Supporting Information Li 2 FeSiO 4 Nanorod as High Stability
advertisement
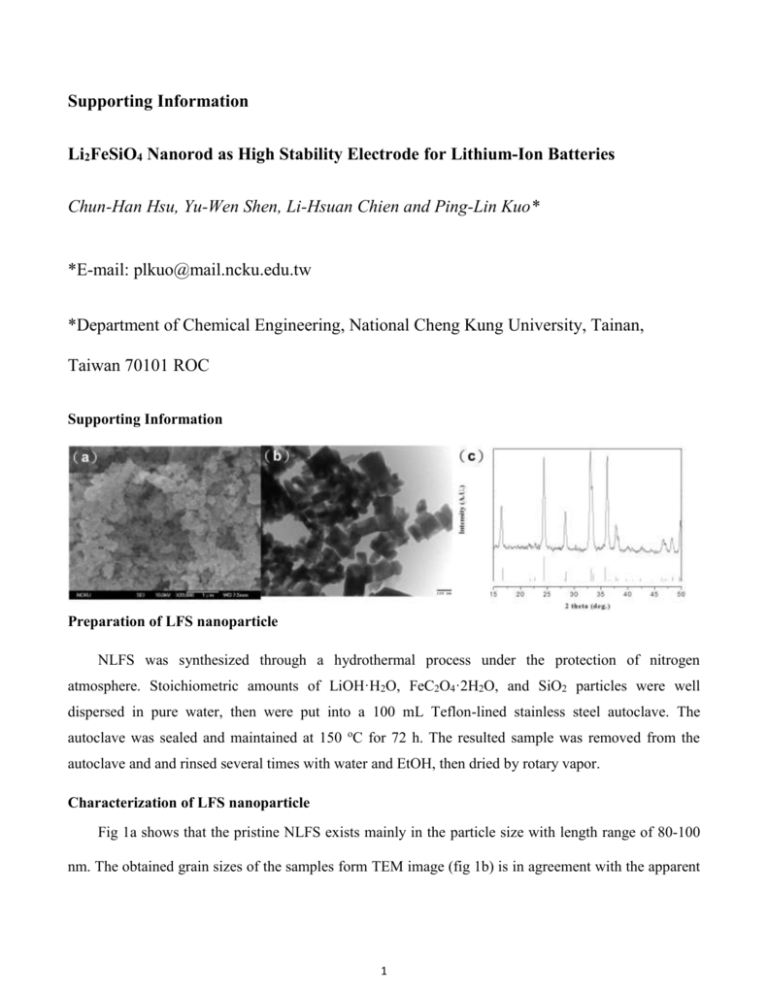
Supporting Information Li2FeSiO4 Nanorod as High Stability Electrode for Lithium-Ion Batteries Chun-Han Hsu, Yu-Wen Shen, Li-Hsuan Chien and Ping-Lin Kuo* *E-mail: plkuo@mail.ncku.edu.tw *Department of Chemical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan 70101 ROC Supporting Information Preparation of LFS nanoparticle NLFS was synthesized through a hydrothermal process under the protection of nitrogen atmosphere. Stoichiometric amounts of LiOH·H2O, FeC2O4·2H2O, and SiO2 particles were well dispersed in pure water, then were put into a 100 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave. The autoclave was sealed and maintained at 150 oC for 72 h. The resulted sample was removed from the autoclave and and rinsed several times with water and EtOH, then dried by rotary vapor. Characterization of LFS nanoparticle Fig 1a shows that the pristine NLFS exists mainly in the particle size with length range of 80-100 nm. The obtained grain sizes of the samples form TEM image (fig 1b) is in agreement with the apparent 1 sizes determined by SEM. Furthermore, Fig. 1c shows the X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) patterns of the NLFS composites. The main diffraction peaks of all samples can be attributed to the standard orthorhombic Li2FeSiO4 (ICDD #00-040-1499, space group Pnmb), indicating that the obtained samples are of high purity and exhibit high crystallinity. 2