Analog to Digital Converter
advertisement

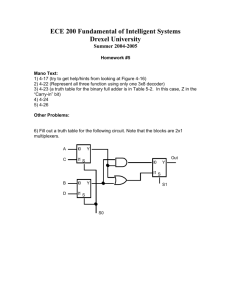
Analog to Digital Converters (ADC) Ben Lester, Mike Steele, Quinn Morrison Topics Introduction Why? Types and Comparisons Successive Approximation ADC example Applications ADC System in the CML-12C32 Microcontroller Analog systems are typically what engineers need to analyze. ADCs are used to turn analog information into digital data. Process Sampling, Quantification, Encoding Outpu Discrete t Voltage States Ranges (V) 0 0.00-1.25 1 1.25-2.50 2 2.50-3.75 3 3.75-5.00 4 5.00-6.25 5 6.25-7.50 6 7.50-8.75 7 8.75-10.0 Output Binary Equivalent 0 000 1 001 2 010 3 011 4 100 5 101 6 110 7 111 Resolution, Accuracy, and Conversion time Resolution – Number of discrete values it can produce over the range of analog values; Q=R/N Accuracy – Improved by increasing sampling rate and resolution. Time – Based on number of steps required in the conversion process. Comparing types of ADCs Flash ADC Sigma-delta ADC Wilkinson ADC Integrating ADC Successive Approximation Converter Flash ADC Speed: High Cost: High Accuracy: Low Sigma-delta ADC Speed: Low Cost: Low Accuracy: High Wilkinson ADC Speed: High Cost: High Accuracy: High Wilkinson Analog Digital Converter (ADC) circuit schematic diagram Integrating ADC Speed: Low Cost: Low Accuracy: High Successive Approximation Converter Speed: High Cost: High Accuracy: High but limited Topics Introduction Why? Types and Comparisions Successive Approximation ADC example Applications ADC System in the CML-12C32 Microcontroller Successive Approximation ADC Example Mike Steele Goal: Find digital value Vin • 8-bit ADC • Vin = 7.65 • Vfull scale = 10 Successive Approximation ADC Example • MSB LSB • Average high/low limits • Compare to Vin • Vin > Average MSB = 1 • Vin < Average MSB = 0 • Bit 7 • (Vfull scale +0)/2 = 5 • 7.65 > 5 Bit 7 = 1 1 Vfull scale = 10, Vin = 7.65 Successive Approximation ADC Example • MSB LSB • Average high/low limits • Compare to Vin • Vin > Average MSB = 1 • Vin < Average MSB = 0 • Bit 6 • (Vfull scale +5)/2 = 7.5 • 7.65 > 7.5 Bit 6 = 1 1 1 Vfull scale = 10, Vin = 7.65 Successive Approximation ADC Example • MSB LSB • Average high/low limits • Compare to Vin • Vin > Average MSB = 1 • Vin < Average MSB = 0 • Bit 5 • (Vfull scale +7.5)/2 = 8.75 • 7.65 < 8.75 Bit 5 = 0 1 1 0 Vfull scale = 10, Vin = 7.65 Successive Approximation ADC Example Vin = 7.65 • MSB LSB • Average high/low limits • Compare to Vin • Vin > Average MSB = 1 • Vin < Average MSB = 0 • Bit 4 • (8.75+7.5)/2 8.125 • 7.65 < 8.125 Bit 4 = 0 1 1 0 0 Successive Approximation ADC Example Vin = 7.65 • MSB LSB • Average high/low limits • Compare to Vin • Vin > Average MSB = 1 • Vin < Average MSB = 0 • Bit 3 • (8.125+7.5)/2 = 7.8125 • 7.65 < 7.8125 Bit 3 = 0 1 1 0 0 0 Successive Approximation ADC Example Vin = 7.65 • MSB LSB • Average high/low limits • Compare to Vin • Vin > Average MSB = 1 • Vin < Average MSB = 0 • Bit 2 • (7.8125+7.5)/2 = 7.65625 • 7.65 < 7.65625 Bit 2 = 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 Successive Approximation ADC Example Vin = 7.65 • MSB LSB • Average high/low limits • Compare to Vin • Vin > Average MSB = 1 • Vin < Average MSB = 0 • Bit 1 • (7.65625+7.5)/2 = 7.578125 • 7.65 > 7.578125 Bit 1 = 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 Successive Approximation ADC Example Vin = 7.65 • MSB LSB • Average high/low limits • Compare to Vin • Vin > Average MSB = 1 • Vin < Average MSB = 0 • Bit 0 • (7.65625+7.578125)/2 = 7.6171875 • 7.65 > 7.6171875 Bit 0 = 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 Successive Approximation ADC Example 0.8 Voltage • 110000112 = 19510 • 8-bits, 28 = 256 • Digital Output • 195/256 = 0.76171875 • Analog Input • 7.65/10 = 0.765 Vin = 7.65 1 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 7 6 5 4 3 Bit • Resolution • (Vmax – Vmin)/2n 10/256 = 0.039 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 1 0 ADC Applications • Measurements / Data Acquisition • Control Systems • PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) • Sensor integration (Robotics) • Cell Phones • Video Devices • Audio Devices e*(∆t) t t ∆t Controller 1001 0010 1010 0101 e* 0010 0101 0011 1011 e u*(∆t) ∆t ATD10B8C on MC9S12C32 Presented by Quinn Morrison MC9S12C32 Block Diagram ATD 10B8C ATD10B8C Block Diagram ATD10B8C Key Features Resolution Conversion Time 8/10 bit (manually chosen) 7 usec, 10 bit Successive Approximation ADC architecture 8-channel multiplexed inputs External trigger control Conversion modes Single or continuous sampling Single or multiple channels ATD10B8C Modes and Operations Modes Stop Mode Wait Mode All clocks halt; conversion aborts; minimum recovery delay Reduced MCU power; can resume Freeze Mode Breakpoint for debugging an application Operations Setting up and Starting the A/D Conversion Aborting the A/D Conversion Resets Interrupts ATD10B8C External Pins There Are 12 External Pins AN7 / ETRIG / PAD7 AN6/PAD6 – AN0/PAD0 Analog input General purpose digital I/O VRH, VRL Analog input channel 7 External trigger for ADC General purpose digital I/O High and low reference voltages for ADC VDDA, VSSA Power supplies for analog circuitry ATD10B8C Registers 6 Control Registers ($0080 - $0085) 2 Status Registers ($0086, $008B) Formatted results (2 bytes) 1 Digital Input Enable Register ($008D) Allows for analog conversion of internal states 16 Conversion Result Registers ($0090 - $009F) General status information regarding ADC 2 Test Registers ($0088 - $0089) Configure general ADC operation Convert channels to digital inputs 1 Digital Port Data Register ($008F) Contains logic levels of digital input pins ATD10B8C Control Register 2 ATD10B8C Control Register 3 ATD10B8C Control Register 4 ATD10B8C Control Register 5 ATD10B8C Single Channel Conversions ATD10B8C Multi-channel Conversions ATD10B8C Status Register 0 ATD10B8C Status Register 1 ATD10B8C Results Registers ATD10B8C Results Registers ATD10B8C ATD Input Enable Register ATD10B8C Port Data Register ATD10B8C Setting up the ADC References • Dr. Ume, http://www.me.gatech.edu/mechatronics_course/ • Maxim Integrated Products, AN1870, AN 1870, APP1870, Appnote1870, Appnote 1870 • "An Introduction to Sigma Delta Converters." Die Homepage Der Familie Beis. 10 June 2008. Web. 27 Sept. 2010. <http://www.beis.de/Elektronik/DeltaSigma/SigmaDelta.html>.