Organizations
advertisement

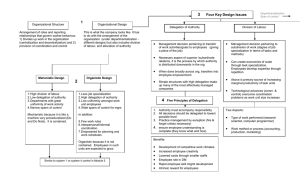
Organizations Organization A group of people working together in a coordinated effort to reach certain goals. In business, organizations help people achieve better results than they could working individually. All organizations need managers to make sure everyone works together in a coordinated manner to help the organization in a positive way. Why do Businesses Organize Organizations are formed for 3 basic reasons 1. To create a clear lines of authority 2. To improve productivity 3. To make it easier for people within a company to communicate with each other. Workers feel a sense of stability and belonging when working for an effective organization Authority The power based on the rights that come with a position. Without clear lines of authority, decisions could be made by people not qualified to make them. Establishing lines of authority means that decisions are made only at the appropriate level Chain of Command The line of authority within an organization. In the business world, the chain of command starts with the CEO Advantages of a Defined Chain of Command Makes it easy for all members of an organization to understand who is in charge. Allows for problems to be handled at the lowest possible level. Only problems that cannot be handled by a lower level supervisor will be introduced to a higher level Disadvantages of a Defined Chain of Command Can create problems if the structure is too rigid and complicated Too many layers make assigning responsibility difficult. Decisions are made slowly often by people with limited understanding of the issues involved. Ford motor company reduced the levels of mgt from 15 to 9. Larger mgt numbers meant longer time to respond to customer needs. This is a crucial advantage in a highly competitive industry Improving Productivity In early industrial times, it was proven that assigning specific tasks to individuals or groups will improve productivity This technique is called Division of Labor. Division of Labor may include: Specialization Job Rotation Job Scope Job Depth Specialization In many companies, groups of workers perform very specific tasks or sets of tasks. Makes training workers easy due to only needing to master a limited set of skills. Specialization can increase productivity Too much specialization may result in employee boredom. Job Rotation Periodically moving of workers from one job to another. This will help prevent workers from becoming bored It also creates a multiskilled workforce Job Scope Refers to the number of operations involved in a job. A narrow scope means a worker performs a small number of operations frequently A narrow scope may result in boredom and decline in job performance quality A broad scope means performing many job functions Most people find a broad scope more satisfying. Job Depth The freedom employees have to: Plan and organize their work Interact with co-workers Work at their own pace A job with depth allows for the workday to be much less regulated than those with minimal job depth Improving Communication Review Members of an organization need to communicate to help their organization achieve goals Managers must communicate Goals, Strategies, Policies, and Procedures to their staff Employees must communicate ideas, results, and problems to their managers Improving Communication Organizational structure allows companies that employ hundreds of thousands to communicate in an organized manner. This is done through: Meetings Memos Emails Telephone Informal Encounters between employees Communication ensures all employees understand company expectations. What makes an Organization Effective Responsive to the Market Customer Centered Committed to maintaining networks and alliances Developed around a vision Focused on creating top-quality products and services Dedicated to positive learning and change Attentive to meeting responsibilities to customers, employees, suppliers, and society Committed to measuring their progress against worldclass standards of excellence Able to respond to changing market conditions quickly Tomorrow Decentralization Authority Unity of Command Span of Management Accountability Decentralization The process by which decisions are made by managers at various levels within an organization. During industrial times (late 19th and early 20th centuries) many companies were centralized: Power was held by a few senior managers who were responsible for making most important decisions Managers at all levels making decisions is found to be more effective Decentralization Advantages: Increase an organizations ability to respond to market changes by allowing mgrs to make them close to their customers Frees many senior mgrs from day-to-day tasks and allows them to concentrate on higher-level issues, like planning. Giving decision making authority to lower level mgrs increases their job scope and makes work more interesting Disadvantages: May result in a loss of managerial control Duplication of effort. Maintaining Authority Authority is not effective when abused An effective manager must delegate responsibility to others inside the organization This empowers employees And relieves the manager of all responsibility Delegate To assign responsibility and authority for certain tasks to another person Delegating responsibility to a subordinate means that the manager obligates the subordinate to carry out certain duties, giving the subordinate the ability to act and make decisions. Responsibility The obligation to perform assigned duties Subordinate – Person holding a lower position within the organization Unity of Command Principle that states an employee should have only one immediate supervisor to report to. Confusion may result if the employee has to report to more than one person Span of Management The number of subordinates a manager can effectively control. AKA – SPAN OF CONTROL Too many subordinates might cause the manager to feel overwhelmed and not manage effectively Managers with too few subordinates may have too little to do, not justifying his position Giving Subordinates the Authority to Make Decisions Managers cannot delegate responsibility without delegating the authority to perform the task. Employees must be accountable for the responsibility and actions that ensue. Accountability The obligation to accept responsibility for ones actions. NO T.O.B. Accountability allows managers to monitor the work of subordinates Organization Structure All organizations serve a purpose and have a set of goals. What about the FBLA? What about the Christian Club? What about the Alexandria Football Team? What about Wal Mart? Organizational Structure Business organizations exist to meet their preset goals, and ultimately earn profits. To meet goals, they organize their employees into some kind of structure. This helps minimize confusion over job expectations. Structure clearly identifies who is responsible for which tasks. Types of Organizational Structures Line Structure Line and Staff Structure Matrix Structure Team Structure Each type can be shown by an organizational chart, which is a visual representation of a businesses structure. Shows who reports to whom and what type of work each department does. Line Structure Authority originates at the top and moves downward in a line. All managers perform line functions. Line functions – functions that contribute directly to company profits. EX. Production mgrs, sales reps, marketing mgrs What type of companies have a line structure? Line Structure Chart CEO Senior Managers Mid-level Managers Lower Level Managers Nonmanagement Operatives Line and Staff Structure In a mid to large sized company, line managers cant perform all tasks required to run their department. Other employees are hired to help by performing staff functions. Advise and support line functions EX. Legal dept, human resources, public relations Contribute only indirectly to company profits Staff are usually specialists in one field, and only advise line managers. Line and Staff Structure Chart Top mgrs Line mgrs Staff mgrs President Vice President, Sales Advertising Sales Personnel Vice President, Manufacturing Fabrication Assembly Matrix Structure Allows employees from different departments to come together temporarily to work on special project teams. Allows flexibility to respond quickly to customer needs by a team of people devoting time to the project, then return to their departments after completion. Common for companies that take on very large projects EX. Boeing, new aircraft design Matrix Structure Chart Team Structure Brings together people with different skills in order to meet a particular objective. More and more companies are using this over Line and staff. Allows them to meet customer needs quicker than traditional structures Teams make their own decision instead of having to get approval of senior mgrs Team Structure Chart Team A Senior MGT Team B Marketing, Production Research, Finance Marketing, Production Research, Finance Team C Marketing, Production Research, Finance Flat Structure An organization that has a small number of levels and a broad span of mgt at each level. This calls for a good bit of delegation on the part of the mgr. Employees have more power within the company. Advantages Greater job satisfaction More delegation Increased communication between levels of mgt. Tall Structure Organization that has many levels with small spans of management. Power is centralized on the top levels and there is more employee control by senior mgrs. Advantages Greater control Better performance