File
advertisement

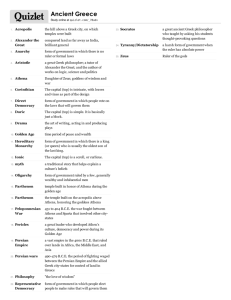
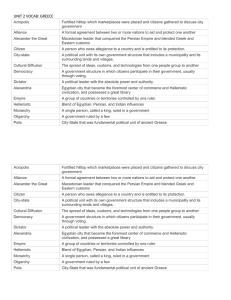
EMPIRES: AN OVERVIEW AP World History Unit 2 THE PERSIAN EMPIRE Location THE PERSIAN EMPIRE Darius the Great built the city of Persepolis. Achaemenid THE PERSIAN EMPIRE Darius the Great Divided the Persian Empire into districts called SATRAPIES (districts) Built the Royal Road system Established a complex postal system (“neither snow, nor rain, nor gloom of night” could keep them from their jobs) Standardized currency (money) Established a network of spies—the “King’s eyes and ears”…why do this? QANATS THE PERSIAN EMPIRE Alexander the Great conquered the Achaemenid Empire. He then destroyed Persepolis. He burned Zoroastrian temples and massacred magi. Alexander the Great died at the age of 33 (323 BCE). THE PERSIAN EMPIRE Parthian Empire: Situated along the Silk Roads trade route Skilled in warfare and horsemanship— archers able to shoot behind them as they rode Weakened by ongoing wars with Rome Fell to internal rebellion of feuding satraps THE PERSIAN EMPIRE Persian Society: Early steppe traditions (family/clan kinship very important) Creation of a bureaucratic class (tax collectors, record keepers, translators) Largest slave class at that point in history (POWs, debtors) Persian Economy: Long-distance trade because of road building Coined money Athens and Sparta A COMPARISON Sparta Founded by Dorian invaders Invaded neighboring city-states and enslaved peoples (helots); Farmed the estates of Spartans Military society Rulers afraid of change and outside influences Two kings with little power; Assembly had most power (male citizens over age of 30) Council of Elders: Supreme Court (28 men over age of 60) Athens Founded by descendants of Mycenaeans Constitution said that all free Athenian-born men were citizens (land ownership not needed) Slaves were 1/3 of the population Symposium: drinking session following a banquet; discussed public affairs, philosophy, and literature (upper class men and men from other city-states) A COMPARISON Spartan Women Athenian Women Expected to exercise and be strong Women stayed at home Could express political opinions but Many learned to read and write could NOT take part in government Could own property Wife Swap: Athens and Sparta Could NOT attend Olympic Games WHAT IS A “GOLDEN AGE”? This is a period in a nation’s history when much is accomplished in terms of culture and technology. Examples: art, architecture, and philosophy Greece: Best example of architecture—the Parthenon Temples were where deities could live. PHILOSOPHY Greek philosophers laid the foundation for history, political science, biology, and logic (science of reasoning). Socratic Method: Asked students questions, then argued with answers (forced students to clarify) PHILOSOPHY PHILOSOPHY PHILOSOPHY PHILOSOPHY HELLENISM Greek language and culture spread in the lands that Alexander had conquered. Greek (Hellenic) ways of life mixed with Persian culture of the Middle East to form of new culture: Hellenistic Hellenistic culture was concentrated in cities. HELLENISTIC CULTURE Largest and wealthiest city was Alexandria in Egypt Had a double harbor with a lighthouse First ever museum Large library Scientific research institute Zoo and botanical garden It was here that Jewish scholars translated the Bible into Greek HELLENISTIC CULTURE Social status of upper-class Greek women improved Could move about freely, learn how to read and write, have certain jobs Commoners’ status did not improve HELLENISTIC PHILOSOPHERS Three systems of thought: 1) Cynicism = live simply and avoid materialism 2) Epicureanism = accept the world as it is, avoid politics, and live simply 3) Stoicism = ignore emotions and follow reason HELLENISTIC ART AND LITERATURE Art often showed people in the grip of emotions Wrote comedies about everyday life SCIENCE, MEDICINE, AND MATH Performed experiments and developed new theories Eratosthenes estimated the circumference of the Earth within 1% Dissected corpses to learn about human anatomy Learned how to use drugs to relieve pain SCIENCE, MEDICINE, AND MATH Euclid organized a book about geometry Archimedes invented the compound pulley (used for lifting heavy objects) and the cylinder screw (for irrigation)