True self Social self
advertisement

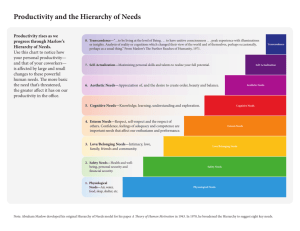
Carl Rogers Carl Rogers . . . the most wonderful miracle in the world took place. .” Subjective Experiences • Inner reality more important than objective reality • Inner experiences • Conscious experiences – Experiences that can be verbalized or imagined • Unconscious experiences – Experiences that cannot be verbalized or imagined Self-Actualizing Tendency • Innate motive toward fulfillment of our potentials • Evidence – Rat and human studies – Evolution • “Innate goodness” So why do people do bad things? • Infants perceive their experiences as reality • Uninhibited by the evaluations of others • All behavior directed toward satisfying need for SA • Organismic Valuing Process – SA is the criterion used to make judgments of worth • As we get older. . . . • Start to experience a need for positive regard – Satisfying the needs for others satisfies this need True self Social self Created through contact with others True self Social self Prevents us from getting into touch with our true self True self Social self Leads to “conditions of worth” True self So why do people do bad things? • Social self hinders movement toward SA • Not behaving like true self causes anxiety • Anxiety causes defense mechanisms So why do people do bad things? Psychotic Positive Development • Avoid conditions of worth • Unconditional positive regard • Congruence between true self and experiences Fully Functioning Person • Open to experience • Characterized by existential living • Trust their organisms • Are creative • Live rich lives Abraham Maslow Abraham Maslow “She kissed back and then life began.” Self-Actualizing Tendency • Innate motive toward fulfillment of our potentials • Environment can cause problems Needs • Can be biological or instinctive • A state of affairs which, if present, would improve the well being of the person • Example: food Needs • An unsatisfied need will dominate an individual's thoughts and behaviors • Once a need is satisfied it no longer has as much influence on a person Example Have not eaten Deficit Need for food Need Hunger Think about food, fantasizing about a big meal Thoughts and Fantasies Motive Behaviors Go to store, buy food, bring it home, cook it Group Activity Thoughts and Fantasies Deficit Need Motive Behaviors Needs • What needs are basic? • Physical – Food, water, air, etc. • Safety – freedom from threat, danger, etc. Needs • What needs are basic? • Social / Belonging – desire for affiliation, beloning, etc. • Self-Esteem – desire for self-confidence, recognition, respect, etc. Needs • What needs are basic? • Self-Actualization – “to become everything one is capable of becoming” Needs • Which needs are more salient to survival? • There is an order that these needs typically occur – Evolutionary explanation Need Hierarchy Theory Physiological Needs Need Hierarchy Theory Safety Needs Physiological Needs Need Hierarchy Theory Social Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs Need Hierarchy Theory Self-Esteem Needs Social Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs Need Hierarchy Theory Self-Actualization Needs Self-Esteem Needs Social Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs Need Hierarchy Theory • 1) Behavior is dominated by the needs that are unfulfilled • 2) Individuals will satisfy the most basic needs first and move up the hierarchy • 3) Basic needs have higher priority than higher needs Group Activity Self-Actualization Needs Self-Esteem Needs Social Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs Where are you? What are you doing to achieve the needs associated with this level? Group Activity • 1. I do not feel ashamed of any of my emotions. • 2. I do not feel I must do what others expect of me. • 3. I believe that people are essentially good and can be trusted. • 4. I feel free to be angry at those I love. • 5. It is not necessary that others approve of what I do. Group Activity • 6. I accept my own weaknesses. • 7. I can like people without having to approve of them. • 8. I do not fear failure • 9. I do not avoid attempts to analyze and simplify complex domains. • 10. It is better to be yourself than to be popular. Group Activity • 11. I have a mission in life to which I feel especially dedicated. • 12. I can express my feelings even when they result in undesirable consequences. • 13. I feel responsible to help others. • 14. I am not bothered by fears of being inadequate. • 15. I am loved because I give love Scores • Men – M = 45.02 , SD = 4.95 – W = 46.07, SD = 4.79 Self-Actualization • “Time you enjoy wasting is not wasted time” • What you are doing when you are not attempting to satisfy another need • Your “true” nature – “to become everything one is capable of becoming” What if. . . . • You won a large sum of money? • What would you do? • Would this make you happy? Are you happy? Are you happy? Why to we value material goods? Stuff Most common response to “what will improve your life” More money! Is this true? • 1950 – present • • • • • • Violent crime Family breakdown Psychosomatic complaints Depression Suicides Happiness has stayed the same (30% very happy) – Although income has doubled! Is this true? • Wealthiest vs. “average” incomes • Very little difference in “happiness” Is this true? • Lottery winners vs. victims struck with severe medical problems • Happiness goes back to before Why? • Habituated to money • How much money would you need to fulfill your dreams? • Under $30,000 – $50,000 • Over $100,000 – $250,000 • Makes evolutionary sense Why? • Energy gets focused on material goods • Loses