Anc. Greece - Dragonwhap
advertisement
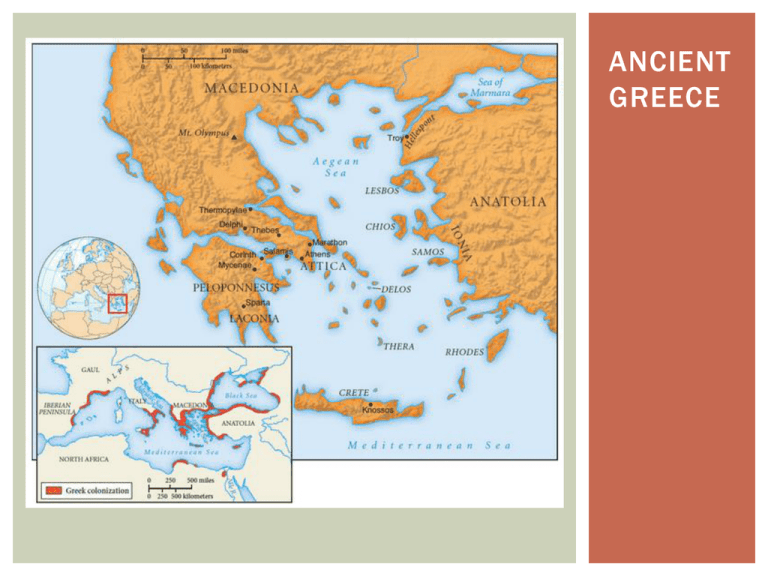
ANCIENT GREECE BEGINNINGS Ancient Greece Timeline Minoan Culture 2600-1200 BCE Mycenaean Culture 1600 -1100 BCE Geometric Period 11-8 th centuries BCE Classical Period c. 507 -323 BCE Hellenistic Period 323 -31 BCE Doric- used in the Archaic period 6th c. BCE Ionic- used in the High Classical period Corinthian- used first in city-state Corinth c. 400 BCE Columns reflect the historical periods and citystates of Anc. Greece MINOANS Located on Crete Writing system Knossos- legendary palace of King Minos and the minotaur? What do these images tell us about the Minoans? MYCENAEANS Located on the Peloponnese Home of King Agamemnon? Ties to the Iliad & Odyssey Linear B writing Citadels & palaces GEOMETRIC PERIOD Period of development for • The polis (city-state) • Trade • Colonies in Asia Minor • Single religion Rely on the works of Hesiod for information • Farming • Mythology CLASSICAL GREECE Period after Persian Wars when Athens was the leading city state Developments in art, architecture, science, math, philosophy ATHENIAN ACROPOLIS The Parthenon (447-438 BCE) Erechtheum (421-405 BCE) THIS & THAT Notable Athenians Greek Wars Draco Solon Cleisthenes Pericles Persian Wars Peloponnesian Wars Compare Athens & Sparta Think about these city -states in terms of SPICE. How are they similar? Different? http://www.schooltube.com/vide o/f8836a3434a31a97579b/HOR RIBLE-HISTORIES-Wife-SwapSpartans-and-Athenians ALEXANDER THE GREAT Son of Phillip II of Macedonia Becomes king after father’s death ~20 yrs Expands Macedonian (Greek) Empire to India Dies ~12 yrs after he becomes king w/o heir Kingdom divided between his 3 generals HELLENISTIC PERIOD Cultural period after the death of Alexander the Great Blending of Greek, Persian, and Egyptian cultures due to unification & expansion of Greek empire Includes art, architecture, science, math & philosophy Comes to an end Rome’s victory at Actium Cleopatra & Marc Antony









