Chapter 8: Photosynthesis
advertisement

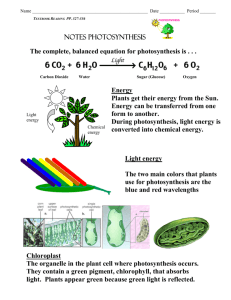
Chapter 8: Photosynthesis Big Idea: How do plants and other organisms capture energy from the Sun? 8.1 Energy and Life Why is ATP useful to cells? ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) is cellular energy. It is used by all cell types. Without the ability to obtain and use energy life would not exist. Energy is needed to grow, respond, move materials, and build new molecules ADP (has 1 less phosphate group) and is how energy is stored. Once the extra phosphate group is added the cell has enough energy to be used. ATP can easily release and store energy by breaking and re-forming the bonds between its phosphate groups. This characteristic makes ATP very useful as a basic energy source for all cells. One way cells use energy is active transport. Many membranes have sodiumpotassium pumps (Na-K), which powers movement, and keeps ions balanced on both sides of the membrane. ATP molecules are large so it is more efficient for cells to only store a small amount at a time. What happens during the process of photosynthesis? Heterotrophs vs. Autotrophs Heterotrophs are organisms that obtain food by consuming other living things (Ex: mammals, insects, amphibians, reptiles, birds, fish, decomposers). Autotrophs are organisms that make their own food (Ex: plants) In the process of photosynthesis, plants convert the energy of sunlight into chemical energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates History of Photosynthesis Many scientists have contributed to understanding how plants carry out photosynthesis. Early research focused on the overall process. Later, researchers investigated the detailed chemical pathways. 8.2 Overview of Photosynthesis What role do pigments play in photosynthesis? Pigments are light absorbing molecules that capture energy from sunlight. A plants main pigments are chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. They do not absorb green light on the light spectrum, but reflect green very well (which makes plants green). Thylakoids are sac-like photosynthetic membranes that are arranged in stacks, known as grana. This is where chlorophyll is located Stroma is the fluidportion of a chloroplast A fraction of the light energy absorbed by plants goes directly to the electrons in the chlorophyll molecule. This raises the energy, giving the plant a steady supply of electrons to help photosynthesis occur What is an electron carrier molecule? A molecule that can accept a pair of high-energy electrons, and transfer them, along w/ most of their energy, to another molecule Ex of a carrier molecule: NADP+ accepts and holds 2 high-energy electrons and a hydrogen ion, which helps to trap light energy and convert it into a chemical form. What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? Photosynthesis used the energy of sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide (reactants) into high-energy sugars and oxygen (products) Light-dependent vs. Light-independent reactions Photosynthesis involves 2 sets of reactions The first are light-dependent reactions, which use energy from sunlight to produce energy rich compounds such as ATP - Occur in the thylakoid membranes, oxygen is produced as a byproduct The second reactions are light-independent use ATP and NADPH to produce high-energy sugars. -occur in the stroma 8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis The light-dependent reactions use energy from sunlight to produce oxygen and convert ADP to NADP+ into the energy carriers ATP and NADPH Photosystems are proteins located in thylakoids that absorb light and generate high energy electrons, that generate the light-independent reactions The electron-transport chain is a series of electron-carrier proteins shuttling highenergy electrons from photosystem II photosystem I. In photosystem I electrons are reenergized and carried into another electron transport chain The pumping of electrons builds a gradient on both sides of the thylakoids, giving the chloroplast energy to make ATP The light-independent reactions do NOT require light to occur and are commonly called the Calvin cycle During the light-independent reactions, ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions are used to produce high-energy sugars. The Calvin cycle used 6 molecules of CO2 to produce a single 6-carbon sugar. It uses energy produced from the light-dependent reactions and CO2 The most important factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis are temperature, light intensity, and the availability of water. Extreme conditions: C4 Photosynthesis: allows photosynthesis to occur in plants located in hot, dry conditions w/ low levels of CO2 CAM Plants: Present in dry climates. Allow plant to obtain CO2 While minimizing water loss by sealing the leaves pores during the day and opening them during night.