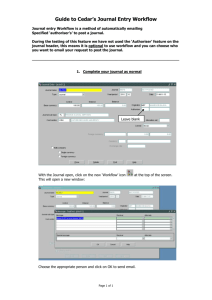
WEEK 3 THURSDAY – Web planning
advertisement

The online customer experience: planning and designing a web presence MGMT 230 WEEK 3 After today’s class you will understand….. • The main steps in the website planning and development process • How to identify goals for a particular organizational website • How the motivations of website visitors can be included in site design • How to design the underlying structure of a web site • How to use today’s material for the website project assignment Developing an effective web presence • Web presence is a key part of online marketing - the most important element of a firm’s owned media • Often the only touch point with a customer – very influential in terms of brand perception • Must be effective for the customer – deliver what they want – relevance and value • Must be effective for the organization – meeting business goals The importance of the interface • Internet technology has caused a shift in the way in which firms interact with their customers – Face-to-face encounters replaced with screento-face interactions. – Interfaces include desktop PCs, laptops/notebooks, web kiosks, handhelds such cellphones, smartphones & tablets – We must design the interface to accommodate the many devices consumers use to access our web presence Ways to get a web site built • Build and code from scratch – bespoke development (HTML, CSS, databases, eCommerce functionality etc) – Wide range of firms offer services of varying expense, sophistication, and levels of expertise (the sky is the limit) • Use a content management system (CMS) as the foundation for the site – Wordpress (it is said that Wordpress powers 23% of the web); Joomla, Drupal etc • Template-based sites – Squarespace, Weebly, Wix etc. Aimed at small business with little or no technical expertise. Disadvantage is that the site is not usually exportable for hosting elsewhere (proprietary systems) & there is very limited customization Typical roles involved in a web project • • • • • • • • Site sponsor / site owner Project manager (balances budget, time, scope) Art director/visual designer Information architect / designer / usability engineer HTML & CSS developer Programmer / backend engineer / DBA QA (Quality Assurance) Content manager / copywriter Goto & Cotler Web ReDesign 2.0: Workflow that Works (2005) New Riders WEB DEVELOPMENT STAGES AND ACTIVITIES Web (re)development workflow: Goto + Cotler’s “Core Process Plan Discovery (define the project) Build and improve Create content and build site Launch and evaluate Build and integrate content Goto & Cotler Web ReDesign 2.0: Workflow that Works (2005) New Riders Design and develop the website structure Design the visual interface Plan Plan Another way of looking at the elements of the web design process https://medium.com/@ireneau/design-is-5b867e9f2614 PLANNING A WEB SITE: DEFINE THE PROJECT AND SET GOALS Steps in planning an effective web presence (this relates to section 1 of the assignment instructions) 1. Determine business objectives, site goals, and success factors 2. Identify the target audience and create user profiles of audience members 3. Conduct market research and competitive analysis 4. Design the site for audience, functionality, and usability Setting organizational and user goals • Goals from the organizational perspective • Goals from the user perspective: what do they want to do on your site? • SMART GOALS (see article on course website) – – – – – Specific Measureable Achievable Realistic / relevant Timebound • Commissioning a Business Website - How to produce a Design Brief – Paul Boag Setting website goals Business Why does your web site exist? objectives Site objectives What do you want site visitors to do? Success criteria Design your site to achieve these What functions and content will your site provide? Identifying the purpose of a web presence for an organization • A web site can have many purposes, both broad and specific. Some examples: – Provide product or service information – Sell a product or service – Increase brand recognition – Provide help, operational instructions, or customer support – Shift customers toward self service – Induce people to subscribe to a newsletter – Provide information for the media – Allow people to make bookings online User oriented design: Motivations and Goals of Web Site Visitors – why are they there? • • • • • • • • to learn about products or services to buy the products or services to obtain information to obtain contact information for a person or department in the organization to interact with other users to search for something in particular to browse to be entertained • Catering to all these different needs in designing a web interface can be challenging • When you set the goals for a site, think about what people want and why they are there Success criteria • Be specific! – “a 25% increase in newsletter signup by 31st December 2015” – “100 dinner reservations booked via the online form in October 2015” – “ 3,000 software downloads at the promotional price during Q1 2016” – “a 5% increase in visitor time spent on the product feature page by 30th September 2015” – Conversion rate (see next slide) Conversion rate • Conversion rate: keeping track of the percentage of your web site visitors that take a desired action. • For example: – – – – registering on your site customizing your site booking an appointment making a purchase • Conversion rate calculation: – Number of purchases divided by number of site visitors – a site that had 1000 visitors who made 50 purchases has a conversion rate of 