biotechusage-of-autoclave-of-sterilizationwkngtgigynendb
advertisement

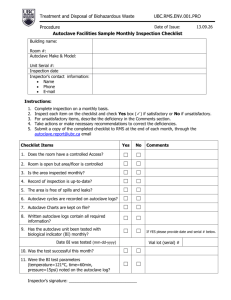
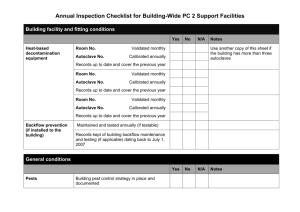
The Usage Of Autoclave For Sterilization I. Vocabulary Words Sterilization the removal of all microorganisms and other pathogens from an object or surface by treating it with chemicals or subjecting it to high heat or radiation. Sterilization also refers to procedures that result in infertility Autoclave a strong, heated container used for chemical reactions and other processes using high pressures and temperatures, e.g., steam sterilization. Charles Chamberland inventor of autoclave and a French microbiologist Apparatus non-machines used in a Lab. It may be a beaker, conical flask, test tube etc… Equipment is a machine which runs on electricity like disintegrator machine, friabalator, stirrer etc... II. Objectives Objectives • To share all the ideas of using the Autoclave Sterilizer • To give information and facts on how the autoclave sterilizer works • To completely view and teach all of the safe ways in performing it III. Discussion: Subtopics I. Autoclaves 3 Safety Guidelines II. Four (4) Basic Parts of an Autoclave III. Autoclave (Further Explanation) IV. Autoclaving Procedures 1. Autoclaves 3 Safety Guidelines Autoclave Safety Guidelines • an autoclave is a common piece of equipment, used in laboratories for the purpose of sterilization of equipment and supplies, which poses several hazards to the user Autoclave Safety Guidelines • Burn Hazards - pressurized heat on steam - be cautious of hot surfaces when loading and unloading autoclave - recently autoclaved contents inside will be extremely hot - make sure to keep face, body and hands away from escaping heat and steam when opening the door of an autoclave Autoclave Safety Guidelines • Explosion Hazards - failure of door seals while in operation - explosions can occur when the seal of the door malfunctions or when autoclave is loaded improperly - pressure and heat in chamber will escape rapidly potentially causing serious injury Autoclave Safety Guidelines • Heavy Lifting Hazards - loading and unloading of autoclave - ask for assistance if the contents you are loading or unloading is heavy - use autoclave rack cart to move removable rack when applicable Preparation of Items for Autoclaving • in preparing items for autoclaving, containers should be unsealed and articles should be wrapped in materials that allow steam penetration • it is more efficient and safer to run two separate, uncrowded loads than a crowded one Importance • moist heat in the form of pressurized steam is regarded as the most dependable method for the destruction of all forms of life, including bacterial spores • reliable sterilization with moist heat requires temperatures above that of boiling water Principle of Autoclaving • a basic principle of chemistry is that when the pressure of a gas increases, the temperature of the gas increase proportionally • in this way steam is a gas, increasing its pressure in a closed system increases its temperature • as the water molecules in steam become more energized, their penetration increases substantially 2. Four (4) Basic Parts of an Autoclave Four (4) Basic Parts of an Autoclave Chamber Control Panel Water Intake Machinery Autoclave Parts 3. Autoclave (Further Explanation) Auto Clave’s Tape • Autoclave tape is an adhesive tape used in autoclaving (heating under high pressure with steam to sterilize) to indicate whether a specific temperature has been reached. Autoclave’s Different Pattern of High Heat • Autoclaves often have an additional drying cycle in which hot air is drawn through the chamber to dry materials after sterilization. Autoclave’s Different Pattern of High Heat: Types • The liquids runs longer than the other two types, but uses lower temperatures to minimize evaporation of the liquids being sterilized. Autoclave’s Different Pattern of High Heat: Types • The dry goods with vacuum run moves steam and heat into the deepest part of large bags or bundles of materials and produce the best conditions for killing persistent organisms. Autoclave’s Different Pattern of High Heat: Types • The dry goods without vacuum run simply pressurizes the chamber with steam for the duration of the cycle and then returns to normal. Autoclave’s Different Pattern of High Heat • Autoclaves generate extreme heat and high pressures, users should understand and respect the hazards these create. 