Chapter 11 – 12 Monetary Policy
advertisement

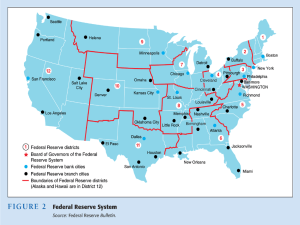
Chapter 11 – 12 Monetary Policy Chapter 11 Section 1 Chapter 12 Sections 1,2, 3 Chapter 11 Section 1 I. Explain the three functions of money. A. Barter Economy – • Moneyless economy that relies on trade. B. Money – • Any substance that functions as a medium of exchange, a measure of value, and a store of value. 3 I. Explain the three functions of money. C. Three functions of money • 1) Medium of exchange • Generally accepted as payment for goods and services. • 2) Measure of value • Expression of worth. • 3) Store of value • Goods or services can be converted into money, which is easily stored until some future time. 4 II. Identify four major types of money used in early societies. A. Commodity Money – • Money that has an alternative use as a commodity (i.e. corn, gunpowder, tobacco). B. Wampum – • Conch and mussel shells used as money by the Narraganset Native Americans. 5 II. Identify four major types of money used in early societies. C. Paper Currency – D. Specie – • Fiat • Money by government decree. • Money in the form of coins. 6 III. Trace the origins of the United States dollar. A. Pesos – • Spanish • Bullion • Ingots or bars of precious metals B. Talers – • Austrian taler • Monetary unit – standard unit of currency 7 IV. Describe the four characteristics of money. A. Portability – B. Durability – • Transferred from one person to another. • Able to last a long time. 8 IV. Describe the four characteristics of money. C. Divisibility – D. Limited Availability– • Easily divisible into smaller units. • Money loses its value when there is too much of it. 9 The Circular Flow Model of a Market System Costs Factors of production Resource Market Income-wages, rents, interest, profit Resources-land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship Taxes Taxes Government Business Households Loans Banking Transfer payments Firms Savings System Loans Retained profits Subsidies Goods and services Revenues Product Market Goods and services Consumption expenditures END CHAPTER 11 Chapter 12 Section 1 I. Identify the unique features of the FED. A. 12 Districts – Atlanta, GA 6 B. Operate independently of one another. C. Private ownership • 1) Member banks – banks that belong to the Federal Reserve System. • 2) The FED is owned by member banks. 13 14 II. Describe the structure of the Federal Reserve System. A. Board of Governors – • 1) • 2) 7 members appointed by President. Regulatory and supervisory agency. B. Federal Open Market Committee – • Makes decisions about the money supply and interest rates. C. Federal Advisory Council – • Provides feedback on the overall health of the economy. 15 Banking Structure Figure 15.1 III. Explain the major regulatory responsibilities of the FED. A. State Member Bank Supervision – • 1) • 2) All depository institutions must maintain reserves. The FED is responsible for state chartered member banks. B. Holding Companies – • 1) • 2) Corporation that owns one or more banks. Formed to avoid government regulations. 17 III. Explain the major regulatory responsibilities of the FED. C. International Operations– • 1) The FED has broad authority to supervise and regulate foreign banks operating in the United States. D. Mergers – • 1) The FED must approve a merger of two or more banks. 18 III. Explain the major regulatory responsibilities of the FED. E. Check Clearing – • 1) Reserves are shifted from one bank to another. F. Consumer Legislation– • 1) • 2) Truth-in lending laws require sellers to disclose info to people who buy on credit. Regulation Z is a provision that requires truth-in lending disclosures. 19 III. Explain the major regulatory responsibilities of the FED. G. Currency – • 1) • 2) Paper component is printed at the Bureau of Engraving and Printing. Metallic coins are coined at the U.S. Mint. H. Margin Requirement – • 1) Minimum deposits left with a stockbroker to be used as down payments to buy other securities. 20 21 Loose Money Policy Expands the Money Supply • Lower discount rate • Lower reserve requirements • Buy government securities Tight Money Supply Contracts the Money Supply • Raise the discount rate • Raise the reserve requirement • Sell government securities Money Supply M1 - The Transactions Approach • Currency - federal reserve notes and coins • Demand Deposits - checking accounts, NOW • • • accounts, SuperNOW accounts, share drafts, ATM, debit cards Unused credit card balances Some traveler’s checks Food stamps Money Supply M2 - The Liquidity Approach • M1 • Savings Accounts • Short Term Time Deposits • CDs • MMDAs • REPOs • Eurodollars • MMMFs The Money Supply M3 L • M2 • Large time deposits - CDs $100,000+ • Large money funds • M3 • Savings bonds • Short-term treasury securities • commercial paper • banker’s acceptances