The ADEPT Digital Library Architecture
advertisement

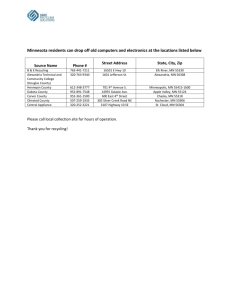
Alexandria Digital Library Project Concept-based Learning Spaces Apply domain-specific KOS principles for organizing collections/services for given applications Terence R. Smith, Marcia L. Zeng, and Alexandria Digital Library (ADL) Project Team University of California, Santa Barbara Alexandria Digital Library Project Outline 1. Viewing an example 2. Explaining the concept model 3. Discussing: why a strongly-structured model Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 2 Alexandria Digital Library Project Science learning spaces: Concept KOS Concepts of science as basic knowledge granules Sets of concepts form bases for scientific representation DL and KOS technology can support organization of science learning materials in terms of concepts – Collections of models of science concepts (knowledge base) – Collections of learning objects (LO) cataloged with concepts – Collections of instructional materials organized by concepts Organize learning materials as “trajectory through concept space” Lecture, lab, self-paced materials Services for creating/editing/displaying such materials Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 3 Alexandria Digital Library Project Application to learning environments Application Collections created Introductory physical geography (F2002, S2003) Knowledge base (KB) of strongly structured concepts Structured lectures and labs Learning objects cataloged by ADN metadata (+ concepts) Services created For concepts – – For instructional materials – – Web-based concept input tool Graphic and text-based display tools Web-based “lecture composer” “Conceptualization” graphing tool For learning objects – Metadata input tool Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 4 Alexandria Digital Library Project Learning environment display (lecture mode) The lecture is presented on three projection screens, showing the Concept window (left) Lecture window (center) Object window (right) Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 5 Alexandria Digital Library Project Current instructional material window The left-hand frame displays the structure of the lecture The righthand frame displays the content of the lecture ADL icons (globe image) attached to a concept link to a display of concept properties in the concept window Other icons attached to a concept link to a display of concept examples in the illustration window Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 6 Alexandria Digital Library Project View of learning material by concepts Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 7 Alexandria Digital Library Project Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 8 Alexandria Digital Library Project Learning environment display (lecture mode) The lecture is presented on three projection screens, showing the Concept window (left) Lecture window (center) Object window (right) Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 9 Alexandria Digital Library Project Current instructional material window The left-hand frame displays the structure of the lecture The righthand frame displays the content of the lecture ADL icons (globe image) attached to a concept link to a display of concept properties in the concept window Other icons attached to a concept link to a display of concept examples in the illustration window Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 10 Alexandria Digital Library Project Item in concept knowledge base Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 11 Alexandria Digital Library Project Outline 1. Viewing an example 2. Explaining the concept model 3. Discussing: why a strongly-structured model Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 12 Alexandria Digital Library Project Model of science concepts Representing a concept involves more than terms Objective, information-rich, scientific representations – e.g., for concepts of heat diffusion, DNA, drainage basin, … Associated semantics – e.g., relating to measurement, recognition,… Many interrelationships – e.g., hierarchical, causative, property,… Models of science concepts Already exist for chemistry (ASA), materials (NIST),… Generalize such models for this application Structure items in concept KB using model Original design Current structure as seen from the lecture Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 13 conceptual model -framework ID Terms Preferred Nonpreferred Descriptions TypeOfConcept ClassOfPhenomena ConceptModel KnowledgeDomain HistoricalOrigins Examples Relationships FieldsOfStudy Topics classification of concepts type of concept observations abstract syntactic (linguistic) measures logical analysis mathematical examples identification/ characterization topics representation methodological understanding models application questions/answers communication problems/solutions measurable concrete concepts hypotheses/evaluations recognizable predictions/tests interpreted abstract statements/deviations applications/evaluations facts/validations classification of phenomena class of phenomena object material process form event state …… conceptual model–relationships Relationships CotainedIn SetMembership Hierarchical ScientificUse Partitive ExplicitFull HasRepresentation ExplicitPartial