Chapter 8: Bandaging and Taping - Florida International University
advertisement

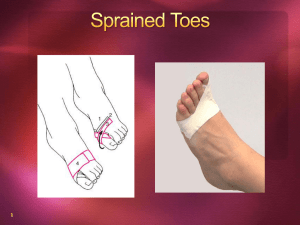
Chapter 8: Bandaging and Taping Jennifer L. Doherty, MS, LAT, ATC Academic Program Director, Entry-Level ATEP Florida International University Acute Care and Injury Prevention Bandaging Contributes to recovery of injuries Must be firmly applied while still allowing circulation When applied incorrectly may cause Discomfort Wound contamination Prolonged healing Bandaging Materials Gauze Elastic bandages Sterile pads for wounds Extensible and very useful with Roller bandages to hold sports Active bandages allowing for movement Provide support and compression for wound healing dressings in place Padding to prevent blisters Cotton cloth Ankle wraps Cohesive elastic bandage Triangular bandages Two-layer, self adhering bandage Exerts constant and even pressure Elastic Bandages Gauze, cotton cloth, or elastic wrapping Length and width vary and are used according to body part and size Length: 6 or 10 yards Widths: 2, 3, 4, or 6 inches Should be stored rolled Should be free from wrinkles, seams, and imperfections that could cause irritation Elastic Bandage Application Hold bandage in preferred hand Loose end should extend from bottom of roll Back surface of loose end should lay directly on skin surface Pressure and tension should be standardized Anchors are created by overlapping wrap Start anchor at smallest circumference of limb Elastic Bandage Application Body part should be wrapped in position of maximum contraction Each turn should overlap by half to prevent separation More turns with moderate tension Fewer turns with maximum tension Circulation should be monitored Elastic bandages may be used to provide support for a variety scenarios: Ankle and foot spica Spiral bandage (spica) Groin support Shoulder spica Elbow figure-eight Gauze hand and wrist figure-eight Cloth ankle wrap Triangle Bandages First aid device Application is easy and fast Primarily used for slings Cervical arm sling Shoulder arm sling Sling and swathe Cervical Arm Sling Provides support for forearm, wrist, and hand injuries Bandage placed around neck and under bent arm to be supported Shoulder Arm Sling Utilized following injury to the shoulder girdle Provides support for the forearm May be used if the cervical arm sling is causing irritation Sling and Swathe Combination of cervical and shoulder arm slings Provides support for the upper extremity Used in instances of Shoulder dislocations Upper extremity fractures Taping Historically an important part of athletic training profession Becoming less important due to questions regarding its effectiveness Utilized in areas of… Injury care Injury protection Taping: Injury Care Retention of wound dressing Stabilization of compression bandages utilized to control internal and external bleeding Support for recent injuries in an effort to prevent additional trauma Provide stabilization during rehabilitation Taping: Injury Protection Used to prevent acute injuries Limits motion Secures special device Brace Splint Soft Cast Padding Non-Elastic White Tape Great adaptability due to: Adhesive mass Adhering qualities Lightness Relative strength Available in varied sizes: 1”, 1.5”, 2” Utilized to… Hold dressings in place Provide support to a joint Protect injured areas When purchasing non-elastic white tape, consider the following: Tape Grade Longitudinal and vertical fibers per inch cost = fibers Adhesive Mass Should adhere evenly Should maintain adhesion with perspiration Should contain few skin irritants Should be easily removed without leaving residue and without removing superficial skin When purchasing non-elastic white tape, consider the following: Winding Tension Critically important for even application If applied for protection, tension must be even Elastic Tape Used in combination with non-elastic tape Good for small, angular body parts Available in varied sizes: 1”, 2”, 3”, 4” Preparation for Taping Skin surface should be clean No oil, perspiration, or dirt Hair should be removed Prevents skin irritation upon tape removal Tape adherent is optional Foam and skin lubricant should be used to minimize blisters and skin irritation Heel and lace pads Proper Taping Technique Tape directly to skin Prewrap may be used Helps protect skin in cases where tape is used daily Only one layer of prewrap should be applied Too much prewrap causes irritation and loosens the tape job Prewrap must be anchored proximally and distally Proper Taping Technique Select tape width based on area to be taped Acute angles require narrower tape Tearing tape Should always hold on to roll of tape Do not bend, twist, or wrinkle tape Tear a straight edge with no loose strands Some tapes may require cutting agents Proper Taping Technique Tape joint in proper position Position for stabilization Overlap the tape by half Avoid continuous taping Keep tape roll in hand whenever possible Allow tape to follow contours of the skin Smooth and mold tape as it is laid down on skin Proper Taping Technique Always start taping with anchors Always finish taping with locking strips Where maximum support is desired, tape directly to the skin Do not apply tape if skin is hot or cold from treatments Altered sensation Altered circulation Tape Removal Tape may be removed by hand Always pull tape in direct line with body One hand pulls tape while other hand presses skin in opposite direction Tape scissors/cutters may be required Be sure not to aggravate injured area with cutting device Tape may also be removed with chemical solvents Common Foot Taping Procedures Arch Technique 1 Function: to support weak arches Arch Technique 2 Function: to support the longitudinal arch Arch Technique 3 X teardrop method Function: to support longitudinal arch and forefoot Arch Technique 4 Fan method Function: to support the longitudinal arch LowDye Taping Technique ( Function: to support longitudinal arch and forefoot Used to support: Fallen arches Forefoot pronation Arch strains Plantar facitis Taping for Sprained Toes Function: to support metatarsophalangeal joint Bunion Taping Turf Toe Taping Function: to prevent excessive hyperextension of metatarsophalangeal joint Taping Hammer or Clawed Toes Function: to reduce pressure of bent toes against shoes Taping for Fractured Toes Function: to splint injured toe to non-injured toe Common Ankle Taping Procedures Routine Prophylactic Taping Closed Basket Weave Function: to minimize ankle motion Dorsiflexion and Plantarflexion Inversion and Eversion Used to support newly sprained or chronically weak ankles U-shaped felt pad can be used to provide focal compression Aids in controlling swelling Closed Basket Weave Technique Open Basket Weave Function: to minimize ankle motion Allows more dorsiflexion and plantarflexion Minimizes inversion and eversion Used to support newly sprained ankles allowing room for swelling Used with elastic bandage and cold application U-shaped felt pad can be used to provide focal compression Aids in controlling swelling Open Basket Weave Technique Continuous Stretch-Tape Technique Common Leg & Knee Taping Procedures Achilles Tendon Taping Function: to prevent over-stretching of achilles Collateral Ligament Taping Function: to provide joint stability following injury to the MCL or LCL ligaments Rotary Taping for Knee Joint Instability Function: to provide joint stability following injury to the ACL and MCL Knee Hyperextension Taping Functions: To prevent knee hyperextension To provide support for hamstrings and cruciate ligaments following injury Patellofemoral Taping McConnell Technique Function: to manage glide, tilt, rotation, and anteroposterior orientation of patella Accomplished by passively taping patella into biomechanically correct position Also provides prolonged stretch to soft-tissue structures associated with dysfunction Common Upper Extremity Taping Procedures Elbow Taping Function: to prevent elbow hyperextension Wrist Technique 1 Function: to provide support to the wrist following mild wrist sprains and strains Wrist Technique 2 Function: to protect and stabilize a badly injured wrist Bruised Hand Taping Function: to protect the hand following injury Thumb Taping Function: to provides support for the thumb joint following a sprain injury Finger and Thumb Checkreins