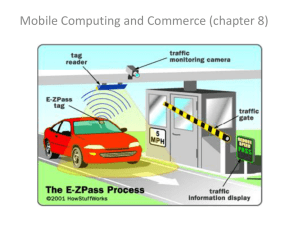
Mobile Commerce
advertisement

Seminar 4 – Part 2 Mobile Commerce Ref: Chapter 7:Turban and Volonino 7-1 Learning Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Discuss the characteristics, attributes, and drivers of mobile computing and m-commerce. Understand the technologies that support mobile computing. Discuss m-commerce applications in financial and other services, advertising, marketing, and providing of content. Describe the applications of m-commerce within organizations (mobile enterprise, intrabusiness). Understand B2B and supply chain applications (interorganizational) of m-commerce. 7-2 Learning Objectives cont’d 6. Describe consumer and personal applications of m-commerce. 7. Describe location-based commerce (lcommerce). 8. Discuss the key characteristics and current uses of pervasive computing. 9. Describe the major inhibitors and barriers of mobile computing and m-commerce. 7-3 Problem – Competition is fierce; profit margins low. Bloom needs appropriate technology to compete with Wal-Mart. Solution – Wireless technology – mobile checkstands, scanners, handhelds, Wi-Fi, RFID. Results – Better customer service & speedier checkout; higher employee productivity; fewer employees overall. 7-4 Wi-Fi – What is it? Wi-Fi stands for "Wireless Fidelity" is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance A Wi-Fi enabled device such as a personal computer, video game console, mobile phone, MP3 player or personal digital assistant can connect to the Internet when within range of a wireless network connected to the Internet. The coverage of one or more (interconnected) access points — called a hotspot — can comprise an area as small as a few rooms or as large as many square miles. Coverage in the larger area may depend on a group of access points with overlapping coverage. In addition to private use in homes and offices, Wi-Fi can provide public access at Wi-Fi hotspots provided either free-of-charge or to subscribers to various commercial services. Organizations and businesses - such as those running airports, hotels and restaurants - often provide free-use hotspots to attract or assist clients. Enthusiasts or authorities who wish to provide services or even to promote business in selected areas sometimes provide free Wi-Fi access. Wi-Fi® Technology Enabling Economic and Social Development in Rural and Urban India 7-5 How Wi-Fi works. 7-6 Value Added Attributes that Drive Development of M-Commerce Ubiquity – refers to the attribute of being available at any location at any given time. (ex: smart phone or PDA) Convenience – Internet enabled; many available hot spots. Instant Connectivity – quick connections to Internet, intranets, other mobile devices & databases. Personalization – preparation of customized information for individual consumers. Localization of products & services – wireless device has GPS. 7-7 Drivers of Mobile Computing & MCommerce Widespread availability of mobile devices – 50% of world population will use mobile phones in 2008. No need for a pc – smart phone may soon become foremost tool connecting people to Internet. Handset culture – widespread use of cell phones. Declining prices, increased functionalities – declined by 50% in recent years while functionalities increase. Improvement of bandwidth – 3G & 3.5G 7-8 Drivers of Mobile Computing & MCommerce (cont’d) Centrino chip – connects to wireless LAN; low usage of electricity; high level security. Availability of Internet access in automobile – numbers of availability continue to increase. Networks – 3G, 4G, and adoption of WiFi as wireless LAN. 7-9 Apple’s iPad a tablet computer developed by Apple Inc. Announced on January 27, 2010, it is part of a category between a smartphone and a laptop computer. 10 Landscape of M-Computing 711 Barriers to Commercial Wi-Fi Growth Cost – ◦ it’s readily available; why pay for it? Security ◦ War Driving 712 Mobile Banking & Stock Trading Services offered include: bill payments & money transfers; access administration & check book requests; balance inquiries & statements of account; interest & exchange rates; sale/purchase of stocks. Increasing % of banks offer mobile access – financial & account information. Mobile Wallets Wireless Bill Payments 713 Mobile Banking at Home…….. 14 Shopping from Wireless Devices 715 M-Commerce Applications – Purchasing a Movie Ticket 716 Advertising and Content Providing Target Advertising - Facebook Getting Paid to Listen to Ads Mobile Portal Voice Portals 17 Mobile Enterprise Applications Supporting salespeople during customer visits Supporting field employees during repairs Supporting traveling of employees Supporting employees working within the organization Supporting employees driving trucks 718 M-Applications - Examples Retailing Sales Force Automation Hospitals Employee Tracking Wearable Devices Job Dispatch Image of the ZYPAD wrist wearable computer from Arcom Control Systems 19 Intrabusiness Applications and Others Inventory Management Customer Service B2B Applications Others ◦ Mobile Entertainment ◦ M-Government 20 Mobile Applications in Sports Nike iPod Nano 721 Location-Based Services location-tracking technology in mobile networks to target consumers with location-specific advertising on their mobile devices. marketer-controlled information specially tailored for the place where users access an advertising medium 722 A smart phone with GPS system in lcommerce. 723 Global Positioning Systems (GPS) For wikipedia & much more, click here! Artist's conception of GPS satellite in orbit Civilian GPS receiver ("GPS navigation device") in a marine application Automotive navigation system in a taxicab GPS receivers are now integrated in many mobile phones. 724 Location-based services involving maps 725 Pervasive Computing a post-desktop model of human-computer interaction in which information processing has been thoroughly integrated into everyday objects and activities. Engaging in many computational devices and systems simultaneously, and may not necessarily even be aware of doing so. Examples ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Home Lighting Water Control – sensors Home Security Home Entertainment Smart Cars – Collision Avoidance 26 RFID Radio-frequency identification (RFID) applied to or incorporated into a product, animal, or person for the purpose of identification and tracking using radio waves. Some tags can be read from several meters away and beyond the line of sight of the reader. 27 RFID Animal management using RFID technology. Santa Gertrudis cattle: The calf has an 28 Electronic Ear Tag and herd management tag (yellow). How RFID works 729 Managerial Issues Ethical & legal issues. Implementation issues. Failures in mobile computing & mcommerce. Mobile device management plans are too often non-existent. 730 END 31