ImplicitFull PartiallyRepresents Defining Operation AbstractSyntactic Property HasProperty Methodological PropertyOf CoRelated CausedBy other HasParts Applications Representation Causal Contains IsPartOf Causes ImplicitPartial Alexandria Digital Library Project Current Model of science concepts ID TYPE and FACET CONTEXT (KNOWLEDGE DOMAIN) TERM(S) (P/NP) DESCRIPTION(S) HISTORICAL ORIGIN(S) EXAMPLE(S) HIERARCHICAL RELATIONS DEFINING OPERATIONS SCIENTIFIC REPRESENTATION(S) As displayed in the lecture mode – Scientific classifications – Data/Graphical/Mathematical/Computational reps PROPERTIES CAUSAL RELATIONS CO-RELATIONS APPLICATION(S) Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 18 Apply KOS principles to domain-specific applications ADL Model ID TYPE and FACET DOMAIN CONTEXT TERM(S) (P/NP) DESCRIPTION(S) HISTORICAL ORIGIN(S) EXAMPLE(S) HIERARCHICAL RELATIONS DEFINING OPERATIONS CONCEPTUALIZATION SCIENTIFIC REPRESENTATION(S) Traditional KOS Faceted analysis Classification Codes Descriptors, entry terms Scope notes Instances Hierarchical relations (BT/NT) Concept map, semantic network Scientific classifications Data/Graphical/Mathema tical/Computational reps PROPERTIES CAUSAL RELATIONS CO-RELATIONS APPLICATION(S) Other Semantic Tools Slot-instance, attribute-value Associated relations (RT/RT) Associated relations (RT/RT) Associated relations (RT/RT) Alexandria Digital Library Project Outline 1. Viewing an example 2. Explaining the concept model 3. Discussing: why a strongly-structured model Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 20 Types of structured models 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Term lists KOS Classification and categorization schemes Relationship groups Metadata content standards General knowledge representation languages They typically take the form of structured sets of terms representing concepts and their interrelationships. Graphical representations of concepts and interrelationships derived from such KOS typically take the simple form of a set of named nodes connected by named links. Alexandria Digital Library Project Values of these models They support, for example, access to traditional knowledge containers, such as texts and journals, in which term-based representations of concepts occur. They are also of value in supporting high-level graphical views (or “concept maps”) of the interrelationships among concepts. Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 22 Alexandria Digital Library Project Limits of these models They could not provide deep organization of, and access to, scientific knowledge that is important for learning. Accessing knowledge is largely restricted to the traditional information containers. They cannot easily support access to, or integration of, knowledge concerning many of the attributes of concepts that make them useful in SME modeling activities. Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 23 A Taxonomy of KOS Relationship Groups: Classification & Categorization: Term Lists: Natural language Ontologies Semantic networks Thesauri Classification schemes Taxonomies Categorization schemes Subject Headings Authority Files Glossaries/Dictionaries Gazetteers Controlled language Alexandria Digital Library Project Toward Strongly-Structured Models These models focus on such attributes as the objective representations, operational semantics, use, and interrelationships of concepts, all of which play important roles in constructing representations of phenomena that further understanding of MSE domains of knowledge. Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 25 Alexandria Digital Library Project Toward Strongly-Structured Models Taxonomy + metadata (or attribute-value pairs) Ontology for knowledge based systems Taxonomy and thesaurus + domain-specific markup languages Specialized models for learning scientific concepts Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 26 ADLP Activities Alexandria Digital Library Project EDUCATIONAL APPLICATIONS • knowledgebase and lecture composing, visualization, and presentation tools • physical geography concept space and learning object collections • applications to undergraduate education • educational evaluation • learning services and DL integration • digital classrooms • metadata content standards • learning objects • computational models USER INTERFACES • reusable user interface components • contextual maps, footprint creation • KOS navigation • lightweight GIS functionality • Digital Earth visualization • image processing • query-by-content, classification • spatial extent determination GEOREFERENCED DIGITAL LIBRARIES • • • • • • • distributed georeferenced DL services NSDL core infrastructure data environment (e.g., GIS) integration hardware acceleration for spatial data collaborative tools Z39.50 support ingest and workflow systems KNOWLEDGE ORGANIZATION • gazetteers: research and community • gazetteer content standard • web service protocols for gazetteers, thesauri, and other KOS • ADL gazetteer • thesauri for feature and object types • duplicate detection for gazetteers • textual-geospatial integration services OPERATIONAL APPLICATIONS • • • • georeferenced DL tutorials distributable software packages operational libraries: UCSB library, ... outreach; federated nodes Smith et al • NKOS • May 31, 2003 27