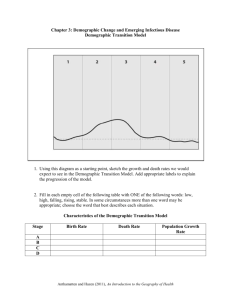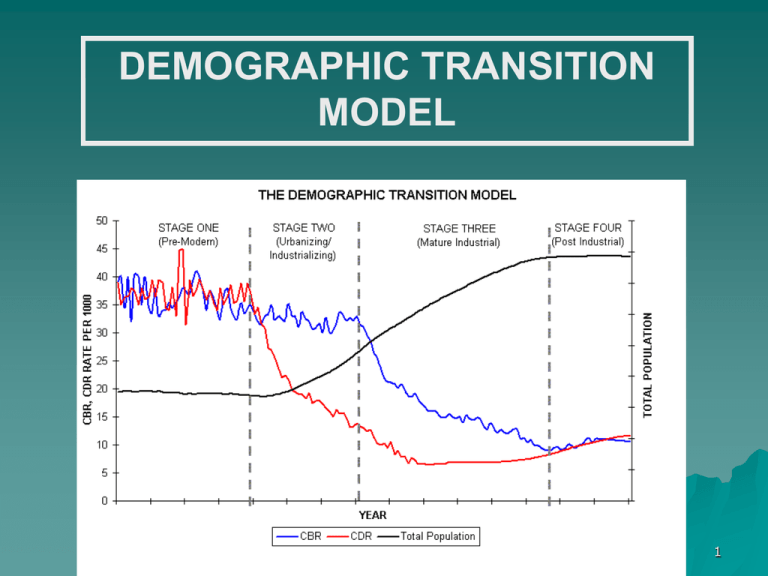
DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION
MODEL
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
1
Start with Hans Rosling
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jbkSRLYSojo
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
2
Today
Investigate the Demographic
Transition Model
Investigate Types of Diagrams used
to display and map Demographics
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
3
1. DEFINING
GENERAL
TERMS
AND
CONCEPTS
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
4
Basic Terms
Crude Birth Rate
Crude Death Rate
Rate of Natural Increase
Infant Mortality Rate
Fertility Rate
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
5
Crude Birth Rate
CBR
Number of live births per year =
3,180
Divided by population = 200,000
Times 1,000
CBR = [(3,180)/200,000] x 1,000
CBR = 15.9 births per 1,000 people
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
6
Crude Death Rate
CDR
Number of deaths per year = 1,860
Divided by population = 200,000
Times 1,000
CDR = [(1,860)/200,000] x 1,000
CDR = 9.3 deaths per 1,000 people
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
7
Rate of Natural Increase
RNI
CBR = 15.9
Minus CDR = 9.3
Divided by 10
RNI = (CBR – CDR)/10
= [(15.9 -9.3) /10
= 0.66% growth per year
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
8
Infant Mortality Rate
IM
number of newborns dying under
one year of age = 40
divided by the number of live births
during one year = 5,300
Time 1,000
IM = (40/5,300) x 1,000
IM = 7.6 deaths per 1,000
births
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
9
Fertility Rate
Average
Number of child births
Per woman
Since
a couple is 2 people, need a
little more than 2 births to replace
the parents
2.1 is considered a stable growth
fertility rate in the US of a Developed
Country
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
10
Types of Diagrams
Demographic
Transition Model
Population Pyramid
Trend Diagrams
– Temporal (over time)
– Spatial (over space
Survivorship
Diagram
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
11
2.DEMOGRAPHIC
TRANSITION
MODEL
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
12
Birth rate
Natural
increase
Death rate
Time
Note: Natural increase is produced from the excess of births over
deaths.
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
13
What is the Demographic
Transition Model?
The
"Demographic Transition" is a
model that describes population
change over time.
– Our main concern has been growth
– Now in Industrial Countries it is decline
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
14
What is the Demographic
Transition Model?
It
is based on an interpretation
begun in 1929 by the American
demographer Warren Thompson, of
the observed changes, or transitions,
in birth and death rates in
industrialized societies over the past
two hundred years or so.
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
15
What is the Demographic
Transition Model?
The
"Demographic Transition" is a
model a scientific hypothesis
– Until the 1990s it seemed to work well
with Developed Countries
– It worked pretty well with Less
Developed Countries
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
16
What is the Demographic
Transition Model?
