BUSINESS CYCLE
advertisement

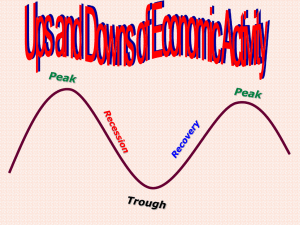
THE BUSINESS CYCLE THE TRADE CYCLE / THE ECONOMIC CYCLE The economy hits a peak – then starts to contract again fluctuations – ups and downs BOOMS – the economy works at full capacity There is a rise in: consumer demand investment production prices profits employment interest rates RECESSION - the economy works below its potential There is a decline in: investment output employment profits commodity and share prices interest rates If a downturn lasts: for more than six months = recession for a year or two = depression / slump The cycle upturn boom recovery peak downturn trough depression recession INTERNAL THEORIES (endogenous) Good times - people consume - people run up debts - - THEN ????? debts have to be paid demand decreases interest rates rise people consume less fall of demand Spend? Borrow? Save? Consumption falls if - interest rates rise - people are worried about the possibility of losing their jobs Result: no demand / no investment EXTERNAL THEORIES (exogenous) Causes outside economic activity: scientific advances / technological inventions natural disasters elections / political shocks demographic changes “Creative destruction” - - - free news on the internet threatens traditional newspapers downloading music and films threatens CD and DVD industry free internet telephone services (Skype) threaten telecommunications companies ECONOMY WORKS STRONGLY WITH: level of consumption changes in interest rates changes in people’s beliefs in the future level of wages and salaries level of investment technological, political and demographical changes GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT (GDP) goods & services produced within a country’s borders GDP = C + G + I + X C = all private consumption/consumer spending G = government spending I = investment / all the country’s business spending on capital (linked to consumption) X = total net exports (total exports minus total imports) THE BUSINESS CYCLE The regular pattern of a country’s economy periods of success – growth periods of difficulty – recession happen regularly one after another CHANGES IN ECONOMIC GROWTH 1. 2. 3. 4. peak / boom (high growth) average growth / long-run trend recession (negative growth) trough / slump INSERT THE FOLLOWING WORDS: recession, investment, boom, downturn, recovery, upturn, trough, peak, depression, consumption The business cycle is like a roller coaster: there are periods when _________________ rises, then follow periods when spending and _______________________ fall, and unemployment rises. A period during which economic activity increases is an __________ or upswing. If it lasts a long time it is called a ______________. The highest point of the business cycle is a __________, which is followed by a __________________ when the economic activity decreases. If the economy keeps contracting for more than six months, it is called a ______________ which may turn into a _______________ or a slump. The lowest point is a _____________, which is followed by a __________________, when economic activity increases again, and a new cycle begins. MATCH UP THE WORDS BELOW INTO PAIRS WITH OPPOSITE MEANINGS: supply, exogenous, spend, trough, depression, expand boom - ________ contract - __________ demand - __________ endogenous - _________ peak - _________ save - ______ MATCH UP THE WORDS BELOW INTO PAIRS WITH SIMILAR MEANINGS: production, spending, encourage, slump, upturn, expand boost - _____________ depression - _________ expenditure - _________ output - _____________ recovery - ____________ stimulate - ___________ MK: p. 114 – Vocabulary 1 p. 115 – Complete the sentences… p. 116 – Vocabulary 2 RB: p. 29 - 36