What is light? - CMSTURTELYTAG
advertisement

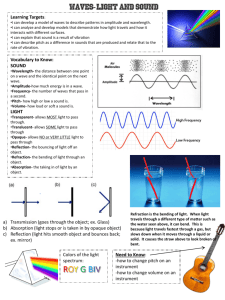
WARM UP ON YOUR INDEX CARD, WRITE ONE SENTENCE ABOUT THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM! Light and Sound In this SECTION: 1) 2) 3) 4) What is light? Electromagnetic Spectrum Interactions of Light Color What is light? Light is an electromagnetic wave! An electromagnetic wave is a wave that travels through empty space or matter and consists of changing electric and magnetic fields! How are EM Waves Produced An EM wave can be produced by the vibration of an electrically charged particle. When the particle vibrates, the electric field around it also vibrates. When the electric field vibrates, it creates a vibrating magnetic field. The vibration of both fields together produces an EM wave. The transfer of energy as electromagnetic waves is called RADIATION! Properties of Light Light travels in straight lines: Laser Light travels VERY FAST – around 300,000 km/sec. This is 880,000 times faster than sound. At this speed it can go around the world 8 times in one second. Light travels fastest through empty space! Light travels much faster than sound. For example: 1) Thunder and lightning start at the same time, but we will see the lightning first. 2) When a starting pistol is fired we see the smoke first and then hear the bang. Shadows Shadows are places where light is “blocked”: Rays of light Properties of Light summary 1) Light travels in straight lines 2) Light travels much faster than sound 3) Shadows are formed when light is blocked by an object 2. The Electromagnetic Spectrum Entire range of EM waves! Divided into regions according to wavelength Where is the highest energy? EM SPECTRUM Description Region of EM spectrum 1. Used by police officers to detect the speed of cars by radar 2. Energy from the sun that can cause sunburn 3. Used in a device that takes images of bones 4. Carry television signals to your home 5. Can produce rainbows when there are water droplets in the sky 6. Used to treat forms of cancer or sterilize food 1.MICROWAVES/RADAR 2.ULTRAVIOLET 3. X-RAYS 4.RADIO 5.VISIBLE LIGHT 6. GAMMA RAYS VISIBLE LIGHT:NARROW RANGE OF WAVELENGTHS LONGEST TO SHORTEST WAVELENGTH Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet 3. INTERACTIONS OF LIGHT REFLECTION/LAW OF RELFECTION TYPES OF REFLECTION LIGHT SOURCE V. REFLECTED LIGHT ABSORPTION SCATTERING REFRACTION DIFFRACTION We see things because they reflect light into our eyes: Homework Reflection Reflection from a mirror: Normal Reflected ray Incident ray Angle of incidence Angle of reflection Mirror The Law of Reflection Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection In other words, light gets reflected from a surface at ____ _____ angle it hits it. The same !!! Clear vs. Diffuse Reflection Smooth, shiny surfaces have a clear reflection: Rough, dull surfaces have a diffuse reflection. Diffuse reflection is when light is scattered in different directions Luminous and non-luminous objects A luminous object is one that produces light. An illuminated object is one that reflects light. Luminous objects FIREFLY SUN LIGHT BULB Illuminated A VISIBLE OBJECT THAT IS NOT A LIGHT SOURCE ABSORPTION THE ABSORPTION OF LIGHT ENERGY BY MATTER-CAUSES LIGHT TO BECOME DIMMER. THE FARTHER LIGHT TRAVELS FROM THE SOURCE, THE DIMMER IT BECOMES SCATTERING INTERACTION THAT CAUSES LIGHT TO CHANGE DIRECTION ALLOWS YOU TO SEE OBJECTS OUTSIDE THE BEAM, BUT BECAUSE LIGHT IS SCATTERED, BEAM BECOMES DIMMER. Refraction Refraction is when waves ____ __ or slow down due to travelling in a different _________. When a pen is placed in water it looks like this: In this case the light rays are slowed down by the water and are _____, causing the pen to look odd. The two mediums in this example are ______ and _______. Words – speed up, water, air, bent, bend. medium REFRACTION AND COLOR SEPARATION Violet light, which has a