Job Analysis - session 4

Tehzeeb Sakina Amir
HRM-session 4
Spring 2011-MBA
Job Analysis
Job Analysis
• Analyze a job
– What the job entails
– What kind of people should be hired for the job
Job Analysis
• Job Analysis
– The procedure for determining the duties and skill requirement of job and the kind of person should be hired for it
– Job Descriptions
• A list of job duties , responsibilities, reporting relationships, working conditions, safety hazards and supervisory responsibilities – one product of JA
– Job Specifications
• A list of job’s ‘human requirements ’ that is the requisite education, skills, personality and so on – another product of
JA
Job Analysis
• Uses of JA
– Recruitment and Selection
– Compensation
– Training
– Performance Appraisal
– Discovering unassigned duties
– Legal Compliance
Job Analysis
• Basics of JA
– Work activities
– Human behaviors
– Machines, tools, equipments, work aids
– Performance standards (quality or quantity level of the job use to assess employee)
– Job context – physical working conditions, work schedule, social context, incentives
– Human requirement – education, work experience, aptitude, physical & personality characteristics
Job Analysis
• Steps in JA
– Step 1 – determine purpose of JA so you collect the data in the way that is most useful (interviews vs
PAQ)
– Step 2 – review background information as organization chart, process charts and job descriptions
• Organization chart – title, interacting lines etc
• Process chart – a work flow chart show the inputs & outputs from a particular job
– Step 3 – select ‘ representative ’ positions
Job Analysis
• Steps in JA
– Step 4 – actually analyzing ! Use more than one methods
– Step 5 – verification of information collected
(worker and supervisor input)
– Step 6 – develop job description and job specification
Guidelines for collecting JA info
• Some practical considerations!
1.
It’s a joint effort
2. Get information from several people – subject matter experts
3. Understand context
4. Questions must be clear and comprehensible
5. Pre observation and questioning
Methods for collecting JA info
• Qualitative Approaches
– Interviews
– Questionnaires
– Observation
– Daily logs
• Quantitative Approaches
– Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ)
– US Department of Labor job analysis procedure
• Internet based JA
Methods for collecting JA info
• The Interview
– Unstructured to highly structured interviews
– Group interviews OR individual interviews
– With or without supervisor
– These interviews are NOT 'efficiency evaluations !’
– Pros and Cons
• Simple and quick, undiscovered areas are brought up, vent out feelings, etc
• Distortion of information, exaggeration of job, inflate job importance
– Typical questions
Structured interviews
• Structured or
checklist
format
• Includes detailed questions regarding matters like purpose of job, responsibilities, duties, education etc
• These structured lists can also be used as questionnaires.
Interviewing Guidelines
• Several guidelines:
– Job analyst and supervisor must work together to identify workers to be interviewed
– Establish rapport with the interviewee
– Follow the structured guide or list
– Identify critical yet infrequently performed duties too
– Review and verify data with supervisor and interviewee
Methods for collecting JA info
• Questionnaire
– Have employees fill out questionnaires to obtain JA information
– Structured questionnaire and what questions to be included
– Open ended questions too
– It is a quick and efficient way to obtain information from large number of employees, less costly
– Developing & testing questionnaire can be a tiresome job!
Methods for collecting JA info
• Observation
– Direct observation (physical activities not mental activities)
– Infrequent yet important behaviors need to be cared for..
– Reactivity (aware of being observed)
– Use observation followed by interviews. Or simultaneously interviewing
Methods for collecting JA info
• Participant Diary / Logs
– Daily listings made by workers of their activities
– Records the activity, time taken, frequency, etc
– Followed by subsequent interviews
– Beware of Exaggeration and Undermining
– Hi-tech logs
Quantitative Method - PAQ
• Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ)
– A questionnaire used to collect quantifiable data concerning the duties and responsibilities of various jobs
• Very structured, contains 194 items each of which represents a basic element
• Provides a quantitative score or profile of job in terms of five basic activities
– Decision making, communication, social responsibility
– Performing skilled activities
– Being physically active
– Operating vehicles / equipment
– Processing information
• The PAQ score is used to determine pay levels
Quantitative Method - PAQ
Information input – visual sources of information input
1 4 Written materials (books, reports)
2 2 Quantitative materials (graphs, accounts)
3 1 Pictorial materials (pictures, drawings, maps)
4 1 Patterns/related devices (stencils, templates)
5 2 Visual displays (dials, gauges, signal lights)
6 5 Measuring devices (rulers, scales, thermometer)
Quantitative Method - DOL
• DOL Procedure
– It quantitatively rate, classify and compare different jobs
– The heart of this analysis is a data, people and things rating for each job
– Use a set of standard basic activities called worker functions to describe what a worker can do with respect to data, people and things
– Each worker function gets an importance level
– Functional Job Analysis is similar to DOL method but rating goes further to task requiring specific instructions, reasoning, judgment, verbal, language & mathematical abilities
Quantitative Method - DOL
Data
0 Synthesizing
1 Coordinating
2 Analyzing
3 Compiling
4 Computing
5 Copying
6 Comparing
People
0 Mentoring
Things
0 Setting Up
1 Negotiating
2 Instructing
3 Supervising
4 Diverting
1 Precision working
2 operating/control
3 Driving
4 Manipulating
5 Persuading 5 Tending
6 Speaking/signaling 6 Feeding
7 Serving 7 Handling
Internet based JA
• Internet – Based JA
– O*Net …US Occupational information network www.onetcenter.org
– DOT Dictionary of Occupational Titles now it is SOC (Standard
Occupational Classification) – it classifies all workers into 23 major groups of jobs which are subdivided into minor groups of jobs and detailed occupations.
