Prisions and punishments - timeline task
advertisement
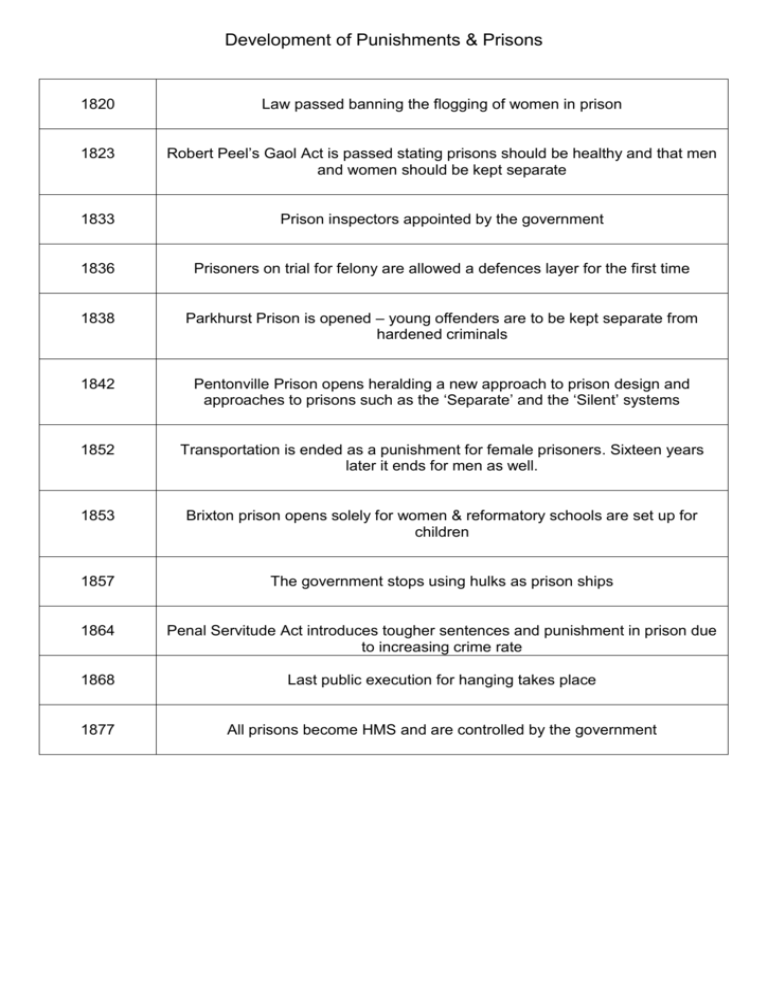
Development of Punishments & Prisons 1820 Law passed banning the flogging of women in prison 1823 Robert Peel’s Gaol Act is passed stating prisons should be healthy and that men and women should be kept separate 1833 Prison inspectors appointed by the government 1836 Prisoners on trial for felony are allowed a defences layer for the first time 1838 Parkhurst Prison is opened – young offenders are to be kept separate from hardened criminals 1842 Pentonville Prison opens heralding a new approach to prison design and approaches to prisons such as the ‘Separate’ and the ‘Silent’ systems 1852 Transportation is ended as a punishment for female prisoners. Sixteen years later it ends for men as well. 1853 Brixton prison opens solely for women & reformatory schools are set up for children 1857 The government stops using hulks as prison ships 1864 Penal Servitude Act introduces tougher sentences and punishment in prison due to increasing crime rate 1868 Last public execution for hanging takes place 1877 All prisons become HMS and are controlled by the government 1900 By now only two crimes are punishable by hanging – murder and treason 1900 First borstals introduced as an alternative for juvenile offenders 1907 Introduction of probation service to reduce prison population 1938 The age of criminal responsibility was increased to 8 and then thirty years later to 10 1953 The execution of Derek Bentley for murder of a policeman, although he did not commit the crime but was with a juvenile who did provokes outrage 1955 The execution of Ruth Ellis – the last woman in Britain to be hanged 1965 The abolition of capital punishment











