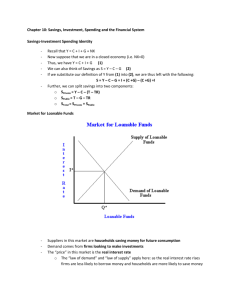
Mgmt 673 Problem Set 7
advertisement

Running head: MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 Mgmt 673 Problem Set 7 Name Tutor Institution Course Date 1 MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 2 MGMT 673 – Global Economic Analysis Problem Set 7 The largest portion of the Current Account is international trade in goods. For the US, this account is tracked by the US Census Bureau (somewhat strangely). Use a web search or search within the US Census Bureau homepage for “US trade in goods with world seasonally adjusted.” What is the most current full year balance? What does this balance mean in terms of exports and import As examiners reconsidered the development prospects for the world economy, the part of the U.S. current record deficiency had retreated out of spotlight. Truth be told, the present record deficiency had declined from a normal of right around 5% of GDP from 2000 through 2007 to around 3% of GDP in 2011 and 2012.1 Much of the purpose behind that control was apparently not long haul: the moderate U.S. development had diminished imports. The money related partner of the U.S. current record shortages was the proceeding with capital inflow from abroad, as nonnative’s financed Americans' spending in overabundance of their salary (Savona, 2010). As these inflows gathered, the crevice between U.S. possessions of outside resources and remote property of U.S. resources (known as the net universal venture position, or NIIP) was sinking to a remarkable nadir. Generally U.S. policymakers had since quite a while ago made light of the dangers inferred by the substantial current record shortage and net global venture position. They demanded that the shortfall and NIIP just mirrored the engaging quality of the U.S. economy as a destination for worldwide speculation. For instance, the 2006 Economic Report of the President concentrated on the present account's partner, to be specific outside interest in the United States (Walmsley, 2011). 2. Household finances are similar in some ways to a nation’s international transactions.a. Suppose a household consumes (spends) more than its income. What are 3 legal ways it can finance this deficit? MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 3 Give an example of each. There are three main ways the government can finance a deficit. Firstly, the legislature can obtain stores from alternate segments of the economy. This includes the offering of new Commonwealth Government Securities (CGS, for example, treasury bonds through a delicate framework. This is the favored government strategy for raising stores, as it doesn't add to net remote obligation, in light of the fact that the legislature is not acquiring from abroad. Notwithstanding, there is an impediment to this type of obligation financing. The second conceivable system for financing a shortfall is for the Commonwealth Government to offer CGS to the Reserve Bank. This type of acquiring from the Reserve Bank fundamentally implies that the administration prints cash to back the deficiency. The Government has not utilized this system for shortage financing following the deregulation of the Australian money related business sector in 1982(Uzawa, 2007). This is on account of it is profoundly inflationary: when the legislature spends the cash, there is an increment in the cash supply; if the economy is close full work, request expansion happens quickly, as there is an excess of cash pursuing a restricted supply of products. The third conceivable strategy used to back a financial plan shortage is for the legislature to obtain stores from global money related markets. The administration has not obtained from abroad since the late 1980s to back the shortage. At the point when utilizing this strategy, the Reserve Bank offers new CGS to abroad purchasers, and gets outside supports that are changed over into Australian dollars. This system for financing the deficiency adds to outside obligation when hobby is paid on the securities (net wage segment of the parity of installments). b. How can a nation that runs a persistent Current Account deficit finance its excess consumption? A present record shortfall implies the estimation of imports of merchandise/administrations/speculation MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 4 livelihoods is more prominent than the estimation of fares. It is some of the time alluded to as an exchange shortage. In spite of the fact that an exchange shortfall (products) is just piece of the present record. f a present record shortage is financed through acquiring it is said to be more unsustainable. This is on the grounds that acquiring is unsustainable in the long haul and nations will be loaded with high intrigue installments. In the event that you run a present record shortage, it implies you have to run a surplus on the money related/capital record. This implies outsiders have an expanding case on your benefits, which they could yearn to be returned whenever. For instance, in the event that you run a present record shortfall, it could be financed by remote multinationals putting resources into your nation or the buy of advantages. There is a hazard that your best resources could be purchased by nonnatives, lessening long haul wage. 3. A nation with a large current