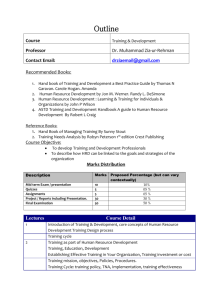
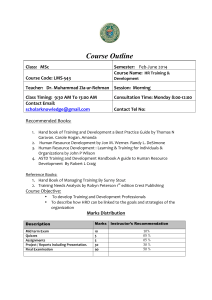
Performance Improvement Quarterly
advertisement

Assuring that HRD Creates Future Value Korean HRD Conference September 15, 2015 Roger Kaufman, Ph.D. CPT Florida State University 1123 Lasswade Drive, Tallahassee, Florida USA 32312 850-386-6621 © rkaufman, 2011 roger@megaplanning.com How often do we get a chance to shape our future? … and shape the future of our field? How often do we get a chance to add measurable value for ALL stakeholders? We have that opportunity now. And that opportunity includes building from and going beyond the conventional wisdom in our field… We can help create the future and add measurable value. 2 WHAT DOES KOREAN HRD WANT TO BECOME AND CONTRIBUTE? Korean HRD organizations and professionals can make choices in order to add measurable value to all stakeholders, including organizational talent and performance improvement But individual talent and their performance improvement is necessary but not sufficient for organizational and client success 3 The essential ingredient of any organization is people: • People and their talent, individual performance and competence, is essential • The development of people must be effective and efficient • Everyone should be competent, confident, and caring . . And they must be motivated to deliver useful results • Motivation—incentives—must be based on the value they add to themselves as well as within and outside the organization 4 Human talent and their performance is the basic building block for everything… ..everything any organization uses, does, produces, delivers and the value it add within and outside the organization. This means people must know the right things to do…and do it But how do we develop talent—improve performance and create performance—to make useful contributions? We must plan for it and make internal and external valueadded as part of their development, mentoring, evaluation, and continual improvement. 5 Your Challenge Given this, what should you and your organization, with its current resources and capabilities, become? What should they do and deliver? Who should be their clients? What measurable value can they add? How should it position itself in the world of individual and organizational improvement? 6 The Trend in HRD and (Talent Development) The profession is moving from a primary concern for HOW (to improve performance) to include WHAT (to deliver) to now include WHY (do we deliver what we do) 7 Assuring future value for HRD: HOW WHAT WHY 8 While we know a lot about how to design successful learning and performance, we are now also asking “what should successful performance look like,” and additionally now asking “why do we want this performance in the first place? How does it add measurable value for all stakeholders?” 9 Value in what we do is based on the measurable value we add to three levels of results: ● Societal ● Organizational ● Individual 10 This means we have to expand the framework of what we use, do, produce, and deliver …and change old assumptions about performance improvement in order to be responsive to our new realities. ….We must stop the conventional wisdom of our field that only pays attention to just parts of the system and not all of the system: 11 SYSTEM PERSPECTIVE SYSTEM S PERSPECTIVE 12 © rkaufman, 2015 The New Realities of Strategic Planning and Thinking to Assure Performance Improvement and Talent Development is Responsive and Responsible • Tomorrow is not a linear projection of yesterday: You can’t solve today’s problems with the same paradigms and tools that created them. • Everything we use, do, produce, and deliver must add value at the societal level—Mega level--a “system approach.” • There are two “bottom lines” for any organization: conventional and societal. • We must be both reactive—fix current problems—and proactive—create the future. 13 ..and • Performance data from each of these three levels may be derived by documenting the gaps between current results and contributions and desired results and contribution; needs. • It is vital that all parts of any organization operate successfully individually as well as together to add value to all internal and external stakeholders. Assuring that is the function of a practical strategic plan. • A useful method for obtaining this data is called “needs assessment” where needs are gaps in results, not gaps in means or resources. 14 Real and important value comes from outside-to-inside thinking …from our shared ecosystems to define what we should and can contribute using performance improvement of our talent as the primary vehicle. 15 © rkaufman, 2015 This Conference—you-- can help provide leadership to create the future by defining what societal and organizational needs – gaps in results- can and should be met. …..And then decide what performance we should improve and what performance we can create. 16 © rkaufman, 2015 The purpose of any organization—public-or privatesector include: 1. Adding value to all internal and external stakeholders, and then (and only then), 2. Providing positive return on investment, and then 3 Designing and delivering products and services, understanding that there are complex activities, and then 4.. Evaluate and revise as required. © rkaufman, 2015 17 We can measure our success in a number of ways, but all ways will link to the survival, self-sufficiency and quality of life of all of our partners 18 © rkaufman, 2015 Linking Performance Improvement and Talent Development to the New Realities External Client and Societal Value ↨ What Organizations Deliver ↨ What Individuals Deliver ↨ Performance/Talent Improvement ↨ Human Resources 19 © rkaufman, 2015 Here are some basic concepts and tools for adding value…as we move from outside each of our organizations to inside…so individual talent will add value for all stakeholders To define and deliver measurable success. 