0part_6_chapter_13.1_closer_look_and_13
advertisement

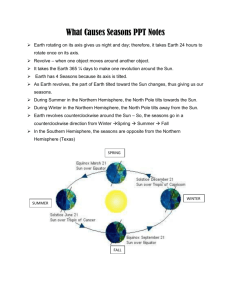
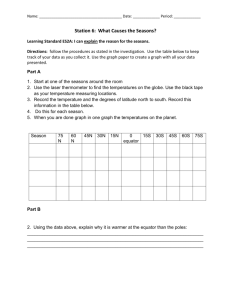
Unit 4-Weather 13.1 & 13.3 A Closer Look at the Earth and Why we have Seasons http://youtube.com/watch?v=s76Qn7bpCsQ&feature=related BLM 13.1A Quick Review Question Sheet Weather and Climate (Q3) Weather… What is It? – Day to day environmental conditions Examples: – Rainy / snowy – cloudy / sunny – Windy / calm Climate – Environmental condition averaged over many years Examples: – Average rainfall – Average daily temperature Weather and Climate Variable used to describe weather and climate: – Temperature – Wind Speed and Direction – Visibility – Cloud cover – Atmospheric Pressure – Dew Point – Humidity Formation of Weather and Climate Now some questions for you to think about… I’ll read the question to you and then ask you what the first thing is you think about… 1. 2. 3. Now that you know what weather is can you tell me if the weather is the same here as it is in St. John? Why not? Geographically, how is St.John different than Fredericton? Would any of these geographical features affect the weather in that area? If so which ones and how? Here are the facts: Components that influence weather and climate include: Latitude and Longitude Atmosphere Oceans Land Masses Science 10 – Oct. 4th What is something you’ve always wondered about weather? – A saying – How a weather phenomena works or is formed? Influences on Weather and Climate and Latitude/Longitude (Q1) Components that influence weather and climate include: Latitude and Longitude Atmosphere (later) Oceans (later) Land Masses (later) Lat & Long Longitude (Meridians) (Q4) Angle of measure east or west of the Prime Meridian Imaginary vertical lines Label on Your Map Prime Meridian 0o (Greenwich, England) International Dateline 180o Latitude (Parallels) (Q5,6,7) Angle of measure north or south of the Equator Imaginary horizontal lines Label on Your Map: (BLM 13.1A) Equator 0o North Pole 90oN South Pole 90oS Arctic Circle 67.5oN Antarctic Circle 67.5oS Tropic of Cancer 23.5oN Tropic of Capricorn 23.5oS Earth’s Rotation and Revolution Rotation (24 hours) – The Earth rotates on its axis – The axis (imaginary line) runs North to South 23.5o angle – One Earth rotation takes one day Rotate East to West Revolution (365 Days) – The Earth revolves around the Sun The movement of one object traveling around another – It takes the earth one year to revolve (travel) around the Sun counter clockwise Any ideas as to how earth’s tilt towards or away from the sun can effect the 4 season’s we experience here in Canada?? Bill Nye: Seasons Handout: Seasons Worksheet (24 min) https://secure.e-registernow.com/cgi-bin/portal.cgi?state=210 Reason for the Seasons • The average tilt, 23.5o, of the Earth is the reason for the seasons) • As the Earth revolves around the Sun, the seasons in the northern and southern hemispheres are opposite. http://geovideos.fliggo.com/video/NY5Lxu6q Earth’s Seasons I. Tilt of the Earth’s axis towards or away from the sun creates the seasons When the north pole tilts toward the sun, it gets more radiation – more warmth during the summer When the north pole tilts toward the sun, the south pole tilts away So when it’s summer in the north, it’s winter in the south SUMMER (Northern Hemisphere) WINTER (Southern Hemisphere) Earth’s Seasons I. Tilt of the Earth’s axis towards or away from the sun creates the seasons When the north pole tilts away from the sun, it gets less radiation – So it’s colder during the winter When the north pole tilts away from the sun, the south pole tilts toward it… When it’s winter in the north, it’s summer in the south WINTER (Northern Hemisphere) SUMMER (Southern Hemisphere) Reason for the Season Video: Answer Key 1. What does the term axis mean? A. Axis is an imaginary line that runs through the North and South poles of the Earth. The earth spins on it at a 23.5o angle. 2. What is the angle of tilt for the earth’s axis? A. 23.5o 3. How long does it take the earth to spin or rotate on its axis? A. 24 hours 4. How long does it take the earth to orbit or revolve around the sun once? A. 365 ¼ days 5. What are those seasons? A. Autumn, spring, winter, summer Reason for the Season: Answer Key 6. Why is the angle of rays of sunlight so important in determining the amount of energy collected by the earth? A. Slanted rays spread out over a larger area therefore the heat and energy is also spread out. 7. What does the term migration mean? A. Animals moving from one point of the country or world to another during certain seasons. 8. Plants are the only organisms capable of making their own food. That food making process is called: A. Photosynthesis 9. Plants produce more than food. One gas that plants release into the air is used by animals. It is called: A. Oxygen 10. What is the average distance of the earth from the Sun? A. 93 million miles Reason for the Season: The Earth’s Tilt 1. Why is the tilt of the earth the cause for the seasons? A. Seasons are not connected to Earth's distance from the Sun our northern winter takes place when the Earth is actually closest to the Sun - but due to the fact that the Earth's axis is tilted away perpendicular to the ecliptic, winter takes place. The greater the angle, the less energy transferred. Reason for the Season: The Earth’s Tilt Q2. The North pole and South Pole each have long periods of complete sunlight and complete darkness. Why? A. When the Earth is tilted away from the Sun, the North Pole has no Sun for about 6 months. During the same time, the South Pole is pointed toward the Sun and receives nothing but Sun. NEXT… What is wind? And how is it formed… Mapping Activity Short Worksheet – – Part A: students to determine latitude and longitude of a location – Part B: students to determine location based on latitude and longitude.