Reading Club 1/22/09
advertisement

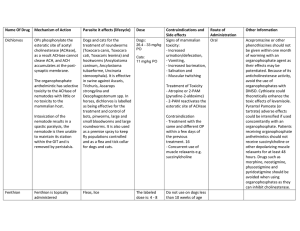
Toxicology Antidepressants and Pesticides (Illustrated by the Book of Bunny Suicides) A 25-year-old female with a history of depression was found unconscious. She has a non focal exam and she gets intubated. T 99.0F; HR 140/min; RR 14 on vent; BP 80/40 mmHg. Pupils are midpoint and reactive and axillae are dry. An ECG shows sinus tachycardia with a QRS interval of 0.15 seconds. ABG: pH 7.42; pCO2 37, PO2 106. Your next step should be to give: A. glucagon. B. physostigmine. C. propranolol. D. sodium bicarb. E. calcium. In a pt with suspected serotonin syndrome, it is reasonable to give: A. benztropine (Cogentin). B. bromocriptine. C. cyproheptadine. D. dantrolene. E. ondansetron The most significant toxicity of a pure bupropion (Wellbutrin) overdose is: A. neuroleptic malignant syndrome. B. orthostasis. C. seizures. D. serotonin syndrome. E. wide complex tachycardia. Which of the following is CORRECT regarding an overdose of tranylcypromine (Parnate): A. asymp pts need 24hrs of obs B. bradycardia & hypotension occur early in the course C. beta blockers are the drug of choice for ventricular dysrhythmias D. hemodialysis should be considered for severe ODs E. sxs start w/in 1-2hrs of the overdose Pralidoxime (2-PAM) reverses organophosphate poisoning by: A. a direct beta-agonist effect which treats bradycardia. B. increasing acetylcholine release from nerve endings. C. increasing norepinephrine release from nerve endings. D. breaking down the organophosphate molecules E. reversing the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. As an antidote, pralidoxime (2PAM) is: A. typically used before atropine B. effective against chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticides. C. necessary to treat carbamate insecticide toxicity. D. is often given in conjunction with physostigmine. E. necessary to reverse nicotinic effects of insecticide poisoning. A 2-year-old boy is found unresponsive a barn with muscle twitching, vomiting, diarrhea, and wheezing. It is likely he has accidentally ingested: A. parathion. B. jimson weed. C. DDT. D. nitrate fertilizers. E. Oil of wintergreen. A potentially lethal medication combination would be: A. phenelzine (Nardil) and meperidine (Demerol). B. imipramine (Tofranil) and bronchodilators. C. lithium and acetaminophen (Tylenol). D. theophylline and high dose steroids. E. thioridazine (Mellaril) and cimetidine (Tagamet). Which of the following EKG abnormalities is NOT expected in a TCA overdose? A. Prolonged QT interval B. QRS interval 0.13 seconds C. Right axis deviation D. Shortened PR interval E. Sinus tachycardia Which of the following is INCORRECT regarding cyclic antidepressant overdose? A. a-Adrenoceptor blockade B. Anticholinergic effects C. Calcium channel blockade D. Inhibition of reuptake of serotonin & norepinephrine E. Sodium channel blockade A 17yo F stated that she took an unknown amount of nortriptyline tabs 2.5 hrs PTA has endured 6 hrs of ED observation. Which of the following would prevent her from being medically cleared for psych? A. Absent bowel sounds B. Heart rate of 110 C. QRS duration 88 msec D. PR interval of 180 msec Which of the following statements regarding tricyclic antidepressants is INCORRECT? A. After a TCA overdose, the onset & progression of toxicity is rapid B. Neurologic impairment is rare. C The development of QRS prolongation is a sign of serious TCA toxicity D. Sodium channel blockade can result as a part of tricyclic overdose. Which of the following is CORRECT regarding tricyclic antidepressant overdose: A. CNS depression (disorientation, slurred speech, coma, respiratory depression), szs, myoclonus B. Anticholinergic toxicity marked by flushed skin, tachycardia, mydriasis, decreased bowel sounds, urinary retention C. ECG: R > S in aVR D. All of the statements are true. Which of the following is INCORRECT regarding the newer cyclic antidepressants? A. Trazodone (Desyrel): a triazolopyridine with almost no cardiac toxicity and only CNS depressive effects without seizures B. Amoxapine (Asendin): little cardiovascular toxicity, but high incidence of seizures & death C. Maprotiline (Ludiomil): a tetracyclic compound with less cv toxicity but more risk of szs D. Doxepin: significantly fewer cardiovascular toxic effects than other tricyclics. Which of the following is NOT a pharmacologic effects of the cyclic antidepressants? A. inhibition of norepinephrine, serotonin & dopamine reuptake in the CNS B. direct stimulation of anterior horn