20 © rkaufman, 2015 Planning—Strategic Planning—to Assure Performance Improvement and Talent Development will be Successful • Measurable results are good and useful measurable results are even better • Everyone must deliver useful results that add value within and outside the organization • Strategic planning is about ends, results and consequences, not about means, programs, activities, courses, or delivery. • Strategic planning requires that criteria are based on evidence. © rkaufman, 2015 21 Keys to your success to Add Value: Performance and Useful Results • All organizations are means to societal ends. • If we are not adding value within and outside of the organization we will fail. • Results, results. Performance, performance. • Strategic plans identify what value we will add to ourselves, our organization AND to our shared society. • People—from inside and outside the organization-- must help define where we are headed and how to tell when we have arrived. Without this inclusion of all stakeholders we will not succeed. …so what must we do to define and achieve success? 22 Basic Ideal Vision: The world we want to help create for tomorrow's child There will be no losses of life nor elimination or reduction of levels of well-being, survival, self-sufficiency, quality of life, from any source including (but not limited to): – war and/or riot and/or terrorism – unintended human-caused changes to the environment including permanent destruction of the environment and/or rendering it non-renewable – murder, rape, or crimes of violence, robbery, or destruction to property – substance abuse – disease – starvation and/or malnutrition – destructive behavior (including child, partner, spouse, self, elder, others) – accidents, including transportation, home, and business/workplace – discrimination based on irrelevant variables including color, race, age, creed, gender, religion, wealth, national origin, or location Poverty will not exist, and every woman and man will earn as least as much as it costs them to live unless they are progressing toward being self-sufficient and self-reliant. No adult will be under the care, custody or control of another person, agency, or 23 substance: all adult citizens will be self-sufficient and self-reliant as minimally indicated by their consumption being equal to or less than their production. © rkaufman, 2015 Alignment of Mega, Macro and Micro Ideal Vision Mega Macro Organization’s Mission Organizational functions, & tasks Micro Development, Operations, Evaluation/Continuous Improvement Missions derive from the Ideal Vision. An organization selects what portion of the Ideal Vision it commits to deliver and move ever closer to it. © rkaufman, 2015 24 Recommended Next Steps to Complete the Strategic Plan the Assures Future Value 1. Identify and select a representative and unbiased strategic planning team— including internal and external planning partners. 2. Identify needs at the three levels of contributions and derive the Mission Objective 25 © rkaufman, 2015 3. Place the gaps in priority order on the basis of the costs to meet the needs (performance gaps) and the costs to ignore them. 4. Develop a tactical and operational plan including schedules, fiscal resources, personnel, buildings, equipment. 5. Design performance improvement and talent development objectives, methods, and delivery based on the mission objective. •26 Recommended Next Steps to Complete the Strategic Plan (cont’d) 6. Obtain approval from the internal and external planning partners or revise as required. 7. Implement. 8. Track progress against the performance requirements and revise as required. •27 Recommended Next Steps to Complete the Strategic Plan (cont’d) 9. Determine value-added for the implemented strategic plan and identify what should be continued and what should be changed. 10.Always and continually collect performance data to decide if and how the strategic plan should be revised •28 IF YOU ARE COMMITTED TO ADDING VALUE TO ALL STAKEHOLDERS, YOU CAN HELP CREATE A BETTER TOMORROW FOR ALL STAKEHOLDER ..Work together to define, design, and deliver measurable success. Help define and create the kind of community, Country, and world we want for tomorrow’s child.. Using HRD as the vehicle. © rkaufman, 2011 Now we an help decide: • What should Conference participants, with their current resources and capabilities, become? • What should they do and deliver? • Who should be their clients? • What measurable value can they add? • How should it position itself in the world of individual and organizational 30 31 Some references • • • • • Addison, R. M. Haig, C. and Kearny, L. (2009) Performance Architecture: The Art and Science of Improving Organization, San Francisco, Pfeiffer Bernardez, M. (2005). Achieving Business Success by Developing Clients and Community: Lessons from Leading Companies, Emerging Economies and a Nine Year Case Study. Performance Improvement Quarterly, Vol. 18, Number 3. Pp. 37-55. Bernardez, M. (2009). Minding the Business of Business: Tools and Models to Design and Measure Wealth Creation. Performance Improvement Quarterly. 22(2) Pp. 17-72. Guerra, I. & Rodriquez, G. (2005). Educational Planning and Social Responsibility: Eleven Years of Mega Planning at the Sonora Institute of Technology (ITSON). Performance Improvement Quarterly, Vol. 18, Number 3. Pp. 56-64. Kaufman, R. and Watkins, R. (2000) Getting Serious About Results and Payoffs: We are what we say, do, and deliver. Performance Improvement Journal, 39(4), 23-32. • Kaufman, R. (2006b). Change, Choices, and Consequences: A Guide to Mega Thinking and Planning. Amherst, MA. HRD Press Inc. • Kaufman, R, Oakley-Browne, H., Watkins, R., & Leigh, D. (2003). Practical Strategic Planning: Aligning People, Performance, and Payoffs. San Francisco, JosseyBass/Pfeiffer. 32 © rkaufman, 2015 Some references • Kaufman, R, & Guerra-Lopez, I. (2008) The Assessment Book: Applied Strategic Thinking and Performance Improvement Through Self-assessments. Amherst, MA. HRD Press Inc. • Kaufman, R. (2011) A Manager’s Pocket Guide to Strategic Thinking and Planning,. Amherst, MA. HRD Press, Inc. • Kaufman, R. (Summer, 2012). Defining and Applying Organizational Vital Signs for Creating a Better Tomorrow. Leader to Leader. No. 65, Pp. 21-26. • Kaufman, R, & Guerra-Lopez, I. (2008) The Assessment Book: Applied Strategic Thinking and Performance Improvement Through Self-assessments. Amherst, MA. HRD Press Inc. • Kaufman, R., & Guerra-Lopez, I. (2013). Needs Assessment for Organizational Success. Alexandria, VA., American Society for Training and Development. • Panza C. M. (April, 2012) The Future Starts Now. Performance Improvement Quarterly, Vol 25, Issue 1, Pp. 13 - 21. • Rodriguez, Villanueva, Gonzalo & Lagarda Leyva, Ernesto (2009). Using Technology and Innovation for Planning Social and Economic Transformation in a Region of Mexico. Performance Improvement Quarterly. 22(2) Pp. 53-77. l 33 © rkaufman, 2015