The Christian Bible, Part II The New Testament Dr. Craig Ho
advertisement

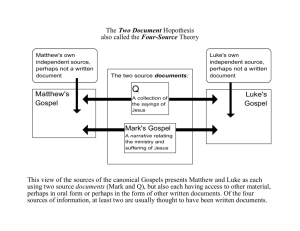
The Christian Bible, Part II The New Testament Dr. Craig Ho BibleNT 1 OT and NT: the story of God’s salvation • The OT ends with the Jews living under foreign rule. • The Jews longed for the coming of a new king (the messiah) who would restore their national fortune (Haggai 2:20-23). => Religio-political and collective salvation • The NT begins with the Jews being ruled by the Roman Empire. • Some Jews believed that Jesus was the long awaited king and they were the first Christians. • The NT tells the story of how this new “king” rules the hearts of his followers in a spiritual kingdom (the kingdom of God), the church (Luke 17:21). => Spiritual and personal salvation. BibleNT 2 Lecture Objectives • To get an overview of the organisation of the New Testament (NT) Canon • To learn about the historical process from which the NT has emerged • To discuss the main issues to which the NT authors were addressing • To get to know the basics of the of the synoptic problem • To survey the main themes of the Paul’s letters • To survey the main themes of the non-Pauline letters BibleNT 3 Structure of the NT Canon • Gospel books • History book • Letters written by St. Paul • Letters written by other leaders of the early Church BibleNT 4 The three stages in the formation of the New Testament • Jesus of Nazareth (6 BC-AD30) – preached the Kingdom of God – killed and resurrected • The Christian communities (30 - 70) – preached Jesus as Christ and saviour – collected sayings and stories about Jesus – Paul and other Christian leaders wrote letters to the churches to deal with their problems • The Redaction of writings (70 - 100) – the passing away of the disciples – the need to produce written records about Jesus BibleNT 5 Problems faced by early Christians • Problem of Identity – What is the relationship between Jews and Christians? (or between Moses and Christ, or Judaism and Christianity) • Theological Problems – Is Jesus just a man, a half-god half man, a god? – Why is Jesus late in returning to earth? • Organisational Problems – How should the Church be organised? • Political Opposition – How to face persecution from the Roman government? BibleNT 6 The Gospels • The Synoptic Gospels: the first three gospels – “Synoptic” seeing from similar points of view – “Gospels” means good news • Matthew – written for Jews (AD 80-90) • Mark – written for the Romans (AD 70) • Luke – written for well educated Gentile Christians (80-90) • The Fourth Gospel: John – a meditation on Jesus as the Word of God BibleNT 7 What is a gospel? • Not a biography. • A literary form used to announce great events in the life of the emperor. • Borrowed by gospel writers to announce the arrival of salvation through the person and work of Jesus of Nazareth. • The earliest gospel (Mark) begins with adult Jesus at about 30 and ends with his resurrection. BibleNT 8 The phenomenon of synoptic Gospels • Why are the first three Gospels so similar? • What is the literary relationship among them? BibleNT 9 The two source hypothesis for the synoptic problem A source called Q (material found only in Matthew and Luke) Mark Matthew Luke BibleNT 10 There are 13 letters written by St. Paul • Romans - a theological treaty on justification by faith alone • 1 & 2 Corinthians - dealing with church discipline • • • • • • • • Galatians - Justification by faith, freedom in Christ Ephesians - Church organisation Philippians - Christian unity Colossians - the all-sufficiency of Christ 1 & 2 Thessalonians - the delay of Christ’ s return 1 & 2 Timothy - Advice to his successor Titus - Advice to a Church leader Philemon - A personal letter BibleNT 11 Other NT writings • Hebrews - to Jewish Christians: do not return to Judaism because of persecution • James - good work is as important as faith • 1 & 2 Peter - encouraging the suffering Christians to face persecuation • 1, 2 & 3 John - the message of love • Jude - warning against false teachers • Revelation - how to face Roman persecution BibleNT 12 Overview of this lecture • All NT writings were produced to address specific needs of the earliest Christians. • The Gospels are good news and not biographies. • The similarity of Synoptic Gospels (Matt., Mark, and Luke) is best explained by the two-source hypothesis. • The Acts of the Apostles addresses issues of Christian relationship with Jews, nature of the Christian movement and the cause for the expansion of the church etc. • Paul wrote to tackle theological, disciplinary and organisational issues faced by the early churches. • Other letter writers addressed the issues of religious persecution and signs of heretic development in the church. BibleNT 13