The
"Demographic Transition" is
based on the Scientific Method,
– so we are continually “experimenting”
with it and improving it
In this class we will experiment with it
in Mexico & Sweden
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
17
Impacts and Consequences
The next several sets of tables summarizes the
measures of impacts of the Transition
Four Stages Impacts
1. Very Low Growth
2. High Growth
3. High but Slowing
Growth
4. Low Growth
Some now see a fifth stage
5. ??? Decline sets in ????
Factors That Change over the
Stages
Family Size
Infant Mortality & Fertility
Rates
Family Economics
Status of Kids
Gender Roles
Health Conditions
Transportation Facilities
Child Deaths
Population Size
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
18
Demographic Transition Model
CBR
Family Size
-- planned
Stage 1 :
Pre
industrializa
tion: Stable
population
growth
Stage 2:
Rapid
population
growth
High Birth
rates
High Birth
rates
Stage 3:
Continued and
decreasing
population
growth
Stage 4:
Stable low
population
growth
Falling Birth rates
Low Birth
rates
Family Planning -The plan is to have
fewer kids
Trends
stabilize
with 2 kid
families or
less
Family
Planning -The general
plan is to
have many
kids
Family
Planning -The general
plan is to
have many
kids
Infant
Mortality
Rate/
Fertility
Rate
Many children
because few
survive, high
fertility rate
Still many
kids because
expect few to
survive high
fertility
Lower infant
mortality rates -less pressure to
have children,
fertility declines
Small family
size low
fertility rate
Family
Economics
Many children
are needed to
work the land
Children are
still useful for
work
Increased
mechanization and
industrialization
means less need
for labor/kids
Women are
working in
great
numbers
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
19
Demographic Transition Model
Stage 1 :
Pre
industrializ
ation:
Stable
population
growth
Stage 2:
Rapid
population
growth
Stage 3:
Continued
and
decreasing
population
growth
Stage 4:
Stable low
population
growth
High Birth
rates
High Birth
rates
Falling Birth
rates
Low Birth
rates
Status
of Kids
Children are
a sign of
virility &
status and
old age
insurance
Children are
a sign of
virility &
status and
old age
insurance
Increased
desire for
material
possessions
and less desire
for large
families
Kids are an
expense &
“bling”
Gender
roles
Strong sex
roles
Strong sex
roles
Emancipation
of women
Emancipation
of women
CBR
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
20
Stage 1 :
Pre
industrializ
ation:
Stable
population
growth
CDR
Stage 2:
Rapid
population
growth
Stage 3:
Continued
and
decreasing
population
growth
Stage 4:
Stable low
population
growth
High Death
Rates
Falling Death
Rates
Death rates
Low
Death rates
Low
Health
Conditi
ons
Poor Diet &
Sanitation,
Famine and
Disease
Improved
diet,
sanitation &
medical care
Slight
No change
improvement
Transp
ort
Faciliti
es
Limited
transport,
trade &
travel
Improved
transport to
move food
and doctors
Slight
Stable
Improvement
Child
Deaths
High child
mortality
before age 5
A decrease in Child
child
mortality
mortality
very low
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
After Copper, Models of Demography,
Stable
21
Stage 1 :
Pre
industrializ
ation:
Stable
population
growth
Stage 2:
Rapid
population
growth
Rate
Natural
Increase
Very Low
Growth
High Growth Slowing
Growth
Population
Size
Small
Population
Bigger
Stage 3:
Continued
and
decreasing
population
growth
Bigger
Stage 4:
Stable low
population
growth
Low Growth
Biggest
After Copper, Models of Demography,
http://www.bized.ac.uk/virtual/dc/copper/theory/th10.htm
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
22
Examples
Sweden – Historic Industrial Country
Mexico – An Industrializing Country
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
23
Developed Country
Example
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
24
Developing Country
Example
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
25
Combination emphasizing
changes over time, Sweden takes
longer and Sweden starts from
lower CBR and CDR
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
26
3. TYPES
OF
DIAGRAMS
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
27
Types of Diagrams
These
diagrams help us to
understand the mechanism causing
the Demographic Transition Model to
operate and its impact
– Survivorship Diagram
– Stabilization Ratio Diagram
– Population Pyramids
– Temporal Trends
– Spatial Trends
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
28
Emphasis on longer life
expectancy as CDR drops
Now 90%
live past
55yrs old
Less then
10%
reached
25yrs old
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
29
Public Health: One of the many
past causes of high child
mortality rates
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
30
Recent Exponential Growth of World’s Population as countries
enter Stage 2 and Stage 3 of the Demographic Transition
HIGHLIGHTS IN WORLD POPULATION
GROWTH
1 billion in
1804
3 billion in
1960 (33
years later)
5 billion in
1987 (13
years later)
2 billion in
1927 (123
years later)
4 billion in
1974 (14
years later)
6 billion in
1999 (12
years later)
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
About 6.8 bil.
