Introduction to Criminal Justice 2003
advertisement

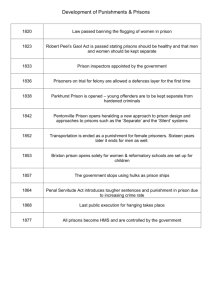
Prisons and Jails Chapter 13 Introduction to Criminal Justice 2003: A Microsoft® PowerPoint® Tool Slides prepared by: Larry Bassi SUNY Brockport © 2002 Wadsworth Publishing Co. William Penn • New, more humane system introduced forbidding torture • Imprisonment at hard labor & moderate flogging with restitution • All lands and goods were to be forfeited • Ordered houses of corrections to be built Pennsylvania Prison System Characteristics • Solitary confinement with in-cell labor • Cells large by existing standards • Modestly appointed: – bed, table, chair, bucket & bible • A place to reflect on wrong doings and improve one’s moral character - to get right with God Eastern State Penitentiary Eastern State Penitentiary in Philadelphia was considered one of the most progressive designs. It was studied and replicated throughout the world. The New York (Auburn System): An Alternative to the Pennsylvania System • Sometimes called the “tier system” • Based on fear of punishment & silent confinement • Congregate work conditions • Separate & silent conditions at night • Enforced silence was the key to discipline Reforms & Reformers: The Elmira Reformatory People like Zebulon Brockway • End corporal punishment • Education • Meaningful industries and vocational training • Focus on reintegration The Inmate Population of the United States 2,000 Total Inmates In Custody (x 1,000) 1,500 - 1,000 - 500 | 1985 | | | | | | | | | | | 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 Year Why Have Prison Populations Grown? Stricter enforcement of drug laws Increased probability of incarceration Inmates serve more time for each crime Revocation of community-based sanctions Rise in incarceration rates of women Models of Prison Organization Custodial Model Rehabilitative Model Reintegration Model State Prison Organization Basic classifications: Gender Age Security Male Super Max Max Med Min State Prison Dept. Female Juvenile Male Female Organization Chart for a Typical Correctional Facility • • • • Maximum Security Prisons Fortresses Cells / Blocks / Wings Standard uniform & dress codes Everything based on security (lock psychosis) Security Levels in Virginia Medium Security Prisons • Similar appearance to maximum security • Security is less intense • More privileges • More treatment effort Minimum Security Prisons • No armed guards or walls • House most trustworthy & least violent offenders • Dormitory style housing or small rooms • Critics complain they are “country clubs” in a prison setting Prison Mission The mission of a prison is to keep prisoners - to keep them in, keep them safe, keep them in line, keep them healthy, and keep them busy - and to do it with fairness, without undue suffering and as efficiently as possible. Two Models of Prison Management • CONTROL MODEL Inmates forced to abide by stringent prison rules infractions summarily punished. • PARTICIPATION MODEL Programs established that allowed inmates to govern some aspects of their prison lives Private Prisons Save money through: •Less labor costs •Competitive bidding •Less red-tape Arguments Against Private Prisons Punishment is sanctioned by the government, therefore it should be carried out by the government “Corner cutting” to save costs Manipulation of inmate behavior to insure that maximum sentences will be served (thereby creating its own supply and demand relationship. Purpose of Jails in America • • • • • • A branch of local government - county Pre-trial detention Detain offenders awaiting sentencing Confine misdemeanants Hold probation & parole violators Relieve prison overcrowding through contracts with the state The Characteristics of America’s Jail Population Profile of Jail Inmates 1996 Jail Conditions • Operated under concept of custodial convenience • Understaffed, underpaid • Lack of basic programs and services • Suicides common Jail Populations Jail populations have been increasing ‘84 • • • • “00 Arrests increased Increase in admissions to jail Increase in felons sentenced to local jails Increase in the number of inmates charged or convicted of drug offenses • More held in jail because of crowded prisons Consequences of High Rates of Incarceration • A significant number of criminal acts are prevented by repeat offenders • Severe social and psychological consequences for prisoners and their families • Loss of public dollars for other worthy projects