account deficit is consuming more than it produces or living beyond its means. Is this necessary bad? What is your judgment for the United States? The U.S has had shockingly high development in the most recent couple of years, yet the present record deficiency has likewise developed and is its biggest on record. An extensive current record shortage and solid development are signs that a nation is living past its methods. The mix of solid GDP development and an extensive current record deficiency could be a notice sign that development is being fuelled by over the top obtaining as opposed to solid monetary essentials. The stress is that when whatever remains of the world concludes that it wouldn't like to give that nation any more cash, development comes slamming down. The shortfall on the present record of the parity of installments happens on the grounds that our imports of products and administrations surpass our fares (the exchange shortage), and installments of interest and profits to nonnative’s surpass our receipts of interest and profits from outsiders MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 5 4. If the central bank does not intervene in the foreign exchange markets (the RA balance is zero), briefly explain why CA + KA = FA (see Exhibit 16-3). Balance of payments accounting (1) BOP = CA + KA + FA = 0 (Balance of Payment Identity) CA: Current Account (recording the stream of products and administrations, the stream of element administrations, and the stream of non-market genuine asset exchanges, i.e. NUT) KA: Capital Account (recording the stream of non-market capital exchanges) FA: Financial Account (recording the stream of money related resources) The BOP's segments character let us see the subtle elements behind why the records must adjust. On the off chance that an item has one or more sign, it is known as a parity of installments credit or BOP credit. On the off chance that a thing has a short sign, it is known as a parity of installments charge or BOP charge. The present record measures outside uneven characters in merchandise, administrations, element administrations, and one-sided exchanges. The money related and capital records measure resource exchanges. Surpluses on the present record side must be balanced by deficiencies on the benefit side. So also, shortfalls on the present record must be balanced by surpluses on the advantage side. By letting us know how current record lopsided characteristics are financed, the equalization of installments makes the association between a nation's salary and spending choices and the development of that nation's riches. MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 6 5. Suppose that the US current account deficit must be reduced. Explain in terms of CA ? (S – I) + (T – G) what must be done to reduce the current account deficit. Why will this be difficult? (Hint: It may be helpful to think about the household that has been living beyond its means, perhaps by borrowing on credit cards). Income is separated into utilization, sparing and assessments. (Successively, perhaps it is more sensible to say, first we pay charges, then spend, and spare the rest of. Alternately perhaps you spare first? In the event that we are normal, every one of these choices ought to be at the same time made.)From these two personalities, Y and C offset X - M = (S - I) + (T - G) Keeping in mind, this is still a character (which implies it generally holds, whether in harmony or nonbalance). The CA (= X - M) is indistinguishably equivalent to net private sparing (S - I) in addition to net government sparing (T - G). The present record is the net sparing of the two areas consolidated. As per this view, a CA shortage implies that either the private segment or the legislature (or both) has negative sparing As a rule; the administration overspends its financial plan. Expansion net private sparing or expand net government sparing. To expand net private sparing (S - I), debilitating venture is for the most part undesirable (unless there is a speculation bubble). The better arrangement is to empower private sparing. This should be possible by different institutional changes in accordance with fortify motivators to spare and evacuate impetuses to expend excessively, in the expense framework, saving money, lodging, annuity, government managed savings and protection, and so on. To build net government sparing (T G), one must either expand charge income or cut spending. supply or demand curve that demonstrate An increase in aggregate demand for a nation’s goods and MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 7 services, such as would occur if the government increased spending, normally causes an increase in the amount produced and a higher average price level. This leads to an increase in the demand for goods, shifting the IS curve to the right. This leads to an increase in output and the interest rate. The increase in the interest rate implies an appreciation in the Home currency that decreases the current account. This is illustrated in the following figure. supply or demand curve to demonstrate An increase in a nation’s supply of goods and services, as would occur if the oil prices fell in the world market, tends to raise the amount sold per time period and lowers the nation’s average price level. Greater