sense of other important aspects of life Need Hierarchy Theory Self-Actualization Needs Self-Esteem Needs Social Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs Achieving Happiness • Happiness is a mental state • Achieving it can be done via cognitive means Questionnaire Flow • Self-Actualization and “Flow” – Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi • Optimal Experiences – Doing something for its own sake, even though it may have no consequences outside itself • Moment-to-moment CS experience • Examples? Flow • Engaged deeply in an activity 1) Know clearly what they have to do moment by moment 2) Immediate feedback 3) Tremendous concentration 4) Little distractibility 5) Elevated mood 6) Time passes quickly Flow • How do you find flow? • Engage in activates that are challenging – Not too easy – Not too hard Flow • Happiness • Not felt while in flow – Feel on reflection • Important, but not sufficient for happiness Need Hierarchy Theory Self-Actualization Needs Self-Esteem Needs Social Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs Flow and Self-Actualization • Self-Actualization – What you do when you are not attempting to satisfy a need – “Time you enjoy wasting is not wasted time” – Peak Experiences • Flow – Optimal Experience – Done for its own sake, even though it may have no consequences outside itself • Flow is what “self-actualization” feels like George Kelly Activity • Questionnaire • 1) Put names on the top • 2) For row #1 • Look at the three people marked with a “O”. Determine how two of these people are different than the third. • Mark these two people with a check mark. • Write how they are different (one or two words) in the “similarity pole” box. Write how the third is different in the “contrast pole” box. • 3) Repeat for each row • 4) Score everyone else in each row with a check mark • How do you describe people • Commonly use Constructs that are learned – Start to see the world a different way Every Person is a Scientist • We have our own theories about human behavior • We have constructs that we think are important – Not as “scientific” as traditional science • It is our VIEW of reality that is important – Not reality itself Construct • Our constructs determine how we interpret an event • Constructs are bipolar – What is the other pole is also subjective • Thus two people may see the same event differently s • Charlie Sincere Insincere • Willy Sincere Morally degenerate • Charlie Sincere Insincere • Willy Sincere Morally degenerate • If they see Veruca Salt do something that is not sincere • If they see Veruca Salt do something that is not sincere Will think she is insincere React with mild disapproval • If they see Veruca Salt do something that is not sincere Will think she is morally degenerate Will be angry and upset Constructs • Hierarchical Constructs • Hierarchical Good versus Bad Superordinate Constructs • Hierarchical Good versus Bad Intelligent vs. Stupid Constructs • Hierarchical Good versus Bad Kind vs. Mean Attractive vs. Ugly Intelligent vs. Stupid Basic Assumptions • Construction Corollary • Person anticipates events by construing their replications • If Jenny thinks Linda is helpful one day, she will think Linda is likely to be helpful again Basic Assumptions • Individual Corollary • Idiosyncratic construct systems • Two people might interpret an event differently – Will act differently Basic Assumptions • Commonality Corollary • When two or more people share similar construct systems • They will likely interpret an event in a similar manner – They will act alike Constructs • Core Constructs – Resistant to change • Peripheral Constructs – Easier the change Constructive Alternativism • All of us are capable of changing our interpretation of events – Our constructs • Behavior is never determined Research • Using RCRT • Can understand constructs person uses to see the world • Can understand how a person sees self – Look at the check marks (and missing check marks) • How a person sees self in relation to others – Who do you think you are most similar too? – Are you similar to anyone? • Look at number of check marks in the self column Research • Cognitive Complexity • Did you use different constructs across all people? – Cognitive simplicity • Do not differentiate how you perceive others – Cognitive complexity • Highly different views of others Research • Cognitive Complexity • Differentiate among many different events in the environments – should be able to make more accurate judgments Research • Cognitive Complexity • Better able to anticipate school stresses • Make more realistic occupational choices • Better able to predict the behavior of others Review • Freud • Key ideas – – – – – – Psychic Determinism Unconscious Internal Structure Psychic Conflict Mental Energy Doctrine of Opposites • Parts of the mind Review • Freud • Psychosexual stages • Defense mechanisms – – – – – – – – Denial Repression Reaction Formation Projection Rationalization Intellectualization Regression Sublimation Review • Freud • Parapraxes • Humor Review • Neo-Freudians • Carl Jung – Archetypes – Collective Unconscious • Alfred Adler – Feelings of inferiority – Striving for superiority – Importance of birth order Review • Neo-Freudians • Karen Horney – Anxiety – Coping with anxiety (types) • Erick Erikson – Eight stages of development Review • Existentialism • Phenomenonological • Humanistic – Free will – Awareness – Meaning Review • Carl Rogers – – – – Self-Actualization True self vs. social self Conditions of wroth Unconditional positive regard • Abraham Maslow – Hierarchy of needs • Flow • George Kelly – Constructs