Heat Capacity & Specific Heat: Lecture Notes
advertisement
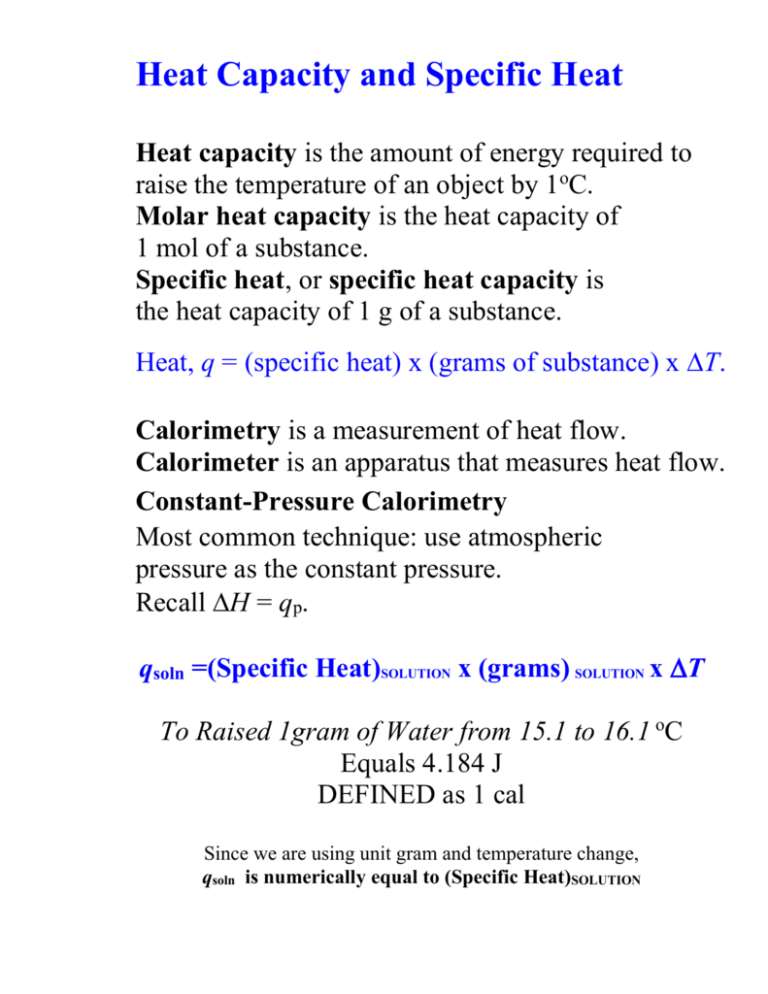
Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Heat capacity is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of an object by 1oC. Molar heat capacity is the heat capacity of 1 mol of a substance. Specific heat, or specific heat capacity is the heat capacity of 1 g of a substance. Heat, q = (specific heat) x (grams of substance) x T. Calorimetry is a measurement of heat flow. Calorimeter is an apparatus that measures heat flow. Constant-Pressure Calorimetry Most common technique: use atmospheric pressure as the constant pressure. Recall H = qp. qsoln =(Specific Heat)SOLUTION x (grams) SOLUTION x T To Raised 1gram of Water from 15.1 to 16.1 oC Equals 4.184 J DEFINED as 1 cal Since we are using unit gram and temperature change, qsoln is numerically equal to (Specific Heat)SOLUTION Bomb Calorimetry (Constant-Volume Calorimetry) Reactions can be carried out under conditions of constant volume instead of constant pressure. Constant volume calorimetry is carried out in a bomb calorimeter. The most common type of reaction studied under these conditions is combustion. If we know the heat capacity of the calorimeter, Ccalorimeter, then the heat of reaction, qrxn = –Ccalorimeter x T. Since the reaction is carried out under constant volume, q relates to E.