output creates more jobs which reduces the unemployment rate. A decrease in the price level raises the real value of money and makes consumers feel wealthier, which in turn encourages them to spend more. The increase in consumer spending means a larger quantity of goods and services demanded. A fall in oil prices is effectively like a free tax cut. In MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 8 theory, the fall in oil prices could lead to higher spending on other goods and services and add to real GDP. Macro economic impact of falling oil prices 1. Lower inflation 2. Higher output supply or demand curve that demonstrate An increase in borrowing demand, as would occur if the government borrows more money to finance the budget deficit, causes the real risk-free interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of real loanable funds per period of time to rise. MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 9 The market for loanable funds is a business sector where the individuals who have loanable stores offer to the individuals who need loanable stores. The accessibility of loanable trusts is dictated by the measure of national sparing, which is the aggregate wage in the economy in the wake of paying for utilization and government purchases. It is the crossing point of the supply and interest of loanable stores that sets the interest rate. Like the supply of anything, more loanable trusts are accessible at higher interest rates, and the other way around. The interest for loanable stores, then again, is contrarily relative to the interest rate higher interest rates decrease request. Under this disentangled model of microeconomics, families are dealt with as a wellspring of most loanable finances and firms are the demanders of loanable store supply or demand curve that demonstrate An increase in the supply of a nation’s real loanable funds, as would occur if the central bank engaged in open market purchases of financial securities, reduces the real risk-free interest rate and increases the quantity of real loanable funds per period of time. This demonstrates the general design of the Loanable Funds Model. It is a similar statics harmony display that utilizes a supply and interest bend to find a business sector clearing balance cost. The exceptional cost in this model is the expense of credit - the interest rate, spoke to by the MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 10 variable r. There is, obviously, a full range of interest rates in the U.S. economy, going from fleeting rates on currency market resources, for example, U.S. Treasury Bills to long haul rates, for example, and the premium rates on 30-year home loans. Interest rates all through this range are never the same - by and large on any given day there are the same number of interest rates as securities speak to them. supply or demand curve that demonstrate An increase in the demand for a nation’s currency, as would arise if foreigners wished to increase purchases of domestic goods, raises both its international value (exchange rate) and equilibrium quantity per period of time. The foreign exchange market involves firms, households, and investors who demand and supply currencies coming together through their banks and the key foreign exchange dealers. MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 11 supply or demand curve that demonstrate An increase in the supply of a nation’s currency, as would occur if the central bank engages in open market purchases, lowers the exchange rate and raises the equilibrium quantity per period of time The two demands for the money curves can be summed horizontally to get the total demand for money. This total demand shows the total amount of money demanded at each interest rate. The equilibrium interest rate is determined at the intersection of the total demand for money curve and the supply of money curve. With an increment total money demand previus rate (i0) is unsustainable on the grounds that with the new interest for cash (Dm1), the amount of cash requested will surpass the amount of cash supplied. There would be a lack of stores and upward weight on the interest rate 12 MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 Rate of interest, i (p ercent) Sm i1 i0 Dm 0 Dm1 Qm Amount of money demanded and supplied supply or demand curve to demonstrate A decrease in the real interest rate encourages borrowing and spending by households (C) and firm’s (I) thereby increasing real GDP. Equilibrium Balance in the merchandise business sector happens when the total supply of products (Y) parallels the total interest for products (Cd + Id + G). Since wanted national sparing (Sd) is Y – Cd – G, a proportionate condition is Sd = Id. Harmony is accomplished by the genuine's alteration premium rate to make the coveted level of sparing equivalent r S Id $ please pay to this pa pal address bancywangari254@gmail.com 13 MGMT 673 PROBLEM SET 7 References Savona, P. (2010). Making global economic governance effective: Hard and soft law institutions in a crowded world. Farnham, Surrey: Ashgate Uzawa, H. (2007). Economic analysis of social common capital. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Walmsley, T. L. (2011). Dynamic modeling and applications in global economic analysis. Washington, DC: Cambridge University Press.