samuel Gompers Goal was to use strikes to convince employers to give workers shorter work days, better working conditions, higher wages, and greater control over how they carried out their workplace responsibilities Muckrakers ► Muckrakers- journalists who investigated and exposed political corruption, child labor, slum conditions, and other social issues Upton Sinclair ►Wrote The Jungle which exposed poor labor practices and unsanitary conditions in the meat packing industry Ida Tarbell ►Criticized Standard Oil Company’s unfair business practices; her findings contributed to the government’s decision to break up the Standard Oil Trust Jim Crow Laws ► Segregation laws that required separate public and private facilities for African Americans ► Resulted in inferior education, health care, and transportation systems for African Americans ► Plessy v. Ferguson- 1896 Supreme Court decision that upheld the constitutionality of Jim Crow Laws; “separate but equal” doctrine NAACP ► Founded by a group who sought full social and economic equality for African Americans Progressive Reforms ► Progressives- reformers who were inspired to make improvements in America’s political and social environment Initiative- collect voters’ signatures on an issue to force the government to present the issue to the voters Referendum- when the government present the issue to the public for a vote Recall- the removal of public officials from office before their term expires by the voters 17th Amendment- Direct Election of Senators U.S./FOREIGN RELATIONS AT THE TURN OF THE 20TH CENTURY Chinese Exclusion Act ► Passed after white workers were angered that Chinese immigrants accepted low wages for jobs whites had held ► Passed in 1882 and banned all future Chinese immigration Spanish-American War ► Began after Spain refused to grant independence to Cuba ► 1st battles of the war were fought in the Philippines The U.S. Navy defeated the Spanish Navy and the U.S. kept the Philippines as a territory until 1946 Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine ► The U.S. had the right to intervene in Latin American countries in economic crisis, whether or not a European power planned to intervene Panama Canal ► Built because the U.S. was seeking a faster sea route from the Atlantic to the Pacific ► Opened in 1914 CAUSES AND EFFECTS OF WWI Causes of World War I ► Balkan Nationalism The Balkan people believed that Bosnia should be part of a new Slavic state, but Bosnia was under Austro-Hungarian control Russia secretly helped finance the assassination of Archduke Francis Ferdinand (catalyst for WWI) ► Entangling Alliances European nations made alliances with each other to end conflict ► Militarism Treaty of Versailles ► Ended World War I ► Required Germany to pay for the damages of the war (reparations) U.S. Involvement in WWI ► In 1914, President Wilson wanted to guarantee U.S. neutrality and keep the U.S. out of the war ► Lusitania- luxury liner that was sunk by a German submarine (U-boat); killed most onboard including 100 U.S. citizens ► 1917- Germany resumed unrestricted submarine warfare that endangered U.S. trade and American lives Great Migration ► The movement of African Americans from the South to the northeastern and midwestern cities to find jobs created by the war Fourteen Points & the League of Nations ► Fourteen Points- speech given by Wilson in which he described ways to avoid future wars ► League of Nations one of the Fourteen Points International peacekeeping organization The Senate refused to ratify the Treaty of Versailles because of the League of Nations The U.S. never joined th 18 ► 18th and th 19 Amendments Amendment- Prohibited the manufacture, sale, or transportation of intoxicating liquors (alcohol) ► 19th Amendment- Gave women the right to vote KEY DEVELOPMENTS IN THE U.S., EUROPE, & ASIA BETWEEN WWI AND WWII Russia ► Russian Soviet Union Revolution Russia suffered military and economic failures during WWI, which forced the Czar to step down Russia instituted a provisional government A party of soviets (councils of workers and soldier) called the Bolsheviks and led by V.I. Lenin seized power ► Stalin- leader of the Soviet Union; took over after Lenin’s death Five Year Plan- Plan to transform the Soviet Union from an agricultural into an industrial economy Fascism ► Fascism a political philosophy that emphasizes the state over the individual Propaganda is used to convince the people that a strong central government led by a dictator is the way to economic and military success Opposition is suppressed by the threat of violence Benito Mussolini ► The Fascist Leader of Italy who rose to power after WWI Adolf Hitler ► The Fascist leader of the Nazi Party and Germany ► Wrote Mein Kampf- a book outlining AntiSemitism (hatred for Jewish