4. Autoclaving Procedures Container Selection • Polypropylene bags • Polypropylene containers/ pans • Stainless steel containers and pans Preparation and Loading of Materials - Fill liquid containers only half full. - Loosen caps or use vented closures. - Always put bags of biological waste into pans to catch spills. - Position biohazard bags on their sides, with the bag neck taped loosely. - Leave space between items to allow steam circulation. - Household dishpans melt in the autoclave. Use autoclavable polypropylene or stainless steel pans. Cycle Selection - Use liquid cycle (slow exhaust) when autoclaving liquids, to prevent contents from boiling over. - Select fast exhaust cycle for glassware. - Use fast exhaust and dry cycle for wrapped items. Time Selection - Take into account the size of the articles to be autoclaved. A 2-liter flask containing 1 liter of liquid takes longer to sterilize than four 500 mL flasks each containing 250 mL of liquid. - Material with a high insulating capacity (animal bedding, high sided polypropylene containers) increases the time needed for the load to reach sterilizing temperatures. - Autoclave bags containing biological waste should be autoclaved for 50 minutes to assure decontamination. Removing the Load - Check that the chamber pressure is zero. - Wear lab coat, eye protection, heat insulating gloves, and closed-toe shoes. - Stand behind door when opening it. - Slowly open door only a crack. Beware of rush of steam. - After the slow exhaust cycle, open autoclave door and allow liquids to cool for 20 minutes before removing. IV. Summary Summary • Autoclaves are used in many areas to sterilize materials by high heat and pressure. Used to kill microorganisms. • Burns can result from physical contact with the autoclave structure and from contact with the steam leaving the unit. Summary • Explosive breakage of glass vessels due to temperature stresses can produce mechanical injury, cuts and burns during opening and unloading the unit. • Burns can also result from careless handling of vessels containing hot liquids. Summary • Explosive breakage of glass vessels due to temperature stresses can produce mechanical injury, cuts and burns during opening and unloading the unit. • Burns can also result from careless handling of vessels containing hot liquids. • There are safety Guideline you really must obey and it was simply distributed in 3 parts, the Burn Hazzard, the Explosion Hazzard, and the Heavy Lifting Hazzard. Summary • The 4 major or basic parts of a common autoclave is the water intake, chamber, control panel and the machinery which gives you the perfect sterilization process. • Additionally, because of the extreme conditions created inside steam autoclaves, they can easily malfunction if not carefully maintained. • Because each autoclave make / model has unique characteristics, it is imperative that you read and thoroughly understand the manufacturers operating procedures before you use an autoclave for the first time. Summary • An autoclave uses different patterns of high heat, vacuum and pressure to sterilize material. • The main types of runs are: - liquids, for any type of water-based solutions, - dry goods with vacuum, and - dry goods without vacuum V. Sources Sources • 1. Microbiology, Jacquelyn Black, Prentice Hall,1993 pg 334 • 2. "Chronological reference marks - Charles Chamberland (1851–1908)". Pasteur Institute. Archived from the original on 19 December 2006. Retrieved 2007-01-19. • 3. Hugo WB (July 1991). "A brief history of heat and chemical preservation and disinfection". J. Appl. Bacteriol. 71 (1): 9–18. doi:10.1111/j.13652672.1991.tb04657.x. PMID 1894581. • 4. "Online Etymology Dictionary". Etymonline.com. Retrieved 2012-06-04. Sources • 5. "Sterilization Cycles". Consolidated Machine Corporation. Retrieved 2009-06-30. • 6. Seymour Stanton Block (2001). Disinfection, Sterilization, and Preservation. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-683-30740-5. Retrieved 19 January 2013. • 7. R. B. Simpson (28 February 2002). Rubber Basics. iSmithersRapra Publishing. p. 161. ISBN 978-1-85957-307-5. Retrieved 19 January 2013. VI. Short Quiz (1-10) 1. What is a strong, heated container used for chemical reactions and other processes using high pressures and temperatures? a. b. c. d. Apparatus Autoclave Sterilizer Sterilization Process using Autoclave Sterilized Apparatus 2. The process that destroys or removes all microorganisms and microbial forms including bacterial endospores on inanimate objects is called ___________. a. b. c. d. Sterilization Disinfection Degermination Sanitation 3. Which of the following is not a factor that affects germicidal activity? a. The material being treated b. The length of exposure c. The microorganism being raced d. All of these are factors 4. Sterilization is achieve by _______________. a. b. c. d. Flash pasteurization Boiling water Steam autoclave Hot Water 5. It is a reservoir for the small autoclave and a hose for a bigger autoclave where the water that is needed by the machine intakes. a. b. c. d. Control Center Water Intake Machinery Chamber 6. ______________________ indicators can be found on medical packaging and autoclave tape, and these change color once the correct conditions have been met. a. Carbon b. Chemical substance c. Oxygen d. Chemistry 7. Which of the following Safety Guidelines is loading and unloading of autoclave perform? a. b. c. d. Burn Hazzard Heavy Lifting Hazzard Explosion Hazzard All answers are correct except for B. 8. There are__________________, chemical, and biological indicators that can be used to ensure an autoclave reaches the correct temperature for the correct amount of time. a. b. c. d. Particle Physics Physics Universe Quantum Mechanics 9. Who is the Inventor of the Autoclave Sterilizer? a. b. c. d. Charles Chaimberland Charles Chamberland Charles Clamberland Charles Chumberland 10. Which Autoclave’s pattern of high heat runs the longest? a. Dry goods without vacuum b. Liquid c. Dry Goods d. All answers are correct except for letter A. Answer Key 1. What is a strong, heated container used for chemical reactions and other processes using high pressures and temperatures? a. b. c. d. Apparatus Autoclave Sterilizer Sterilization Process using Autoclave Sterilized Apparatus 2. The process that destroys or removes all microorganisms and microbial forms including bacterial endospores on inanimate objects is called ___________. a. b. c. d. Sterilization Disinfection Degermination Sanitation 3. Which of the following is not a factor that affects germicidal activity? a. The material being treated b. The length of exposure c. The microorganism being raced d. All of these are factors 4. Sterilization is achieve by _______________. a. b. c. d. Flash pasteurization Boiling water Steam autoclave Hot Water 5. It is a reservoir for the small autoclave and a hose for a bigger autoclave where the water that is needed by the machine intakes. a. b. c. d. Control Center Water Intake Machinery Chamber 6. ______________________ indicators can be found on medical packaging and autoclave tape, and these change color once the correct conditions have been met. a. Carbon b. Chemical substance c. Oxygen d. Chemistry 7. Which of the following Safety Guidelines is loading and unloading of autoclave perform? a. b. c. d. Burn Hazard Heavy Lifting Hazard Explosion Hazard All answers are correct except for B. 8. There are__________________, chemical, and biological indicators that can be used to ensure an autoclave reaches the correct temperature for the correct amount of time. a. b. c. d. Particle Physics Physics Universe Quantum Mechanics 9. Who is the Inventor of the Autoclave Sterilizer? a. b. c. d. Charles Chaimberland Charles Chamberland Charles Clamberland Charles Chumberland 10. Which Autoclave’s pattern of high heat runs the longest? a. Dry goods without vacuum b. Liquid c. Dry Goods d. All answers are correct except for letter A. The Usage of Autoclave for Sterilization • Submitted To: Mrs. Maria Victoria A. Cello • Submitted By: 8-Linnaeus, Group 5 Reported by: Group 5 Group Members: Lean Kate Peña [Leader] John Nover Alama [Assistant Leader] Bernice Racca Jerald Buniag Kimberly Flores Limitations and Disadvantages of Autoclave • the autoclave also has certain limitations • heat requires extra time to reach the center of solid materials, such as canned meats, because such materials do not develop the efficient heat-distributing convection currents that occur in liquids