currently
31
Total Population of the World by
Decade, 1950–2050
http://www.infoplease.com/ipa/A0762181.html
Total world population
(mid-year figures)
Ten-year growth
rate (%)
1950
2,556,000,053
18.9%
1960
3,039,451,023
22.0
1970
3,706,618,163
20.2
1980
4,453,831,714
18.5
1990
5,278,639,789
15.2
2000
6,082,966,429
12.6
6,848,932,929
10.7
7,584,821,144
8.7
8,246,619,341
7.3
8,850,045,889
5.6
9,346,399,468
—
Year
(historical and projected)
2010
2020
2030
2040
2050
1
1
1
1
1
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
32
Stabilization of World’s population is
still over a generation away
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
33
Guatemala Stage 2
Population Pyramids
• Demonstrate where the
population is by age cohort
• Also can see Demographic
Stage
Mexico is going
into Stage 3
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
34
Stage 4: Sweden
Demographic Indicators
Birth Rate: 12 per thousand
Total fertility rate: 1.8 births
Natural increase: 0.1% per
year 1990-2000
Age structure: 18% under 15
yrs.age
Italy with declining
population. Will there be a
Stage 5???
Demographic Indicators
Birth Rate: 9 per thousand
Total fertility rate: 1.2 births
Natural increase: -0.1% per
year 1990-2000
Age structure: 14% under 15
yrs.age
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
35
USA – what Stage would you say each of these are???
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
36
Interactive Pop Pyramid for USA
http://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2011/02/04/business/aging-population.html?ref=business
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
37
Japan, an upside down pyramid in the making?
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
38
Example of how
families adjust to
lower infant
mortality rates with
lower fertility rates.
Result is a decline
in CBR
This is a temporal
trend diagram.
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
39
Spatial Trend Diagram: Countries
with higher IM have higher Fertility
Rates.
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
40
Comparative Temporal and Spatial Data Diagram
What is occuring here? Speculate why.
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
41
Comparison of Development and Wealth to Population
Growth Rates across Countries
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
42
Where is the World’s Population Growing? Declining?
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
43
Declining World Mortality Rates Map
At the end of the second and the beginning of the third stages of
the demographic transition, death rates declined.
Where did they first decline and where did they last decline?
Created by Ingolf Vogeler on 1 February 1996 http://www.uwec.edu/geography/Ivogeler/w111/dempop.htm
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
44
ONE LAST
CONCEPT
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
45
Dependency Ratio
Ratio
of non-working population to
working age population
Non-Workers are the young and
aged retirees
– young are usually 15 yrs old and below
– retirees are usually 64 yrs old and
above
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
46
Pakistan’s High
Dependency Ratio now
and in the future based
on lots of kids but few
elderly.
However note how the
young population is
expected to stabilize
and elderly grow.
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
47
Dependency Ratio Woes
A
© Copyright 2006, From The Wilderness Publications,
www.fromthewilderness.com. All Rights Reserved. This story may NOT be
posted on any Internet web site without express written permission. Contact
admin@copvcia.com. May be circulated, distributed or transmitted for nonprofit purposes only.
rising dependency ratio is also a
concern in many countries that are
facing aging populations, since it
becomes difficult for pension and
social security systems to provide to
retirees.
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
48
Japan showing its
high number of
dependants to
working age
population
•lots of elderly
(nearly black color)
• Working age
population (purple
color)
•few kids (dark
purple color)
Result is high
Dependency Ratio
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
49
Play time: Hans Rosling
http://www.ted.com/talks/hans_rosling_shows_the_best_stats_you_ve_ever_seen.html
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
50
Play time: gapminder.com
http://www.gapminder.org/
http://www.gapminder.org/
Demographic Transition Egeo 312
51