Asymmetric conflict us iran ppa 601
advertisement

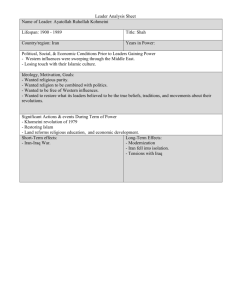
ASYMMETRIC CONFLICT GROUP # 3 Kunhui Cai, Madan Chauhan, Jim Jacaruso, Manoj Pant, Vinay Srivastava, Yoji Tsubaki PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict Theory of Asymmetric Conflict Asymmetric Conflict is a term that describes a military situation in which two belligerents of unequal power or capacity of action , interact and take advantage of the strength and weaknesses of themselves and enemies. The interaction often involves strategies and tactics outside the bounds of conventional warfare. ( Wikipedia) Synonymous with Terrorism/ Not synonymous with Terrorism? Two Schools: 1) Descriptive in nature and Asian in its approach: It assumes that asymmetric and indirect are synonyms. Indirect warfare as described by Sun Tzu, Mao Tse-tung, B.H. Liddell-Hart…. Mao advises that one should come from the East and yet attack from the West.. 2) Reductive . ..Political scientist believe that asymmetric conflict involves two actors – ‘strong’ and ‘weak’. Demographic, military and scientific strengths. PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict …Theory and Concept Other definitions – a) Defined by transformational use of familiar and unfamiliar ‘capability clusters’ or by pitting of different organizational structures against each other. – b) Involves states of unequal aggregate power capabilities, measured in terms of material resources i.e. size, demography, military capability and economic prowess, strategy and tactics. (T.V. Paul) – c) Asymmetric warfare is “leveraging inferior tactical or operational strength against the vulnerabilities of a superior opponent to achieve disproportionate effect with the aim of undermining the opponent’s will in order to achieve the asymmetric actor’s strategic objectives.(Kenneth McKenzie). PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict …Theory and Concepts “If you use pressure, we will deploy pressure and force. We know that you can harm us although we do not threaten you. But we too can harm you. Everyone can cause harm according to their ability and their size. We cannot come all the way to you in the United States, but individual Arabs may reach you.” -Saddam Hussein, 1990 Put simply, asymmetric threats or techniques are a version of not "fighting fair.” Asymmetric strategy may not only sidestep opponents or hit them where they ain’t but also go over them ( Desert Storm), or under them( terrorist attacks or cyber attacks). PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict SOME THOUGHTS ? Trends in correlations of war data show that strong actors have been losing more asymmetric conflicts. A)1800-1849: 34 asymmetric conflicts . – 88.2% won by strong actors. Greek war of Indep, US second seminole war,1835-42, First Zulu War 1838-42, First British Afghan War 1838-42. B)1850-1899:69 asymmetric conflicts, – 79.5 % won by strong actors. The Second Opium War1856-60, Second Schleswig-Holstein war,1864, The Russo-Turkoman War 1878-81, The Second Boer War1899-1902. PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict Trends… C)1900-1949: 31 asymmetric conflicts, – 65.1% won by strong actors. Russo-Japanese War 1904-1905, The First Balkan War1912-1913, The Iraqi-British Conflict1920-1921, The US –Nicaraguan Conflict1927-1933. D)1950-1998:36 asymmetric conflict – 45% won by strong actors,. South vietnam,1961-65, The Anglo Portugal War 1961-75, The Mozambique Conflict1964-75, The Russo- Chechen War 1994-96. PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict REASONS FOR SUCH A TREND The Nature of the Actor (Structural) : Democratic v/s Authoritarian type of regime. Arms Diffusion (Technological): Diffusion of relatively advanced small arms in Developing World raised the costs of conquest for strong actors. The Growth of militant Nationalism ( Cultural): ideological asymmetries, national liberationists were more committed and willing to lay their lives. The role of relative Resolve/ interests (Psychological): Relative vulnerability vis-à-vis relative power and interests. For strong actors survival is not at risk so have lower interest. Strategic interactions ( Strategic/ conceptual): Wrong politicomilitary strategy against weak actor may result in losing. The Key variable is Time. Delay favors weak! PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict What guides Weaker Power to go to Conflict with Stronger power( T V Paul) 1. Politico –Military Strategy in asymmetric war initiation blitzkrieg (lightning strike) attrition/maneuver limited aims/fait accompli. 2. Offensive weapons , limited capability and asymmetric war initiation 3. Alliance Support and war calculation 4. Domestic Structure and asymmetric war initiation 5. Time Pressure PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict SOME EXAMPLES Use of terrorism by much lesser Mongol forces in the creation and control of the Mongol Empire. Non violent struggle by Mahatma Gandhi Israel and Palestine warfare. India-Pakistan: Kargil warfare. U.S. – Cuba Conflict. China- Taiwan Conflict. North Korea- South Korea . U.S.