people), anticommunism, and the right of superior individuals to take control Hirohito ► The Emperor of Japan from 1926 to 1989 ► His reign included internal conflicts, the invasion of China, entry into WWII as an Axis Power, the surrender of Japan, and growth into a modern industrial power Terms to Know ► Totalitarianism- governments that control every aspect of public and private life in the country ► Police State- there is no “rule of law” governing the actions of the government; “law” is the same as the personal beliefs of a country’s dictator ► Authoritarian Government- the leader lacks real legitimacy and lacks charisma that generates loyalty from the people Communism and Socialism in the U.S. ► Communism based on a single-party government ruled by a dictator No private ownership; all property is owned by the state ► Red Scare the fear in the U.S. of international communism which led to the government pursuing suspected communists and socialists Led to new restrictions on immigration Henry Ford ► Mass productionprocess popularized by Henry Ford in which items can be produced in a large volume Led to the automobile becoming a true replacement for the horse U.S. Society ► Jazz- combined themes and note patterns developed by enslaved African Americans with the syncopated rhythms worked out by musicians in New Orleans ► Louis Armstrong- trumpet player and one of the biggest stars of jazz ► Harlem Renaissance- celebrated African American culture through words and song Langston Hughes- movement’s best-known poet GREAT DEPRESSION & THE NEW DEAL Causes of the Great Depression ► Stock Market Crash 1929- immediate cause ► Causes of the crashExcessive use of credit ( stock on the margin) Overproduction of consumer goods Protective Tariffs ( high) Unequal distribution of wealth Weak farm economy- started in early ’20’s Hoover & Great Depression ► Believed in “Rugged Individualism” ► Hoovervilles communities of homeless people living in crates, and shanties Blamed Hoover for not helping them ► 25% of the population was unemployed F.D.R. & New Deal ► The New Deal was F.D.R’s plan to get America out of the Depression ► T.V.A (Tenn. Valley Authority)- built dams and power plants along the Tennessee River providing jobs and electricity to rural areas ► Wagner Act ( National Labor Relations Act) established collective bargaining for labor unions and prohibited unfair labor practices ► Social Security- retirement, unemployment, and disability ( Second New Deal) Causes of WWII ► Imperialism: Italy, Germany & Japan expand throughout Europe & Asia. ► Nationalism ► Militarism ► Alliances: Allies ( Britain, France, U.S., USSR) & Axis ( Germany, Japan, & Italy) ► Invasion of Poland 1939, started the war in Europe ► Bombing of Pearl Harbor 1941 brought the U.S into the war American Neutrality ► U.S did not want to be involved in another global conflict ► U.S passed Neutrality Acts to keep us out of the war ► Lend-Lease: Nine months before Pearl Harbor the U.S (FDR) found a way to help Britain. We loaned military equipment and supplies to any nation (Great Britain) vital in the defense of America. War Mobilizations ► America expanded the Selective Service Act (draft) which began before Pearl Harbor ► The Women’s Auxiliary Corps (WACS) was started ► Women worked in the war industries ( Rosie the Riveter) ► Japanese Americans were placed in relocation or internment camps. ► America used mandatory rationing to conserve goods ► Factories were converted from peace time to war time production. Major Events in WWII ► Holocaust: Planned extermination of Jews and other ethnic and minority people by Hitler’s Nazi Party ► D-Day: Code name for Operation Overlord the allied invasion of Nazi occupied France. This marked the beginning of the Allied victory ► Manhattan Project: Project to build an atomic bomb ► Los Alamos: Tested the atomic bomb ► U.S. dropped the atomic bomb on Japan August, 1945 & Sept. 1945. Japan surrendered WWII Conferences ► Teheran & Yalta: FDR, Stalin, & Churchill met to paln the DDay Invasion & the occupation of Europe after the war. Potsdam: ► Stalin, Atlee and Truman met at Potsdam to plan for post war Europe and it is here Truman decided to drop the atomic bomb. Cold War ► ► ► ► Marshall Plan: The European Recovery Plan was a plan to loan 13 billion dollars to European countries to help them recover from the war. The offer was made to all countries that would make political reforms (not communist). The Soviet Union and allies refused. Western European countries & U.S. v the Soviet Union and their satellites (sphere of influence) Containment: The U.S foreign policy to stop or contain the spread of Communism. NATO : North Atlantic Treaty Organization started after the Berlin Airlift, collective security for western European countries