Digestion: Chewing & Dissolving
advertisement

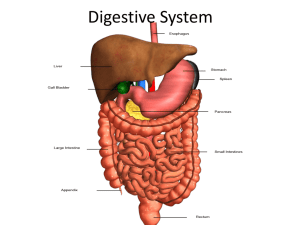
Digestive System Learning Targets 1-5 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Trace the path of food in the digestive tract & describe the general structure & function of each organ mentioned Describe peristalsis & state its function. Describe the wall of the small intestine & relate its anatomy to nutrient absorption. Name the hormones produced by the digestive tract that help control digestive secretions. Name the accessory organs of digestion & describe their contributions to the digestive process. Trace the path of food in the digestive tract & describe the general structure & function of each organ mentioned (LT#1) • Mouth • Pharynx • Esophagus • Stomach • Small intestine • Large intestine • Rectum • Anus The mouth (oral cavity) (LT#1) • Bounded by lips, cheeks, palate, and tongue • Continuous with the oropharynx posteriorly • pg 299 • Carbohydrate digestion starts here when amylase is secreted by salivary glands Palates and their functions (LT#1) 1. Hard palate pg 299 – Assists the tongue in chewing 2. Soft palate – Closes off the nasopharynx during swallowing – Uvula projects downward from its free edge Uvula plays role in voice – gutteral and click consonants Function of the tongue (LT#1) • Gripping and repositioning food during chewing • Mixing food with saliva and forming the bolus • Initiation of swallowing, and speech Pharynx (LT#1) • Where swallowing occurs • Nasopharynx is covered when soft palate moves back – so food doesn’t go up your nose • Glottis is the opening to the larynx @ top of trachea • Epiglottis covers the trachea during swallowing – so food doesn’t get into lungs Esophagus (LT#1) • Connects mouth to stomach • 2 sphincters: one near pharynx = pharyngoesophageal & one near the stomach = gastroesophageal • Swallowing pushes bolus (food ball) into the esophagus & peristalsis carries it to stomach (pg 300) • Peristalsis w/o food = sensation of lump in your throat Stomach (LT#1) • Thick walled, J-shaped, upper left quadrant • Esophagus superior • Duodenum inferior • 3 layers of muscle & rugae (deep folds) • Gastric glands secrete gastric juice containing pepsin (digests proteins) Figure 14.2 Intestines (LT#1) • • • • Small 3 parts Duodenum – base of stomach Jejunum – 1st portion Ileum – final portion before large intestine • Suspended by mesentery (pg 302) Figure 14.11 Small intestine function (LT#1) • Where majority of digestion occurs • Villi increase surface area for absorption of nutrients (pg 303) • Digestive hormones control secretions (Table 15.2 pg 301) Large intestine or colon (LT#1)pg 307 • • • • • • • • Cecum Vermiform appendix Ascending colon Transverse colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus Figure 14.12 Large intestine function (LT#1) • Absorbs water & electrolytes from chyme • Prepares indigestible material for excretion from anus (bile gives color, E. coli gives odor) 6 essential activities of the digestive process (LT#1 summary) • • • • • • Ingestion Propulsion Mechanical digestion Chemical digestion Absorption Defecation Describe peristalsis & state its function (LT#2) pg 300 Describe the wall of the small intestine & relate its anatomy to nutrient absorption (LT#3) pg 302 Name the hormones produced by the digestive tract that help control digestive secretions (LT#4) pg 301-302 Accessory digestive organs & their contribution to digestion (LT#5) • • • • Salivary glands Liver Gallbladder Pancreas Figure 14.5 Salivary glands and their function (LT#5) • Three pairs of glands – parotid, submandibular, and sublingual • Cleanses the mouth • Moistens and dissolves food chemicals • Aids in bolus formation • Contains enzymes that break down starch • Primary function is to begin digestion by breaking down starch to simple sugars Figure 14.10 Liver • Largest gland has 2 lobes • Functional unit is the lobule (100,000) • “triad” consists of (1) branch of hepatic artery brings oxygenated blood (2) branch of hepatic portal vein brings nutrients from intestines (3) bile duct shuttles bile away from liver http://www.hopkinsgi.org/GDL_Disease.aspx?CurrentUDV=31&GDL_Cat_ID=BB532D8A-43CB416C-9FD2-A07AC6426961&GDL_Disease_ID=C8BD9205-E51B-4186-B4E4B5087B21F9EA Liver function (page 304) • Removes toxins from blood brought in from intestines • Removes & stores fat soluble vitamins A, D, E, & K • Makes plasma proteins from amino acids (urea is byproduct) • Pancreas influences liver by insulin & glucagon to maintain blood glucose level Liver function continued • Excess glucose stored as glycogen • Produces bile that contains pigments bilirubin & biliverdin (from breakdown of hemoglobin – rbc pigment) Gall Bladder • Pear-shaped muscular organ attached to ventral side of liver • Stores excess bile produced in liver • Bile enters duodenum to emulsify fats so they can be further broken down by lipase from the pancreas Pancreas • Rests on posterior wall behind stomach • Cells produce pancreatic juice containing sodium bicarbonate to neutralize pH of chyme • Digestive enzyme pancreatic amylase for carbs • Trypsin & chemotrypsin to digest protein aka protease • Lipase to digest fat