Forebrain
advertisement

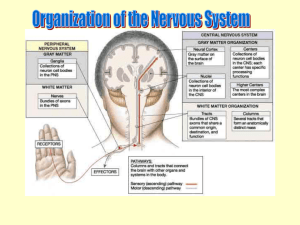
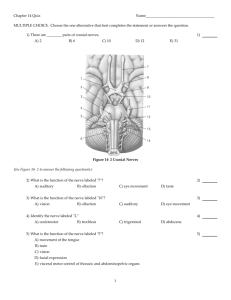
Forebrain • Review Overview – CNS • Components • Function • PNS – – – – Components Function Sensory portion Motor arm • Somatic Nervous System – Function • Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) – Function – Sympathetic and Parasympathetic branches » Function » Antagonists The Human Brain • Development – Embryonic • Neural tube – Structure • Week four – Structure » Prosencephalon » Mesencephalon » Rhombencephalon – Spinal cord The Human Brain • Development – Fetal – Telencephalon • Location – Cerebellum formation – Ventricles The Human Brain • Cerebrum – Location – Lobes • • • • Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital – Landmarks • Gyri • Sulci • Fissures Cerebrum • Longitudinal Fissure – Division • Central Sulcus – Division • Lateral Sulcus – Division • Parieto-occipital Sulcus – Division • Functional areas Cerebrum – Primary Somatosensory Cortex • Location • Function – Somatosensory Association Area • Location • Function – Visual areas • Location – Auditory area • Location – Olfactory area • Uncus Cerebrum • Functional areas – Primary Motor area • Location • Function – Broca’s area • Location • Function • Damage – Pre-Frontal Cortex • Location • Function – Wernicke’s area • Location • Function Cerebrum • Specialization – Left hemisphere – Right hemisphere • Cerebral Cortex • White matter Cerebrum • Internal Structures – Grey matter – White matter • Tracts – Association tracts – Projection tracts – Commissures – Corpus callosum – Fornix – Septum pellucidum The Diencephalon • Location • Embryologic derivation • Ventral surface – Olfactory bulbs and tracts – Optic nerves – Optic chiasm – Optic tracts – Pituitary gland – Mammillary bodies The Diencephalon • Internal Structures – Thalamus • Location • Function – Intermediate mass • Interthalamic adhesion • Location – Interventricular foramen • Location – Hypothalamus • Location • Function – Infundibulum • Location – Epithalamus • Location – Pineal body • Endocrine structure – Choroid plexus • Location • Function The Brain Stem • Pons – Components • Cerebral peduncles – location • Medulla oblongata – Location – Function • Internal Structures – Cerebral aquaduct • Location – Corpora quadrigemina • Location • Superior colliculi • Inferior colliculi Cerebellum • Function • Location • Hemispheres – Lobes • • • • Cortex White matter Vermis Arbor Vitae • Meninges Covering – Brain and spinal cord – Three layers • Dura mater – Leathery, outermost meninx – Double layered – Layers • Periosteal – Attached to the inner surface of the skull • Meningeal – Attached to the outer surface of the brain, continuous with dura mater of spinal cord – Extensions • Dural layers are fused with three exceptions. The inner membrane extends inward to form a septum to secure the brain in the cranial cavity • Falx cerebri – In longitudinal fissure, attaches to the crista galli of the ethmoid bone – Creates the Superior sagittal sinus which drains blood from the brain • Falx cerebelli – Separates the cerebellar hemispheres • Tentorium cerebelli – Separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum Meninges • Arachnoid mater – Middle meninx, web-like, underlies dura – Subdural space separates dura and arachnoid – Subarachnoid space • Contains projections that bridge space between arachnoid and pia mater • Filled with cerebrospinal fluid – Arachnoid villi • Projections of arachnoid villi that protrude through the dura mater to allow CSF to drain back into the venous circulation • Pia mater – Inner layer – Highly vascular – Clings to the surface of the brain, follows convolutions • Abnormalities – Meningitis • Inflammation of the meninges. If infection spreads to the brain, encephalitis may result – Encephalitis • Infection of the brain Cerebrospinal Fluid • Function – Cushion and protect brain • Composition – Much like plasma • • Path of CSF Choroid plexuses • Small capillary knots hanging from roof of ventricles in the brain. CSF made here – – – – – – – – – – – Lateral ventricles Interventricular foramina Third ventricle Cerebral aqueduct Fourth ventricle From the fourth ventricle, some CSF goes down the central canal of spinal cord Most of the CSF goes into the subarachnoid space exiting the Foramina of fourth ventricle Arachnoid villi Dural sinuses Returned to venous blood Cerebrospinal Fluid • Abnormalities – Normally, CSF forms and drains at a constant rate. – Drainage failure, due to obstruction (i.e. tumors, deviations), accumulation of CSF exerts pressure on brain. • Adults – Neurological damage • Infants – Hydrocephalus » “water on the brain” » Soft spots on infants skull allows expansion and accomodation Cranial Nerves • Part of the PNS, not the brain. • 12 Pair – Primarily serve the head and neck • Vagus Nerve – Extends into the thoracic cavity and abdominal cavities • Olfactory and Optic nerves – Only nerves not arising from the brain stem and pass through foramina in the skull. • Names and numbering – Reflect major structures that they control • Table 19.1 Cranial Nerves • Mneumonics On Old Olympus’ Towering Tops, A Finn And German Viewed Some Hops": · In order from 1 to 12: Olfactory (Cranial Nerve I) Optic (Cranial Nerve II) Occulomotor (Cranial Nerve III) Trochlear (Cranial Nerve IV) Trigeminal (Cranial Nerve V) Abducens (Cranial Nerve VI) Facial (Cranial Nerve VII) Auditory [or Vestibulocochlear] (Cranial Nerve VIII) Glossopharyngeal (Cranial Nerve IX) Vagus (Cranial Nerve X) Accessory [or Spinal root of the accessory] (Cranial Nerve XI) Hypoglossal (Cranial Nerve XII) Cranial Nerves • Most are mixed nerves and contain motor and sensory fibers – Cell bodies located in the brain and peripheral ganglia • Optic, olfactory, and vestibulocochlear are sensory only – Cell bodies are located in the ganglia Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia • • • • • • • Caudate Putamen Globus Pallidus Nucleus Accumbens Ventral Pallidum Subthalamic Nucleus Substantia Nigra Basal Ganglia: Inputs • Cerebral cortex: all lobes have projections to striatum; most are (+) and use glutamate. • Substantia nigra pars compacta: to striatum; (+) and (–) connections, uses dopamine. • Thalamus (intralaminar nuclei): to striatum; (+) and use glutamate. • Raphe nuclei: to BG use serotonin. Basal Ganglia: Outputs • Substantia nigra pars reticulata: to VL and VA thalamus; (-) using GABA. • Globus pallidus internal segment: to VL and VA thalamus; (-) using GABA. Limbic System • Olfactory System – Olfaction • Hippocampal formation – Memory • Amygdala – Emotions and drives • Hypothalamus – Homeostasis Olfactory System • Olfactory system of lower mammals is typically large. • In primates and humans, the olfactory system is relatively small resulting in a poorer sense of smell. • Even so, olfaction can have significant impact on behavior in humans. • Primary olfactory cortex is unique among sensory systems in that it receives direct input from secondary sensory neurons without an intervening thalamic relay. Hippocampus • 3 main components – Dentate Gyrus – Hippocampus – Subiculum • 3-layered archicortex • Circuitry has been extensively studied because of its importance in memory • Storage itself is thought to be back in the association cortex not medial temporal lobe Amygdala Amygdala II • Amygdala is especially important in emotions and drives. • Amygdala has extensive connections with other limbic areas and is also involved in memory, olfaction, and homeostasis. • Amygdala is especially important for attaching emotional significance to various stimuli perceived by the association cortex. In animals where both amygdalas have been ablated, behavior is very placid, tame, and nonaggressive. Hypothalamus • Preoptic area – medial preoptic nucleus – lateral preoptic nucleus • Anterior region – – – – anterior hypothalamic nucleus Supraopticnucleus paraventricular nucleus suprachiasmatic nucleus • Middle region – arcuate nucleus – ventromedial nucleus – dorsomedial nucleus • Posterior region – mammillary nuclei – posterior hypothalamic nucleus Cerebral Cortex • Brain’s most complex area with billions of neurons and trillions of synapses – Consciousness – Perceives sensations – Commands skilled movements – Emotional awareness – Memory, thinking, language ability – Motivation – All “higher” mental functions Cerebral Cortex II • • • • Highly developed in primates and cetaceans 50% of total brain weight in humans Surface area of 2.5 square feet in humans 4.5 mm thick in precentral gyrus; 1.5 mm thick in visual cortex • Only 1/3 of surface area visible, 2/3 in banks of sulci • Surface of gyri and sulci • Estimated to contain about 15 billion neurons in humans Cortical Anatomy • 6 lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, limbic and insular • Each lobe has several gyri • Functionally the cortex is divided into numbered areas first proposed by Brodmann in 1909 • Brodmann’s areas were described based on cytoarchitecture; later they were found to be functionally significant Brain Atrophy in MS MRI • Brain Parenchymal Fraction (BPF) decreased in MS – Rudick 1999 • Grey Matter Fraction (GMF) and White Matter Fraction (WMF) decreased in MS – Chard 2002 • Cortical Thinning in MS – Sailer 2003