- Iran Conflict. PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict WHY US – IRAN CONFLICT IS ASYMMETRIC 1. UNEQUAL POWER BASE 2. LEVERAGING TACTICS 3. TERRORISM 4. RELIGIOUS 5. DESIRE TO RISE PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict US - Iranian History 1883 - U.S and Persia appoint diplomatic envoys 1941 - Allied Powers force Shah to abdicate throne to his more pro-allies son. Allied Forces use Iran as staging base for re-supply of Russian forces in WWII. 1951 - Iranian Prime Minister Mossadegh tries to nationalize oil industry and limit the power of Shah 1953 - American and British intelligence services sponsor a coup that overthrows Mossadegh. 1963/64 - Shah’s White Revolution. Ayatollah Khomeini exiled for denunciation of Shah’s status of forces bill for US Military Personnel. 1965/72 - America provides significant military support to Iran. Shah leverages Iran’s strategic position in US containment policy. PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict US - Iranian History 1978 - Iranian Islamic Revolution Council is formed 1979 - Shah is forced into exile - later enters US for cancer treatment - students seize US embassy and diplomats beginning a 444 day hostage crises. 1980 - President Carter severs diplomatic ties with Iran - expels Iranian diplomats from US 1980 - Iraq invades Iran leading to a 10 year war during which the US openly supports Iraq. 1982 - American supported Lebanese Christian forces kidnap Iranian diplomats - begins a nine year period of kidnapping of western hostages. 1983 - Bombing of US embassy and US Marine Barracks in Beirut - US places blame/suspicion for both events on Iranian supported Hezbollah PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict US - Iranian History 1984 - Bombing of Embassy annex in Beirut - US says Hezbollah known to have been involved 1985/86 - Iran-Contra scandal 1988 – USS Vincennes shoots down Iranian Airliner over the gulf killing 290. Iran views this as evidence the US was going to get involved in the Iran - Iraq war. Two weeks later Khomeini accepts UN brokered cease-fire with Iraq 1990 - Iran remains neutral in US led war against Iraq denouncing both the US and Iraq 1993 - President Clinton takes office - institutes a policy to isolate Iran 1995 - Clinton signs an executive order banning all trade with Iran. PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict US - Iranian History 1996 - Khobar Tower bombing in Saudi Arabia - 19 US service personnel killed - Hezbollah blamed. Iran - Lybia Sanctions act passed. 1999 - US eases sanctions against state supporters of terrorism 2000 - US officially acknowledges US role in 1953 coup but does not apologize. 2001 - US releases 46 count indictment against unidentified Iranians in the Khobar Towers case. Iran condemns US air strikes in Afghanistan yet agrees to perform search and rescue missions for US pilots downed in Iran. Iranian President denounces Osama Bin Laden and rejects US assertions that Iran supports terrorism. PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict US & IRAN Current Relationship 2001, President Bush unfreezes the Nuclear program – 2002 - President Bush refers to Iran as part of an Axis of evil and states they are pursuing WMD and Terrorist Activities – Defense Secretary Rumsfeld links Iran to suicide attacks in Israel – 2003, IAEA reports that Iran is Enriching Uranium – Since then: – US asserts that Iran is supporting terrorists – Iran asserts that US is violating Iranian sovereignity – 2007, US arrests Iranian diplomats in Iraq – UNSC imposes sanctions on Iran – Iran arrests 15 British Sailors for venturing into Iranian Waters Is War Imminent? – PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict Tracing the Conflict US MEDIA PORTRAYAL OF IRAN Iran is the country that grabbed U.S. embassy officials as hostages and then embarked on a series of terror strikes against U.S. targets. Iranians will stop at nothing to preserve their homeland – the taking of hostages, terrorism, and nuclear weapons are just instruments for them to scare America out of their backyard. IRANIANS VIEW OF AMERICA America remains an enemy that has repeatedly expressed its desire to overthrow the Iranian government. Most Iranians believe the Khat e-Imam took the American embassy to destroy its network of spies and put an end to American plans to launch a military coup in Iran US INTENTIONS PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict ISSUES OIL Nuclear Aspirations Regional Balance of Power Support of Terrorism UN Sanctions PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict Issues involved Issue 1: Petro$ BY 2010, US NEEDS 50 MILLION BARRELS A DAY OF OIL While many regions of the world offer great oil opportunities, the Middle East with two thirds of the world's oil and the lowest cost, is still where the prize ultimately lies. PETRODOLLARS AND OIL TRADE The world buys and sells oil in dollars, meaning that all the countries of the world subsidise the US economy as the US has a monopoly on printing dollars. PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict Issues involved The oil-producing countries have to trade in dollars