Thermo notes part 2
advertisement

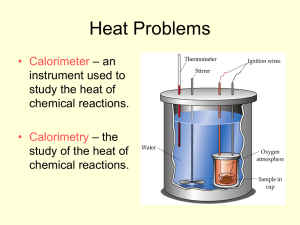
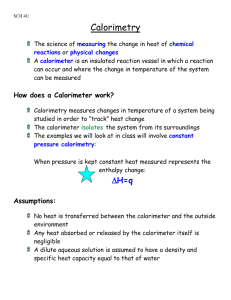
Chapter 16 Notes II Calorimetry What is calorimetry? • Essentially, the science of measuring heat change. • Using the specific heat of something you know to find the specific heat of something you don’t. What is calorimetry? • It takes advantage of the law of conservation of energy. • The principal shows that heat lost by one substance has to equal heat gained by another. When a hot object is put into cool water what happens? Object at 100oC 50g Final temperature of both is 22oC 250g 50g Water at 20oC NOTICE: Heat lost is equal to heat gained, but temperature lost does NOT equal temperature gained So, to find the specific heat of the object… •Solve q=mCDT for heat gained by water THEN •Use q you found to solve q=mCDT for the specific heat of the object. Calorimeters • A calorimeter is a device that measures heat change. • It can be extremely sophisticated, or as simple as two foam cups, a thermometer and water! Ghetto KPHS Style Calorimeter Bomb Calorimeter Practice Problem #1 • What is the specific heat of a metal if a 50.8g sample at 100.0oC raises the temperature of 258.2g of water from 25.2oC to 28.1oC? Practice Problem #2 • What is the specific heat of a substance if a 22.6g sample at 104.5oC raises the temperature of 125.3g of water from 22.6oC to 33.1oC?