Financial Inclusion
advertisement

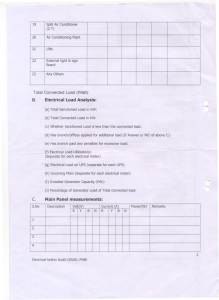
“Innovative use of ICT by PSUs for Customer’s Benefits” Project Financial Inclusion@PNB 1 As per Rangarajan Committee Report Financial Inclusion is the process of ensuring access to appropriate financial products and services needed by vulnerable groups such as weaker sections and low income groups, at an affordable cost, in a fair and transparent manner by mainstream institutional players. 2 Important Milestones on Road to Financial Inclusion in India 1904 Setting up of Rural Cooperatives 1969 Nationalization of 14 major Commercial Banks 1975 Setting up of Regional Rural Banks 1990s Self Help Group 2005 RBI advised banks to open no frill accounts 2006 RBI allowed BC/BF to act as agents of banks Sept. 2010 RBI allowed for - profit companies (excluding NBFC) to act as Business Correspondent 2011 National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI) launched Interbank Mobile Payment System (IMPS) 3 OUR BELIEF Banking to the unbanked is a profitable business MISSION “Banking for the Unbanked” VISION “ To be a leading Global Bank with PAN India footprints and become a household brand in the Indo-Gangetic plains, providing entire range of financial products and services under one roof ” 4 Financial Inclusion Models Adopted by the Bank Financial Inclusion Branch based Model (Brick and Mortar) Branchless Model (ICT Model) Brick & Mortar Model - Opening PNB MITRA-No frill accounts (Zero balance accounts) with relaxed KYC norms - Launched PNB Mitra ATM card; withdrawal limit : upto Rs. 5,000 per day. ICT (Information & Communication Technology) Model – Base Branch acts as a focal point for Business Correspondents (BCs) – BCs are engaged by the Bank/technology providers – BC Agents (BCAs) contact the customers for enrollment and issue biometric smart cards. – BCAs use laptops and POS in Off Line mode. – Relaxed KYC norms 5 Project FI through RRBs • Following Srinivasan Committee recommendation, to leverage technology for business and inclusive growth, the project CBS@RRB implemented in all the 6 RRBs sponsored by PNB in April,2010. • Six RRBs sponsored by PNB: - Haryana Gramin Bank ,Rajasthan Gramin Bank, Punjab Gramin Bank - Himachal Gramin Bank, Sarva UP Gramin Bank, Madhya Bihar Gramin Bank. No. of Service Outlets 1488 Avg. no. of Txn. In Lacs (Post CBS) per day 3.07 Customer Base (In Lacs) 87.94 • Project adjudged as the best IT implementation for year 2010 by PC QUEST Magazine. • Project was awarded SKOTCH AWARD for the year 2010. 6 FI Products Offered by PNB • Products offered – Savings with inbuilt OD facility upto Rs.2500/• OD facility of Rs. 500/- is offered upfront • Proposed new products – Micro Credit – Remittances/ Fund Transfer – Term Deposit & Recurring Deposit – Micro Insurance – Micro Mutual Fund Banking transactions Financial Inclusion in Cash withdrawal Cash deposit Mini statement Balance inquiry Besides Mini Statement facility, Passbook facility is also offered to FI customer. 7 Customer Enrollment Process Web Camera for Photograph Biometric scanner for Fingerprints Pad for Signature capturing Battery Power back-up for undisrupted enrolment 8 FI Vendor ENROLLMENT PROCESS Data conversion Back Office 3 Back Office n FINCBS Server at DC Validation of Data External Firewall Vendor Intermediary server External Firewall FI Intermediary server Back Office 1 Back Office 2 Card personalization centre Card distribution centre 9 Transaction Process Transaction at the village carried out by BCA with Hand Held Terminal (HHT) Machine is used to capture Transactions HHT application supports all products Secured transaction With BCA card & Customer card Transactions are Recorded in customer & BCA card Bank’s security key embedded in SAMsmart chip component of HHT 10 Uniqueness of project FI @PNB • • • • • • • PNB has adopted branchless banking model supported with smart card based technology. It has independent CBS setup for FI server at data centre with DRS setup. The management and control of whole setup is done by PNB team. Data validation, upload and other activities are performed by exclusive FI back Offices. The complete system is secured with symmetric key based Key Management System( owned and managed by Bank) as per IDRBT open standards for FI. Financial transaction happens at HHT only after authentication of BC agent’s smartcard and customer’s smartcard followed by finger print authentication. On completion of any transaction, the HHT prompts transaction amount and the resultant balance of the customer in local language 11 Uniqueness of project FI @PNB • • • • • Contd. An instant receipt generated from the HHT is given to the customer Data transmission is done in encrypted form. Interoperability is achieved through use of centralized KMS facilitating the FI customers to avail banking facilities anywhere within the district/state. Necessary Information security system and policies including Firewall system has been put in place for FI project. FI disaster recovery site has been put in place to meet the challenge of any failure at Data centre. 