Elodea takes in CO2 that the snail breathes out
advertisement

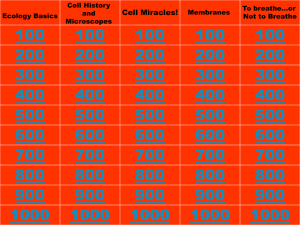
Cell History and Microscopes 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Cell Miracles! Membranes To breathe…or Not to Breathe 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 100 We always begin examining microscope slides with this objective lens in place Continue 200 This category of cells has a definite nucleus and organelles. Continue 300 A bacteria cell is _____________, since it has no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Continue 400 “This” microscope part regulates the amount of light on a standard microscope. Continue 500 The ocular lens of a microscope has a magnification of 10X and the objective lens has a magnification of 40X. The total magnification is…. Continue 600 In the microscope lab, this is the most notable difference between the onion epidermis cells and the Elodea leaf cells Continue 700 This is the highest magnification a scope could have (with an eyepiece at 10X, a low power objective at 10X and a high power objective at 50X) Continue 800 The Cell Theory states that 1)All organisms are made of __________, 2)All existing cells are produced by other living ___________, and 3)The ____________is the most basic unit of life. Continue 900 This “type” of microscope with a light source shining from a)above, b)beneath or c)both gave us the chance to see our pond water sample in “3-D”. Continue 1000 Within a membrane, a cell is filled with a “jellylike substance” called a)______________ that contains dissolved molecular building blocks. In some cells, the cytoplasm also contains b)____________, structures specialized to perform distinct jobs in the cell. What are a)cytoplasm, b)organelles Continue 100 This is a long whip-like tail used for cellular locomotion. Continue 200 This is a major difference between rough and smooth E.R. (endoplasmic reticulum) Continue 300 This is the organelle used in photosynthesis ; it helps to convert the sun’s energy into food. Continue 400 This is the cell organelle that helps to make the proteins that carry out endless jobs in our bodies Continue 500 The process of moving molecules out of a cell Continue 600 These are the cells recycling centers: they contain digestive enzymes to digest damaged or foreign material Continue 700 List three things that all cells have in common Continue 800 This organelle packages, processes and ships proteins and fats; it also functions in producing lysosomes Continue 900 Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain a small amount of this genetic material…it allows them to direct the production of some of their own proteins Continue 1000 V Words! A ____________is a fluid filled sac used for storage of material by the cell whereas a _____________ is a general name describing small membrane-bound sacs that transport materials from place to place. Continue 100 A membrane is said to be “this” if it allows only certain molecules to pass. Continue 200 This is the current cell membrane “model” describing a cell’s texture and appearance Continue 300 Movement of molecules across a cell membrane that does not require energy input from the cell. Continue 400 This is the process by which water travels from areas of higher to lower concentration across a membrane Continue 500 ___________transport drives molecules across a membrane from a region of low concentration to high concentration with the input of energy. Continue 600 A type of endocytosis in which the cell membrane “engulfs” large particles to bring them into a cell. Continue 700 If one of the high energy, unstable phosphate bonds “breaks” from adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy is released, and “this” molecule is produced. Continue 800 When a cell (90% water and 10% salt) is placed into an environment that is 92% water and 8% salt, the cell will likely do “this”. Continue 900 When concentrations of substances on either side of a membrane are the same, the system is said to be in _________________. Continue 1000 Elephants are larger than mice, right? This is the reason why an elephant’s cells are not much larger than a mouse’s cells. Continue 100 This is the color of Bromothymol blue with a large amount of carbon dioxide is present. Continue 200 These are the products of cellular respiration. Continue 300 These are the requirements for photosynthesis. Continue 400 The primary photosynthetic pigment found in the chloroplast. (Its electrons are excited by the sun’s energy). Continue 500 Chlorophyll reflects these colors (or wavelengths of light) most of all. Continue 600 This pigment is a major contributor to a carrot’s orange color. Continue 700 According to our snail/elodea lab results, the following hypothesis would be (supported / not supported / refuted) Elodea takes in CO2 that the snail breathes out (in the light) Continue 800 The ___________ _____________ reactions use energy from the light-dependent reactions to make sugars. Continue 900 This is an example of an electron carrier in photosynthesis or respiration Continue 1000 These are two factors that affect photosynthesis Continue