Example Edexcel A Biology A-Level Programme
advertisement

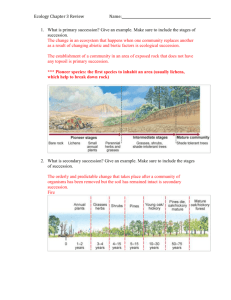
Juniper Hall course programme School / College: FSC course tutor: Course Dates: Course title: Course outline Pre-course: Students research secondary succession using Padlet webpage (Common Practical Assessment Criteria Competency 5) http://padlet.com/marisa_jh/JuniperHallSuccession 2016 AS Edexcel A Biology with Core Practicals EXAMPLE PROGRAMME Safety: Link to FSC risk assessments Clothing: Waterproofs and Wellies. Scarves, hats, gloves & warm clothing. And/or Pre-course: Students research the importance of conservation with reference to Box Hill using Padlet webpage (Common Practical Assessment Criteria Competency 5) http://padlet.com/michelle_lr/JuniperWoodlandsPrecourse Day 1 (1300 start, 2000 finish) - Ecology and chalk grassland secondary succession (or chalk grassland trampling) Check in at reception to start at 1300 Borrow wellies and waterproofs and welcome tour Intro to Ecology, abiotic and biotic factors and intro to secondary succession on chalk grassland. To include species adaptations, nutrient cycling and management and conflicts Core Practical 10: Carry out a study on the ecology of a habitat, such as using quadrats and transects to determine distribution and abundance of organisms, and measuring abiotic factors appropriate to the habitat. Complete succession fieldwork: Investigating the process of secondary succession on Mickleham Downs Return to Juniper Hall Break and cake Population study on Ramshorn snail – mark snails Succession data collation, methods and limitations Set small mammal traps Dinner about 1800 Statistics Workshop Data presentation Introduction to statistics – which to use? Use succession data to complete a worked example of Spearman’s Rank Finish by 2000 Transport: Transport is required on day 2 to travel to and from the River Tillingbourne. This is to guarantee that we have safe access to a river site. The River Mole has been used in the past but this is no longer a reliable river site. We now use the River Tillingbourne, which is a short drive from the centre. The biodiversity in the Tillingbourne is higher and access is always guaranteed. Behaviour: Teachers to support with behaviour & group management during fieldwork activates and classroom sessions and to lead group management during breaks times. Resources: All resources are provided. Day 2 (0915 start and finish by 2000) – Freshwater ecology Open small mammal traps and reset – link to classification e.g. genus and species and create a dichotomous key for identification and estimating population size Introduction to freshwater ecology investigations Morning break Travel to the River Tillingbourne (transport required at a current cost of £8.80 per student if booked with the FSC) Core Practical 10: Carry out a study on the ecology of a habitat, such as using quadrats and transects to determine distribution and abundance of organisms, and measuring abiotic factors appropriate to the habitat. Complete freshwater fieldwork: investigating the abundance of freshwater invertebrates in the River Tillingbourne Bringing Environmental Understanding to All Juniper Hall course programme Lunch in the field Complete fieldwork and return to Juniper Hall with some selected samples of freshwater invertebrates Use microscopes to observe adaptations of freshwater invertebrates Break and cake Collate data and discuss limitations of methodology Data presentation Check and reset small mammal traps Dinner about 1800 Freshwater statistical analysis (either chi squared or student t-test) Or Trophic structure using freshwater data with Excel spreadsheets to create both box plots and ecological pyramids graphs Day 3 (0915 start and finish by 2000) - woodland and sampling techniques Check small mammal traps – not to be reset Intro to woodland study including pre course task quiz on woodlands, conservation and biodiversity Morning break Core Practical 10: Carry out a study on the ecology of a habitat, such as using quadrats and transects to determine distribution and abundance of organisms, and measuring abiotic factors appropriate to the habitat. Students plan and carry out an investigation on the effects of woodland on the abundance and distribution of woodland plants. They can use various sampling techniques to measure biotic and abiotic variables Lunch Return to Juniper Hall with some samples of plants from sun and shade Soil analysis Collate data, data presentation and analysis Break and cake Core Practical 7: separate biological compounds using paper chromatography – using plants from sun and shade collected in the woodland Dinner about 1800 Woodland statistical analysis (either chi squared or student t-test) If time, student data could be used to calculate diversity using Simpson’s Diversity Index Day 4 (0915 start finish by 1200) – population study and animal responses Pond dipping on centre grounds, including recapture of Ramshorn snails and calculate Lincoln Index Collection of an invertebrate such as freshwater shrimp for animal responses practical Morning break Investigation into the effect of an environmental variable on the movement of an animal using a choice chamber or maze Tidy classroom and return waterproofs and wellies Course finishes by 1200 Bringing Environmental Understanding to All Juniper Hall course programme Learning Objectives Edexcel A A/AS level Biology Throughout the course students will have to opportunity to achieve the following objectives: Solve problems set in practical contexts. Apply scientific knowledge to practical contexts. Comment on experimental design and evaluate scientific methods. Plot and interpret graphs. Process and analyse data using appropriate mathematical skills. Evaluate results and draw conclusions with reference to measurement uncertainties and errors. Consider margins of error, accuracy and precision of data. Assessment: Progress assessed by open ended questioning, peer discussions and use of knowledge and skills in different situations. Prior learning: Students should ideally have some understanding of ecological investigation, abiotic and biotic factors, and adaptations of organisms to the environment Bringing Environmental Understanding to All