POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE
advertisement

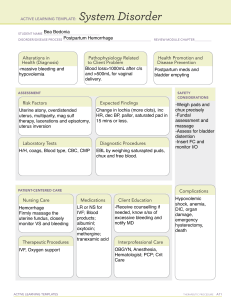
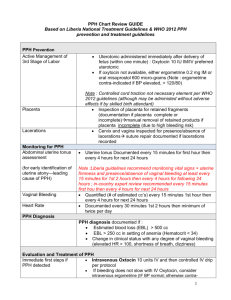
To understand the importance of prompt and appropriate management in saving lives from PPH ◦ Define PPH ◦ List the causes and risk factors for PPH ◦ Discuss the steps taken in managing PPH Bleeding >500 ml after childbirth Pad or cloth soaked in less than 5 minutes Constant trickling of blood OR Delivered outside health center and still bleeding Call for extra help Massage uterus until it is hard and give OXYTOCIN 10 units IM Place cupped palm on uterine fundus and feel for state of contraction Massage fundus in a circular motion with cupped palm until uterus is well contracted When well contracted, place fingers behind fundus and push down in one swift action to expel clots Measure/estimate blood loss and record Give IV fluids with 20 units oxytocin at 60 drops per minute Empty the bladder: catheterize if necessary Check and record BP and pulse every 15 minutes Establish cause of bleeding Uterine atony Tears of the cervix, vagina, or perineum Retained placenta Retained placental fragments Inverted uterus Ruptured uterus When uterus is hard, deliver placenta by controlled cord traction If unsuccessful and bleeding continues – perform vaginal examination (check if placenta is in the cervix). Remove placenta carefully and check if complete. Massage uterus If unable to remove placenta – REFER urgently to hospital During transfer, continue IV fluids with 20 units oxytocin at 30 drops/minute Check placenta If placenta complete ◦ Massage uterus to express any clot ◦ If uterus remains soft, give OXYTOCIN 10 units IM ◦ Continue IV fluids with 20 units Oxytocin at 30 drops/min ◦ Continue uterine massage until it is hard Placenta is not complete or not available for inspection ◦ Remove placental fragments by hand. ◦ If bleeding continues after fragments removed, refer woman urgently to hospital Placenta is complete and vaginal bleeding continuous: ◦ Check for uterine atony ◦ Check for trauma Massage the uterus until it is well contracted Give oxytocin ◦ Initial dose: 10 IU IM/IV or 20 IU IV infusion in 1 liter saline, 60 drops per minute Continuing Dose ◦ IM/IV repeat 10 IU after 20 minutes if heavy bleeding persists OR ◦ 10 IU IV infusion in 1000 ml of saline, 30 drops per minute. ERGOMETRINE – 1st line treatment of uterine atony not responsive to oxytocin Rapid onset of action (2-5 min) after IM injection Clinical effect persists for approximately 3 hours Initial dose: 0.2 mg IM/IV slowly Continuing dose: 0.2 mg IM after 15 minutes if bleeding persists (up to 5 doses=1.0 mg) DO NOT GIVE IF PATIENT IS HYPERTENSIVE, or has heart disease Monitor BP and PR Common side effects: nausea, vomiting, dizziness Store at temperatures below 8°C and away from light Point of compression is just above the umbilicus and to the left Bimanual compression of uterus AORTIC COMPRESSION If uterus contracted and still bleeding: Look for perineal, vaginal or cervical lacerations Determine degree and extent of tear If 3rd degree tear – REFER to CEMONC facility For other tears – apply pressure over tear with sterile pad or gauze and put legs together. Do not cross the ankles. Check after 5 minutes. If bleeding persists – repair the tear. Giving birth should be about giving life not giving up a life.