shorter wavelength, is refracted more than red light Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet DIFFRACTION LIGHT CANNOT BEND VERY MUCH BY DIFFRACTION UNLESS IT PASSES THROUGH A VERY NARROW OPENING OR AROUND A SMALL BARRIER. LIGHT CANNOT DIFFRACT VERY MUCH AROUND LARGE OBJECTS TRANSMISSION LIGHT PASSES THROUGH MATTTER. ALL OF THE LIGHT THAT REACHES YOUR EYES IS TRANSMITTED THROUGH AIR. 3. Colour White light is not a single colour; it is made up of a mixture of the seven colours of the rainbow. We can demonstrate this by splitting white light with a prism: This is how rainbows are formed: sunlight is “split up” by raindrops. TYPES OF MATTER 1. TRANSPARENT-LIGHT IS TRANSMITTED THROUGH EASILY 2. TRANSLUCENTTRANSMITS AND SCATTERS 3. OPAQUE- DOES NOT TRANSMIT LIGHT How is color determined? The colour an opaque object appears depends on the colours of light it reflects. For example, the book only reflects red light so we see it as red! White light Only red light is reflected A pair of purple trousers would reflect purple light (and red and blue, as purple is made up of red and blue): Purple light A white hat would reflect all seven colours: White light Using coloured light If we look at a coloured object in coloured light we see something different. For example, consider a football kit: Shirt looks red White light Shorts look blue In different colours of light this kit would look different: Red light Shirt looks red Shorts look black Shirt looks black Blue light Shorts look blue The white hair reflects all the light….the black hair absorbs all the light Colors of Transparent and Translucent Objects The color of transparent and translucent objects is determined differently. Color is determined by what is transmitted. Glass is clear because it transmits all light. Ginger ale 2-Liters are green because the plastic transmits green light Mixing colours White light can be split up to make separate colours. These colours can be added together again. The primary colours of light are red, blue and green. Combining colors of light is called color addition Adding blue and red makes magenta (purple) Adding red and green makes yellow Adding blue and green makes cyan (light blue) Adding all three makes white again TV SETS USE RED, BLUE AND GREEN PLATES TO MAKE ALL THE COLOR YOU SEE! PIGMENTS A PIGMENT is a material that gives a substance its color by absorbing some colors of light and reflecting others. Chlorophyll is a pigment as is melanin (skin pigment) and paint colors MIXING PIGMENTS WHEN YOU MIX PIGMENTS TOGETHER, MORE COLORS OF LIGHT ARE ABSORBED OR TAKEN AWAY. MIXING PIGMENTS IS CALLED COLOR SUBTRACTION Sound – The basics We hear things when they vibrate. If something vibrates with a high frequency (vibrates very ______) we say it has a _____ pitch. If something vibrates with a low frequency (vibrates ______) we say it has a ____ pitch. The lowest frequency I could hear was… Words – slowly, low, high, quickly Drawing sounds… This sound wave has a _____ frequency: This sound wave has a ___ _frequency: Drawing sounds… This sound wave has a _____ amplitude (loud): This sound wave has a _____ amplitude (quiet): Hearing problems Our hearing range can be damaged by several things: 1) Too much ear wax! 2) Damage to the auditory nerve 3) Illness or infections 4) Old age (not like Mr Richards) Other sound effects… Like light, sound can be… 1) Reflected – sound reflections are called ______. 2) Refracted – this is why you might sound strange if you try talking underwater The Ear Label your diagram with the following: These bones are vibrated by the eardrum This tube carries the sound towards the eardrum This part is used to help us keep our balance This part “picks up” the vibrations This part of the ear contains many small hairs with turn vibrations into an electrical signal This part connects the ear to the mouth This part “channels” the sound towards the ear drum The Ear