Curriculum Overview
advertisement
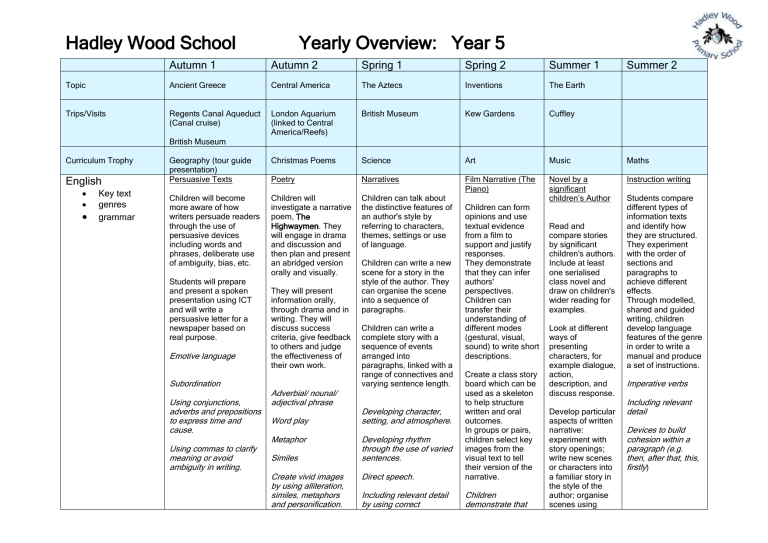
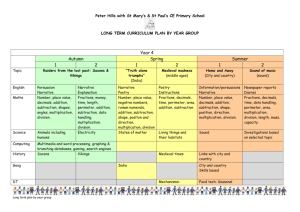
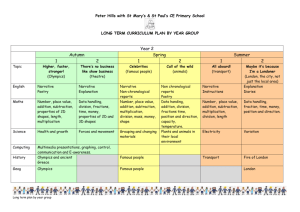
Hadley Wood School Yearly Overview: Year 5 Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Topic Ancient Greece Central America The Aztecs Inventions The Earth Trips/Visits Regents Canal Aqueduct (Canal cruise) London Aquarium (linked to Central America/Reefs) British Museum Kew Gardens Cuffley Geography (tour guide presentation) Persuasive Texts Christmas Poems Science Art Music Maths Poetry Narratives Film Narrative (The Piano) Instruction writing Children will become more aware of how writers persuade readers through the use of persuasive devices including words and phrases, deliberate use of ambiguity, bias, etc. Children will investigate a narrative poem, The Highwaymen. They will engage in drama and discussion and then plan and present an abridged version orally and visually. Children can talk about the distinctive features of an author's style by referring to characters, themes, settings or use of language. Novel by a significant children’s Author British Museum Curriculum Trophy English Key text genres grammar Students will prepare and present a spoken presentation using ICT and will write a persuasive letter for a newspaper based on real purpose. Emotive language Subordination Using conjunctions, adverbs and prepositions to express time and cause. Using commas to clarify meaning or avoid ambiguity in writing. They will present information orally, through drama and in writing. They will discuss success criteria, give feedback to others and judge the effectiveness of their own work. Adverbial/ nounal/ adjectival phrase Word play Metaphor Similes Create vivid images by using alliteration, similes, metaphors and personification. Children can write a new scene for a story in the style of the author. They can organise the scene into a sequence of paragraphs. Children can write a complete story with a sequence of events arranged into paragraphs, linked with a range of connectives and varying sentence length. Children can form opinions and use textual evidence from a film to support and justify responses. They demonstrate that they can infer authors' perspectives. Children can transfer their understanding of different modes (gestural, visual, sound) to write short descriptions. Direct speech. Create a class story board which can be used as a skeleton to help structure written and oral outcomes. In groups or pairs, children select key images from the visual text to tell their version of the narrative. Including relevant detail by using correct Children demonstrate that Developing character, setting, and atmosphere. Developing rhythm through the use of varied sentences. Read and compare stories by significant children's authors. Include at least one serialised class novel and draw on children's wider reading for examples. Look at different ways of presenting characters, for example dialogue, action, description, and discuss response. Develop particular aspects of written narrative: experiment with story openings; write new scenes or characters into a familiar story in the style of the author; organise scenes using Students compare different types of information texts and identify how they are structured. They experiment with the order of sections and paragraphs to achieve different effects. Through modelled, shared and guided writing, children develop language features of the genre in order to write a manual and produce a set of instructions. Imperative verbs Including relevant detail Devices to build cohesion within a paragraph (e.g. then, after that, this, firstly) Hadley Wood School Yearly Overview: Year 5 punctuation Plan, draft, write, edit and improve. they can use speech punctuation accurately. Write cohesively at length. Use a mixture of simple, compound and complex sentences. paragraphs effectively. Write paragraphs that make sense if read alone. Use the techniques that authors use to create characters, settings and plots. Interweave descriptions of characters, settings and atmosphere with dialogue. Maths number concept Number- Place Value Number- Place Value Number - Place value Number – Addition and subtraction Number - Fractions and decimals Number - Addition and Subtraction Number – Addition and subtraction Number - Fractions and decimals Number - Multiplication & Division Number - Multiplication and Division Measurement – Conversion Number - Multiplication and Division Number - Multiplication and Division Measurement - Time Statistics Geometry - Angles Geometry – Position and Direction Geometry – 2D shape Science knowledge skills Earth & Space Forces Knowledge: Knowledge: Movement of moon relative to Earth Gravity/falling objects/parachutes Number - Place value Number - Place value Number - Place Value Number - Fractions and decimals Number - Addition and Subtraction Number - Addition and Subtraction Number – Fractions and decimals Number Multiplication and Division Number Multiplication and Division Measurement – Money, perimeter and area Measurement Time Measurement – Conversion