Matter and Change - Bartlett High School

Chemistry Joke
What do you call iron blowing in the wind?
Febreeze!
“Matter and
Change”
Chemistry - the study of matter and its changes
• Matter - anything that has mass and takes up space
– Air and smoke are examples of matter
– Light and heat are energy, not matter
• Mass - quantity of matter (numbers of atoms or molecules)
• Weight - measure of gravitational attraction
– Dependent on gravity of location
Study of Matter
•
States of Matter
•
Classifications of Matter
•
Physical Properties of Matter
•
Physical Changes of Matter
•
Chemical Properties of Matter
•
Chemical Changes of Matter
States of Matter
• Gas - indefinite volume and shape
•
Liquid - definite volume, indefinite shape
•
Solid - definite volume and shape
•
Plasma – a gas that has a charge because it has been heated and has lost its electrons.
Classifications of Matter plasma
Pure Substances
• Elements
– Simplest form of matter / building blocks
– Composed of only one type of atom
– Cannot be simplified
– Ex: Any element on periodic table
• Compounds
– Substances that can be separated only by chemical means into simpler substances
– Can be written as a chemical formula
– Ex: water, H
2
O; baking soda, NaHCO
3
; ammonia,
NH
3
Mixtures
•
2 Types
– Homogeneous
• Composed of only one phase of matter
•
Completely uniform throughout
• Also called a solution
• Ex: salt water, air
–
Heterogeneous
•
Non-uniform distribution
•
Ex: apple, salad
•
Can be separated by physical means
–
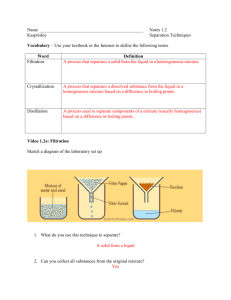
Filtration, distillation, chromatography
Physical Separation of a
Homogeneous Mixture by Distillation liquid alcohol and water alcohol
Physical Separation of a Heterogeneous
Mixture Using Magnetism
Physical Separation of a Homogeneous
Mixture Using Chromatography
Physical Properties of Matter
Properties that can be observed and measured
without changing the composition of the substance
Color Solubility
Electrical
Conductivity
State of Matter
(solid, liquid, gas)
Density
Melting and
Boiling point
Metallic
Characteristics
(malleability, ductility, & luster)
Thermal
Conductivity
Magnetic
Properties
Physical Changes of Matter
Changes in Form not Substance
• Phase changes are physical !!
– Melting, freezing, boiling, condensing, evaporating
• Tearing, breaking, cutting, crushing
• Dissolving is a physical change !!
Chemical Properties of Matter
• Ability of a substance to undergo a chemical reaction and form a new substance
• Flammability / Combustibility
• Acidic or basic
• Reactivity
Chemical Changes of Matter
Indicators that a chemical change may have happened:
Energy is absorbed or released
(temperature changes)
Color changes
Gas is produced (bubbling, fizzing, or odor change; smoke)
Precipitate is formed - a solid that separates from solution (won’t dissolve)
Irreversibility - not easily undone
Words Associated with Chemical Change
Burn Decompose Corrode
Rot
Rust
Ferment Cook
Explode -----------
Chemical Reactions of Matter
Starting substances called reactants change to form products.
Reactant + Reactant → Product
The Law of Conservation of Mass
(of Matter!)
•
In any physical or chemical change, mass is neither created nor destroyed; it is CONSERVED!
•
In other words, the mass of the reactants will ALWAYS equal the mass of the products.
43.43 g Original mass = 43.43 g Final mass reactants → product
Chemistry Joke
Q: H
2
O is water and H
2
O
2
is hydrogen peroxide. What is
H
2
O
4