TOOLS OF TQM
advertisement

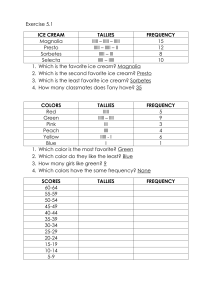
TOOLS OF TQM Abdulla Jassim Abdulla INTRODUCTION Data-Driven Methodology Data generated by processes Statistical interpretation A B C 1 21 17 54 2 16 41 25 3 27 13 25 4 32 21 23 5 43 23 12 Seasonal variations 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 New Technology THE ‘SEVEN SIMPLE TOOLS’ Flowcharts Cause and Effect (Ishikawa / fishbone) Diagrams Check sheets Pareto Charts Histograms Run Charts and Control Charts Scatter plots and Correlation Analysis FLOWCHARTS Remember system theory: (Input, Output, customer supplier and their interactions). Divide complex processes into simple sub-processes. A Qualitative tools Patient Transport Process Example Request made Doctor determines patient needs X-ray Ward contacts dispatcher Log & prioritize request Information taken & request is logged Request prioritized Dispatch transport Required equipment is found Transport is dispatched Take patient to X-ray Transporter arrives on ward Patient transferred from bed Patient taken to X-ray Types of Flowcharts LAYOUT FLOWCHART Example Staff movement DATA FLOW DIAGRAMS leave approval process ISHIKAWA DIAGRAMS Also known as Fishbone or Cause-andEffect Diagrams Non-quantitative tools (Qualitative) Sometimes called the 5M Diagram (Men, Machine, Materials, Measurements and methods) ISHIKAWA DIAGRAM Cause-and-Effect Diagram Measurements Materials Men Effect Environment Methods Machines CHECKSHEETS Central tool for Quality Assurance programs Specially useful for operational procedures Could be derived from the flowchart and fishbone diagrams Example check sheets Patient Transport Problem Sheet Area: Ward 3b Period: June 1996 Type Tally Subtotal Equipment broken IIIII 5 Patient not ready IIIII II 7 Not enough staff III 3 Patient having another exam etc. IIIII IIIII II 12