Measurement Perimeter and Area Statistics Living things and their habitats Properties and changes of material Life cycles Properties of materials – comparing and Reproduction of animals Geometry – 2D shapes and angles Geometry – 2D shapes and position and movement Properties and changes of material Separation – filtering, sieving, Measurement Time Statistics Animals (including humans) Timeline to indicate states in growth and development of Hadley Wood School Day and Night Movement of sun across sky Movement of planets in the solar system Yearly Overview: Year 5 and plants. sorting evaporation humans Growing new plants from different part of parent plant Conductors and insulators Reversible or irreversible changes Changes during puberty – 3 lessons CWP How chemical changes have an impact on our lives. Researching the gestation periods of other animals and comparing them with humans: by finding out and recording the lengths and mass of a baby as it grows. Air resistance Water resistance Friction Mechanisms (levers, pulleys, gears) Scientists (ie. Issac Newton) David Attenborough/Jane Goodall States of matter – solids, liquids, gases. Changing state Scientists (Spencer Silver and Ruth Benerito) History knowledge skills Ancient Greece The Aztecs This unit covers the history of Greece from after the defeat of the Persians until the defeat of Athens by Sparta. Children will learn about advances in democracy, art, literature, and architecture developed within Athens. Children to find out about the social, cultural and religious beliefs of Aztec society, as well as the everyday life in Aztec civilisation, including children. -The golden age of Athens. -The Peloponnesian War -Alexander the Great Children explore some of the reasons for rise and fall of the Aztec civilisation and to note significant places on maps and what is there today. -Contributions of the Greeks Students consider aspects of wars and warfare in Aztec civilisation. Use artefacts, pictures, stories, online sources and databases to find out about the past. How can we learn from artefacts – what can they tell us about the Aztec way of life? Show an understanding of concepts such as civilisation, democracy, parliament and war and Comparison of Ancient Greece to The Aztecs Settlers/Invaders/ Kingdoms (Normans) Children begin to understand the terms ‘invade’ and ‘settle’ in the context of this topic. To understand the features of a good settlement. Who were the Normans? The Norman invasion of England. The Battle of Stamford Bridge. The Battle of Hastings. - Use an artefact to tell me things about the past Hadley Wood School Yearly Overview: Year 5 peace. Geography knowledge skills ***Continuation of Hadley Wood Meadow Project with Rod Armstrong throughout the year. - Use more than one source of evidence for historical enquiry in order to gain a more accurate understanding of history. Central America Countries and cities in Central America Coral Reefs The Panama Canal Deforestation in El Salvador - Name and locate the countries of Central America and identify their main physical and human characteristics. - Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. - Describe and understand key aspects of: • Physical geography, including the rainforests and coral reefs. mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes and the Earth Zones (Climate) Polar Zones Deserts Tropics - Reading and plotting coordinates - Map skills Identify and describe the geographical significance of latitude, longitude, equator, Northern and southern hemisphere. - Animal adaptation (identify the characteristics of animals in different climate zones) - Understand the reasons for geographical similarities and differences between countries. Hadley Wood School Yearly Overview: Year 5 water cycle • Human geography, including: settlements, land use, economic activity including trade (Panama Canal) Art knowledge skills Henri Rousseau inspired Art (Rainforests) Pupils use Henri Rousseau's 'Surprise - Tiger in a Tropical Storm' as a stimulus for them to then create their own version of the painting as a 3D picture. - Collect information, sketches and resources and present ideas imaginatively in a sketch book. - Create a colour palette based upon colours observed in the natural or built world. - Use the qualities of watercolour and acrylic paints to create visually interesting pieces. - Combine colours, tones and tints to enhance the mood of a piece. Mosaics/Sculpture Children research symbolic relationships between Aztec mosaic art and their connection to the land. What could each colour represent (e.g. turquoise may represent water and fertility). Student s sculpture an Aztec mask out of air-dry clay. They then paint tiles with varying shades of their chosen colour before breaking them into pieces and gluing them onto the mask. - Use clay and other mouldable materials. - Add materials to provide interesting detail. Hadley Wood School Yearly Overview: Year 5 - Develop a personal style of painting, drawing upon ideas from other artists. Design Tech knowledge skills Designing Aqueducts Inventions Discuss how Ancient Greeks developed elaborate