cells C. anticholinergic effects and alphaadrenergic blockade D. quinidine-like membrane-stabilizing effects. Which of the following techniques would FAIL to alkalinize the blood in a cyclic antidepressant overdose pt? A. sodium bicarbonate, 0.5-3 mEq/kg IV over several minutes, then 2 amps bicarb in 1 L D5W started at 50 mL/hr and titrated to a pH of 7.5 (7.4 to 7.6). B. hyperventilation to a pH of 7.5 C. hypoventilation to a pH of 7.5 The first clinical sign of toxicity with chlorinated hydrocarbon pesticides is: A. Allergic manifestations, i.e., lacrimation, rhinitis, rhinorrhea, sneezing, throat irritation and pharyngeal & laryngeal edema B. Chemical burns of the oropharynx soon after ingestion C. Hypermetabolic & hyperthermic, i.e., tachycardic, tachypneic, diaphoretic D. Neurotoxic symptoms: seizures, confusion, combativeness, muscle twitching E. The cholinergic syndrome, SLUDGE (salivation, lacrimation, urinary incontinence, defecation, gastroenteritis and emesis) Management of organophosphate toxicity includes: A. a clinical decision and disposition tree since there are no definitive lab studies to confirm suspected exposure B. Discontinuing use of atropine if marked tachycardia & mydriasis occurs C. Prevention of morbidity primarily arising from cv complications D. Use of atropine until drying of respiratory secretions is accomplished E. Use of pralidoxime only if started within the first 24 hrs after poisoning due to aging of the organophosphate-acetylcholinesterase complex Which of the following is CORRECT regarding clinical features seen in substituted phenol poisoning? A. Allergic manifestations, such as, lacrimation, rhinitis, rhinorrhea, sneezing, throat irritation and pharyngeal and laryngeal edema B. May be implicated by the presence of a strong, rancid odor on the patient's clothing, breath or even vomitus C. Produce a characteristic yellow staining of the skin or mucous membranes with dermal exposures D. Selectively concentrates in the lungs because of an amine uptake mechanism in the alveolar cells leading to progressive pulmonary injury E. Skeletal muscle is the target organ for toxicity leading to diffuse myotonia and muscle fasciculations A 3-year old M presents new-onset of seizure activity. You administer benzodiazepines to control the szs. Blood glucose is normal and after the child is placed on the monitor, you find that he is actually in v tach. The mother tells you that she recently treated all of her children with Lindane that she got for a scabies infestation. Which of the following is the most appropriate antiarrhythmic to give? A. Lidocaine B. Magnesium C. Phenytoin D. Procainamide E. Propranolol Which of the following statements is INCORRECT regarding the management of organophosphate/carbamate poisoning? A. All pts exposed to organophosphates or carbamates should be decontaminated by removal of clothes & bathing with soap and water B. Obtain an airway & oxygenate prior to atropine to minimize the chance of v fib. Tx szs & arrhythmias prn C. Atropine: 0.02 mg/kg q 5-30 minutes until atropinization occurs (tachycardia, dryness, mydriasis, flushing, etc.); massive doses may be required D. Pralidoxime, 25-50 mg/kg IV over 15-30 min; repeat in 1-2 hrs, or 0.5g/hr by drip for severe cases. E. Asymptomatic pts may be observed for 4 hrs then safely discharged home. Which of the following statements is INCORRECT regarding the effects of and indications for pralidoxime in organophosphate poisoning? A. Inactivates circulating unbonded organophosphate molecules. B. Reactivates cholinesterase by cleaving the organophosphate-cholinesterase chemical bonds. C. Not indicated in carbamate poisoning, but in doubtful cases it should be given based on clinical impression unless and until the precise toxic substance is known. D. 2-PAM can be given IV push with little to no potential toxicity Signs and symptoms of organophosphate and carbamate poisoning are due to stimulation of what 2 systems? A. nicotinic, muscarinic B. muscarinic, serotonergic C. muscarinic, adrenergic D. adrenergic; serotonergic Which of the following statements is INCORRECT regarding the Intermediate Syndrome seen with organophosphate poisoning? A. The syndrome is marked by respiratory failure, bulbar, nuchal & proximal limb muscle weakness B. Associated w/ exposure to malathion, parathion, diazinon & dimethoate C. Occurs 10 days after resolution of the acute poisoning (cholinergic crisis) D. Patients diagnosed as having an Intermediate Syndrome have red blood cell cholinesterase levels of less than 20%. THE END