and any country wanting to buy oil must first acquire dollars which can only be obtained by trading with the US, that is, buying US products and services. This means that trillions of dollars are traded daily on the major currency exchanges, based in Washington, DC and in London. The surplus generated through these exchanges and sales of US financial instruments subsidizes an otherwise bankrupt US economy. PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict NEW DEVELOPMENTS IN OIL TRADE Over the past four years the value of the euro has appreciated by 13% against the dollar making it a preferred currency to sell oil with, hence Iraq’s switch to the euro in 2002 Upcoming establishment of an Iranian oil bourse based on euros which presents a direct threat to the power of the US dollar Venezuela to trade its oil in euros and in spite of the US’s military supremacy, the US economy is in serous trouble if Iran and Venezuela go ahead with the switch Countries such as Russia are mixing oil sales using a ‘basket’ of currencies PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict Nuclear Issues The IAEA reported in 2003, that Iran had hidden a Uranium enrichment program for 18 years. Western Members of IAEA called on Iran to commit itself to stopping all enrichment activities permanently, but it has refused to do so and has abandoned the temporary halt as well. The clash with Iran escalated in Feb 2006, when the IAEA as a whole reported Iran to Security Council and in March Security Council decided to take up the issue after receiving the copy of the report on Iran. UN had issued dead line to suspend Uranium enrichment program which ended on 21st Feb 2007, but Iran ignored the UN deadline. UNSC slaps sanctions on Iran in March 2007 PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict MILITARY DOCTRINE SO FAR Iran's military doctrine and capacity is defense of its own territorial integrity only Iran has never attacked any of its neighbors in the region in the past 300 years, even when it was badly provoked in 1998 by the Taliban in Afghanistan PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict IRANIAN MILITARY STRENGTH Iran has two kinds of armed forces: the regular forces and the Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps (IRGC), totaling about 545,000 personnel Iran also has a paramilitary, volunteer militia force called the Basij, which includes about 90,000 full-time, active-duty uniformed members, up to 300,000 reservists, and a further 11 million men and women who could be mobilized. Iran's military capabilities are kept largely secret. Since 1992, it has produced its own tanks, armored personnel carriers, guided missiles, submarines, and a fighter plane PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict WEAPON DEVELOPMENT In recent years, official announcements have highlighted weapons such as Fajr-3 (MIRV) missile, Hoot, Kowsar, Fateh-110, Shahab-3, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) The Fajr-3 (MIRV) is currently Iran's most advanced ballistic missile. It is a domestically-developed and produced liquid fuel missile with an unknown range PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict MISSILE PROGRAM The IRIS solid-fuelled missile is a program which is supposed to be Iran's first missile to bring satellites into orbit PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict Stakeholders UN US Iran Russia Israel Saudi Arabia and other US allied Arab nations Turkey Iraq UK EU IAEA PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict Group Exercise Break up into groups Clarify their Frames, their positions, interests. What could be some of the possible ways of resolving or deescalating the conflict PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict Structural Interest Cognitive Emotional Distribution Underlying Beliefs Fear of power & resources ‘Built-in’ structural inequalities interests, goals and objectives Schemas Loss Frames grief Rage Pathology Goals Justice Integration or compromise Reframing Healing Conflict Management Techniques Revolution Negotiation / mediation Facilitated contact Truth-telling Core Concerns Re- distribution Deconstruction compromise bargaining win-win and Public Acknowledgement Forgiveness From PPA 601 class lecture Spring 2007, Framing- Prof Catherine Gerard PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict POSITIONS AND INTERESTS US Position a) b) Iran is Axis of Evil Iran is going Nuclear WMD IRAN Position US Interests a) US is Imperialist evil power out to subjugate Mid East b) Nuclear for peaceful purposesenergy 1)Resourcesoil 2) Power in Mid East 3) Will not like Iran to rise. 4) Control IRAN Interests 1)Major player in the region 2) Bargain and Leveraging 3) Increase d status in world Equation 4)Sovereignity 5) Respect in the Arab/Muslim world 6) Stability in Iraq- Region PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict Strategies for Resolution Diplomacy Dialogue—interest based negotiations Multi-track Diplomacy Economic Pressure Public Diplomacy Military Action Truth and Reconciliation Commissions Reframing PPA 601 Spring 2007 Asymmetric Conflict