means by which to transport water. Students are given the initial challenge of transporting water from one side of a valley to another. Discuss the materials we have to work with, the time frame. What do they need & how can they attach parts, etc (balsa wood and foil). Discuss how they plan to carry the water without it leaking – different methods of waterproofing. Discuss angles. Water shouldn’t rush nor collect. Designs must be to scale before construction commences. Identify some of the great designers in all of the areas of study (including pioneers in horticultural techniques) to generate ideas for designs. - Design with purpose by identifying opportunities to design. - Refine work and techniques as work progresses, continually evaluating the product design. Students identify a ‘need’ in the market and design a new product. Improve upon existing designs, giving reasons for choices. Design with the user in mind, motivated by the service a product will offer (rather than simply for profit). Board Game Design (Link with instruction writing) Students work in groups to create a board game based on a theme from their favourite topic throughout the year. Design purposeful, functional, appealing products for themselves and other users based on design criteria. Generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through talking, drawing, templates, mockups Hadley Wood School PE knowledge skills Net / wall x 2 Develop individual shots ------------------Dance or swimming x 1 Story from another culture Yearly Overview: Year 5 Invasion x 2 Support play and formations ------------------Gym or swimming x1 Flight Gym x 2 Bridges Core Task -----------------Outdoor Ed or swimming x1 Develop orienteering and problem-solving skills. Working as a team Dance X 2 Tudors or Charleston Core Task ------------------Invasion or swimming x1 Shooting and keeping Athletics x 2 Set targets & improve performance in running, jumping and throwing activities. Australian Rules Football Rules: Correct disposal, marking, scoring Handballing, kicking (drop punt) ---------------------Striking/Fielding or swimming x 1 Role of bowler, wicket keeper, backstop, fielder and batter Computing E-Safety Use technology safely. Understand the dangers of making friends online. As a class students communicate with an online buddy from an Australian school. They will be required to describe and draw a picture of what they imagine the class buddy to be like. Researching Information E-Safety Animation Animation Create a brochure or poster, linked to topic work that uses internet based research. Children need to recognise that multiple sources are needed and that adding ‘KS2’ or ‘Kids’ to a search will help find appropriate data. Communication and collaboration in the wider world. Use output/model to animate physical models. Use output/model to animate physical models. Children create and contribute weekly to an individual blog. They show an understanding of how web pages are built and how to maintain them. Children can write a program e.g. Scratch to create a computer game or Flow go. Children use animation software to portray a narrative. Be aware of the need to check information against different websites. Use search terms to increase likelihood of finding suitable information. Independently verify Students create a storyboard to develop an animation narrative. Children can write a program e.g. Scratch to create a computer game or Flow go. Hadley Wood School Yearly Overview: Year 5 and use information from a web page. Latin Music Music knowledge skills Students explore the characteristics of different genres of Latin music such as salsa, cumbia, mariachi, reggae, calypso. They use percussion to add layers/depths to a variety of songs. Understand layers of sounds and discuss their effect on mood and feelings. Modern British Music (50’s – 90’s) Students analyse a range of British musicians throughout the 50’s, 60’s, 70’s 80’s and 90’s. Begin to develop an understanding of contemporary music history. Rewrite lyrics of wellknown songs and perform live. Create songs with verses and a chorus. Develop dance that reflects the mood of a musical piece. Lyrical and Musical Analysis Production Key Stage 2 Production Students write a speech that discusses their interpreted meaning behind a song of their choice. Describe how lyrics often reflect the cultural context of music and have social meaning. Use the terms: duration, timbre, pitch, beat, tempo, texture and use of silence to describe music. • Evaluate music using musical vocabulary to identify areas of likes and dislikes. • Understand layers of sounds and discuss their effect on mood and feelings. RE knowledge skills The Buddha and his teachings The Mosque and the Muslim community Exploring Christian values in the world today Pesach School designed unit The Sikh community and the Gurdwara: What do Sikhs believe is important? Hadley Wood School PSHE/Citizenship knowledge skills Values based PSHE Preparing for year 5 – Independence and expectations Yearly Overview: Year 5 Values based PSHE Values based PSHE Values based PSHE Values based PSHE Values based PSHE