5%. • A success criteria would be to increase your conversion rate • Conversely for an ecommerce site a goal might be to decrease the rate of shopping cart abandonment Understanding the audience • Market research • Demographic and psychographic information • Create a detailed profile for each visitor type (a persona) and do early user testing • Commissioning a Business Website - Know your audience – Paul Boag Goto & Cotler Web ReDesign 2.0: Workflow that Works (2005) New Riders An example of a detailed user profile • Sample of a user profile – make your site user a real person and describe his/her actual use of the site • Example: online store for yoga gear – Jenny is a 22 year old female university student from Victoria, who accesses the web on a daily basis from her iPhone and from her laptop. She is extremely internet savvy and completes online transactions for clothes, music etc on a regular basis. She has high speed internet access both at home and on campus. Typical tasks on the site include browsing for products to purchase, reading and posting reviews, and checking the forums for information about what’s new in yoga. She has a username and password and is able to complete purchases quickly and easily. Aims of design for usability 1. Understand user’s goals 2. Anticipate them 3. Make it easy to accomplish them – a way to meet the goals must be reflected in the design of the web pages themselves DESIGNING AND DEVELOPING WEBSITE STRUCTURE AND CONTENT Developing a web site structure (relates to section 2 of the assignment instructions) • CONTENT VIEW – – – – Addressing content Auditing existing content Outlining content Creating a content delivery plan PAGE VIEW Wireframing Addressing navigation Naming and labeling Goto & Cotler Web ReDesign 2.0: Workflow that Works (2005) New Riders • SITE VIEW – Sitemapping – Addressing existing site organization – Setting naming conventions Site structure: Content view the “What” of the site • Text, pictures, sound and video – both the type of content, and the media with which it is delivered • The offering mix: products, information, services etc • The appeal mix – the “call to action”: promotional and communications messages • The media mix: the multimedia elements included on the site – Widgets for content from 3rd party sites (eg. twitter) • Content type: differentiate between time sensitive information versus “evergreen” information – Freshness keeps bringing customers back – Archives provide a useful service to users Based on: eMarketing eXcellence. 2008. Chaffey et al. BH Community Site structure: Content view • User Generated Content (UGC) engenders strong community - encourages stickiness and loyalty • Community can create attractive content (ie. free content for the site owner) – Web communities can make the user feel that they are valued by the firm – Community can satisfy needs not otherwise able to be satisfied individually (eg. finding people, getting tech support) • Common tools are reviews, support forums, knowledge sharing Based on: eMarketing eXcellence. 2008. Chaffey et al. BH Site structure: Site view and Page view Information architecture is concerned with how the site will function • Function - site layout and functionality – Section breakdown - the way the site is organized into sub-categories • make them clear, and customer focused • Organize by customer type / product / task eg. VIU – Linking structures - navigation • where am I? • how do I get back to where I came from? (breadcrumbs ) – Navigation tools • search functionality and methods • browse capability via category drill-down Based on: eMarketing eXcellence. 2008. Chaffey et al. BH Site structure: Site view and Page view Site mapping • A visual representation of a site’s structure, organization, flow, and grouping of content • Shows an overview of the site structure as a whole and how the pages link together – Includes agreed naming conventions (complex Example) – See course website for simple example to use for your web project Goto & Cotler Web ReDesign 2.0: Workflow that Works (2005) New Riders Site structure: Site view and Page view Wireframes / blueprints • NOT design oriented – show information only • Purpose of wireframes – Aid in communication – Form the basis for visual design – Form the basis for HTML production / templates • Show (at a minimum) – All major page elements – Target window size (in pixels) – Navigation – Media – Functional elements – Messaging / content areas – Complex Example – See course website for example to assist with your web project plan Goto & Cotler Web ReDesign 2.0: Workflow that Works (2005) New Riders WEB PROJECT ASSIGNMENT Web project assignment • Stage 1 of this assignment is the production of a planning document (worth 20%) • Due by: Monday, November 2nd at 4:30pm via email • Stage 2 is the production of the site itself (worth 15%) • Due by Friday December 4th at 4:30pm (via email) • Before you develop your website, you need to PLAN • Assignment instructions, some samples and the marking scheme are on the course website PART 1 – WEBSITE PLANNING AND DESIGN DOCUMENTATION • Sections of your plan – SECTION 1: Goals and target audience – SECTION 2: Information architecture, page layout etc – SECTION 3: Design “look and feel” and usability – SECTION 4: Site content - images, video, search engine optimization Exercise on setting goals for a website • You will need to do this for your web site project • This exercise will give you some practice • Remember the goals you set MUST be able to be achieved via the website Goal =>> =>> website design feature / content / functionality