COMPRO1 Syllabus: C Programming Fundamentals
advertisement

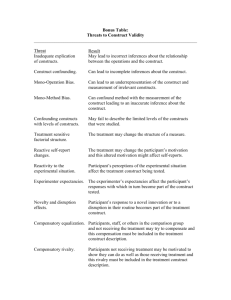
S N De La Salle University • College of Computer Studies Course Syllabus COMPRO1 / Computer Programming 1 Prerequisites Prerequisite to Type of Course Faculty Term : : : : : none COMPRO2 Basic course Dr. Raymund Sison Term 2 AY 2009-10 Course Description: Computer programming is, generally speaking, the writing of coded instructions for a computer to execute. This course, COMPRO1, is an introduction to computer programming using the C programming language, a compact and portable programming language that is used to write software of all levels, from low-level device drivers and operating system components to higher-level applications such as word processors and computer games. It is the base on which the object-oriented language C++ is built, which, in turn, is the immediate ancestor of Java and C#. This course focuses on the basic constructs of structured programming and how to use these constructs to solve problems. It provides the foundation for future software courses and projects in the BSCS curriculum. Objectives / Values: This course aims to introduce students to and familiarize them with structured programming concepts, with emphasis on logic formulation, to solve programming problems using the C programming language. At the end of the course, students should be able to: 1. Describe the components of and strategies in problem solving as applied to procedural programming; 2. Analyze problems; 3. Design algorithms to solve problems; 4. Implement algorithms in the C programming language; 5. Test programming solutions to problems; and 6. Exhibit intellectual honesty and perseverance, upholding Lasallian values of faith and zeal. Topics and Calendar: Week 1 2 3 Topics Orientation Programming Concepts History/Principles of the C Language (Reading Assignment) Basic Program Structure Kinds of Data Variable Declaration Assignment Statement Arithmetic Expressions Logic Formulation and Problem Solving using Functions Concepts and Rules Calling Functions User-defined Functions and Parameter Passing Input/Output Statements Deadlines/Exams 1 of 2 Week 4 5 6 7 8 9 10,11 12 13 14 Topics Logic Formulation and Problem Solving using Conditional Constructs Logical Expressions Single Selection Construct Multiple Selection Construct Deadlines/Exams Midterm Examination Logic Formulation and Problem Solving using Looping Constructs Event-Controlled Loop Count-Controlled Loop Nested Loops Functions and Pointers Pointers Parameter Passing by Reference MP Final Examination Teaching Methods / Strategies: Lectures Discussions Laboratory activities (guided discovery) Pair programming (collaborative learning) Requirements: This course has four requirements: written examinations, hands-on exercises, lab activities, and a machine project. Assessment / Evaluation: Written Assessment Midterm Exam Final Exam Practical Assessment Machine Project (MP) Hands-on Exercises, Assignments, Recitation Lab Activities Total 20% 30% 15% 25% 10% 100% Final Grade < 60 60 – 65.999 66 – 71.999 72 – 77.999 78 – 82.999 83 – 88.999 89 – 93.999 94 – 100 GP 0.0 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 Text / Materials: Alcantara, D. & Marcos, N. (2009) Course Materials for COMPRO1. Ruiz, C. R. (2009). Laboratory Activity Manual for COMPRO1. References: Lim, N. R. (2002). Fundamentals of C Programming: A Course Material for CMPROG1, Revised Edition. Hanly, J., & Koffman, E. (2007). Problem Solving and Program Design in C, 5th ed. Addison-Wesley. Kernighan, B. & Ritchie, D. (2002). The C Programming Language, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall. Faculty Contact Details: E-mail URL : : raymund.sison@delasalle.ph http://mysite.dlsu.edu.ph/faculty/sisonr/#Teaching This URL contains the course syllabus, exercises, and MP specs. 2 of 2