12 BCP in FI (Business Continuity Plan): •Customer Finger print fails to match • BCA can manually perform the transaction ( override) Within the customer wise, day wise limit fixed by Bank It is controlled through the HHT application New smart card will be issued if the failures are continuous •HHT is lost before the transaction upload Copy of the transactions are stored in BCA card Retrieved from the BCA card and uploaded •HHT is lost and BCA card is also lost Second copy of the receipt with the BCA sent to FI back office Transaction created in FINCBS 13 BCP in FI (Business Continuity Plan) cont. •BCA fails to turn up Alternate BCA sent to village Customer card read and the transaction retrieved Uploaded to FINCBS after validation •Customer card lost New card is issued with the data already available with the Bank •Weekly reconciliation between Bank’s account and BC account. Cash management • BC maintains main account with bank - Provides cash to each BCA within the limit - Cash held with the BCA is insured for loss and fidelity -BCA to remit the net amount and the data to Bank atleast once in 48 hours -HHT application will not permit further transaction without sync with TSP server 14 Particulars As on March2011 No Frill accounts opened (lacs) Amount in Rs.(lacs) 73.33 100342 Out of above -ICT based accounts ( lacs) -Under Brick & Mortar model (Branch based) (lacs) 40.89 32.44 Credit Based FI •Accounts •Amount (in lacs) 18328 5380.92 No. FI Back Offices 08 No. of FI SOLs 991 FI Technology Providers 10 Total no. of correspondent (NGOs, sec 25 co. FTC & other bodies) 21 Business Correspondent Agents 2965 Business Facilitators 1633 Farmers’ Training Centers 9 15 Major Financial Inclusion Projects Projects Number States Projects in Rural Area 28 Bihar, Rajasthan, HP, Uttarakhand, UP, Punjab, Jharkhand, MP, Orissa, West Bengal Projects in Urban Area 06 Punjab, Delhi, J&K, Chandigarh, Bihar NREGA/Social Security 05 AP, Haryana, UP, Chattisgarh Total ( ICT projects) 39 14 STATES (Indo Gangetic Plain) + Andhra Pradesh Project ‘BHAMASHAH’ 01 Rajasthan Credit Driven Projects ( Non ICT ) 06 UP, Chhatisgarh, North East, Bihar , Karnataka GRAND TOTAL 46 17 States (14 in Indo Gangetic Plain + AP, Karnataka and North East) 16 Reach under Financial Inclusion Particulars Number of villages with Population > 2000 through Bank Branches (Brick & Mortar Model) As on March 2011 2013 Number of villages with population > 2000 through BC Model (ICT model) 2186 Number of villages with population < 2000 through BC Model (ICT model) 3219 No. of NO Frill a/cs opened in 2010-11 in villages with population over 2000. 10.09 lac 17 PNB’s Jana Mitra Rickshaw Project Making Rickshaw Pullers Rickshaw Owners •Launched in Varanasi on Feb 2, 2008 in association with Centre for Rural Development •Extended to Agra, Allahabad, Kanpur, Meerut, Lucknow, Patna •Targets to cover 10000 rickshaw pullers • 9503 Rickshaws are financed under Rickshaw Projects with outstanding credit of Rs. 9.88 Crore (as on June 2011) 18 Financing Farmers in Bulandsahar in Collaboration with Mother Dairy •ICT Based Financial Inclusion with Credit Driven Project •Farmers supply milk to Mother Dairy and get fair price •No dependency on local milk vendors •Mother Dairy pays back through the accounts (smart card based) on weekly basis •BC agent makes payment to the farmers through smart card •Farmers get loan for milch cattle at affordable interest rate •More than 30000 farmers have been covered under this project 19 Credit Driven FI Projects in PNB (Data as on June 2011) • Financing to Farmers in North East through KCC through BC model. •5439 accounts are opened (tie up with KAKSSUS NGO) with outstanding credit of Rs. 26.99 crore • Financing to Self Help Groups in Rajanandgaon through BC model. • Financing to vegetable growers in Tineri & Punpun (Patna) •741 accounts are opened with outstanding credit of Rs. 2.42 Crore •More than 56000 GCCs issued with outstanding credit of Rs. 1.16 crore •More than 16.53 lac KCCs issued with outstanding credit of Rs. 134.46 crore •2322 accounts are opened under Weaver’s Project, Varanasi with outstanding credit of Rs. 11.61 Crore •190 accounts are financed to Common Service Centres with outstanding credit of Rs. 1.95 Crore 20 Capacity Building Officials of the bank have been trained under the “Train the Trainer” programme of (Indian Institute of Banking & Finance) IIBF A. Training to BC agents •On-locations training programmes are organized for BC agents •Bank provides training on its products & processes. •Technology related training is provided by concerned TSP B. Financial Literacy Counseling Centre (FLCC) 58 FLCCs have been established for spreading Financial Literacy Rural Libraries have been setup for dissemination of Information in remote rural areas. C. 9 Farmer Training Centres (FTCs) have been established under PNB Farmers Welfare Trust to provide customized training to local farmers. D. PNB has established 30 Rural Self Employment Training Institute (RSETI) for organizing employment generation oriented training 21 programmes. The Way Forward • With the improvement of connectivity, transaction model to be implemented. online • Web based kiosk/ mobile based model to be made available at villages • Introduction of combo card (smart chip with magnetic stripe) to enable payments through ATMs. • Integration with UIDAI project. 22 Replicability of the project FI@PNB • The PNB offline FI model can be replicated to offer doorstep banking services in remote rural areas where last mile connectivity is still a challenge. • Credit delivery through smart card model can be implemented to reach a larger section of the society. • FI model will help in minimizing the transaction cost. • This model can be integrated with RSBY, PDS, payment of social security benefits and wages to the MGNREGA. 23 Third Party Assessment/Awards • E-Governance ‘GOLD Award 2010’ under award category “Innovative use of ICT by PSUs for Customer’s Benefits” by Government of India. • Special Technology Award for Financial Inclusion from IDRBT for the years 2008-09 & 2009-10 respectively. • SKOTCH AWARD for the year 2010. 24 Thanks – TEAM IT PNB 25