– Methods are becoming more time & cost consuming, updating is difficult, international perspective is difficult to attain
– Use of on-line methods – quick, easy to update, etc
– May lose critical information, faking and absence of job analyst may lead to these misunderstandings
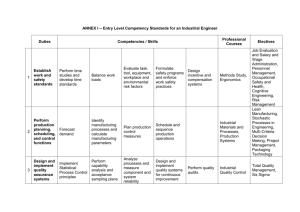
Job Descriptions
Job Description is a written statement of what the worker actually does, how he does it and what the job working conditions are.
• It must have sections like:
– Job identification
– Job summary
– Responsibilities and duties
– Authority of incumbent
– Standards of performance
– Working conditions
– Job specifications
Job Descriptions are important
• Clarifies employer expectations for employee
• Provides basis of measuring job performance
• Provides clear description of role for candidates
• Provides structure and discipline in the organization
• Makes pay & grading system structure more fairly and logically
• Prevents arbitrary interpretations
• Essential reference in matter of disputes
• Identify training & development areas and career planning
• Provides neutrality in performance appraisal
Job Specifications
• Step ahead of Job Description, entails as to
what human skills, knowledge and abilities
are required to perform the particular job.
• What kind of person should be recruited, tested …
Job Specifications
• Trained vs Untrained Personnel job specifications would be different
– Trained - # of years, previous job performance etc
– Untrained – physical traits, personality, interests etc
• Job Specifications are based on
1.
Judgments
2.
Statistical Analysis
• Intelligent judgments or smart guess-works of supervisors/HRMs
– Review job duties and determine human traits and skills the job requires
– Can also refer to competencies listed in JD web-based sites
Job Specifications – work behavior
• Judgments use Common Sense in listing human traits .
• Some Work Behaviors are generic / important in almost all jobs:
– Industriousness - hardworking
– Thoroughness - detailing
– Schedule flexibility – accept flexibility
– Attendance - regular
– Off-task behavior (reverse) – personal work
– Unruliness (reverse) – bully, threatens coworkers
– Theft (reverse) – breaking rules, cheating
– Drug misuse (reverse)
Job Specifications – statistical analysis based
• More defensible approach but more difficult too!
• Statistically determine the relationship between predictor (trait) and some indicator of job performance, it has five steps:
– Analyze job to decide KPIs
– Select personal traits that predict successful performance
– Test candidates for these skills
– Measure candidates subsequent job performance
– Statistically analysis the relationship
Changing the ‘ Job ’ meaning
• Industrial revolution emphasized on specialized
(repetitive) jobs positively related to efficiency!
• Mid 1900s it is viewed as ‘ dehumanizing ’
– Result was: Job rotation, Job Enlargement Job
Enrichment
• Now it is ‘ dejobbing ’ - team-based, self managed, cross-functional multi-skilled teams, reengineering, flatter organizations, are encouraged
The new way to JA
Competency-Based
• Writing JA on the basis of competencies rather than job duties
• Job competencies are observable and measurable work behaviors! (knowledge, skills and/or behaviors)
• “In order to perform the job the employee should be able to …” focus on how the worker meets the expectations of the job and performs it well!
• Traditional JA is job focused , competency based is worker-focused (what he is competent to do)
Reason for Competency based JA
• Three reasons:
– When high performance work system is the organizational goal
– More strategic way to describe the job
– it supports organization performance management process , performance appraisals focused on more skill acquisition
Writing Competency based JA
• Competencies can be broadly divided into
2-3 clusters:
– General competencies (reading, writing, mathematical)
– Technical competencies (specific technical requirements)
– Leadership competencies (leadership, teaching, guiding, strategic thinking)
Writing Competency based JA
• The Traditional way – interviewing, identifying critical areas etc
• The Skill Matrix
– Listing the basic / specific skills needed
– The minimum level of each skill
– Change employee perception from traditional job description to a more flexible and motivating approach
– Focus on specifying and developing new skills
– Skill-based pay plans that rewards rise with skill improvement
The Skill Matrix
E
D
G
F
C
B
A
Technical expertise
E
D
G
F
C
B
A
Business awareness
E
D
G
F
G
F
E
D
G
F
E
D
C
B
C
B
C
B
A A A
Communication
& interpersonal
Decision making & initiative
Leadership & guidance
Group Activity
• Working in group, develop the Job
Description on the basis of guidelines provided in the sheet.
• Redo it with the corrections marked
• Submit it again