Kingdom Plantae Study Guide
advertisement

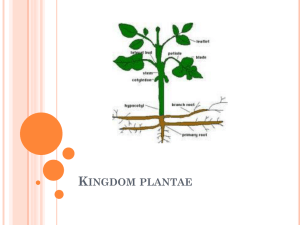
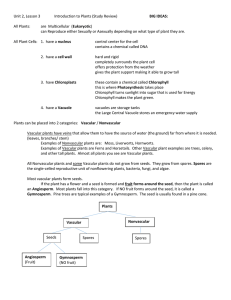
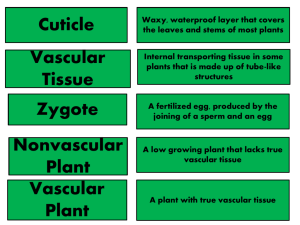
Kingdom Plantae Study Guide General Kingdom Characteristics Producers- Make glucose and oxygen from CO2 & H2O by photosynthesis in chloroplasts Cellulose cell wall “Move” only a little by quick growth- Outside cells of Venus fly trap grow to trap prey Sexual reproduction through spores or seeds 4 Phyla (also called divisions): 1. Phylum Bryophyta- Mosses and liverworts. Nonvascular. Sexual Spores. Must live in moist or wet areas Because they have no vessels to conduct water to leaves. 2. Phylum Pteridophyta- (bird-plant) Ferns. Vascular. Spores. Can live in slightly dryer (not dry) areas, since vessels can conduct water from soil. 3. Phylum Gymnosperma- (Naked seed)- Conifers or cone bearing trees or shrubs. Vascular. Nonflowering. Bare seeds inside cones. 4. Phylum Angiosperma, Class Monocotyledonae- Flowering plants, bulbous plants, grasses, bamboo. Seeds in shell or fruit. Vascular. Veins run parallel to each other. Seeds are in one part. Single first leaf from seed. 5. Phylum Angiosperma, Class Dicotyledonae- Flowering plants, trees, most edible fruit trees except plantains. Seeds in shell or fruit. Vascular. Veins are branched. Seeds are in 2 parts like beans or split peas. Two first leaves from seed. Plant Responses to Stimuli: Different from animals, even if they might appear the same. Photoperiod (length of day) for flowering, leaf color, and reproduction Phototropism- Stems & leaves turn towards light Geotropism- Roots grow towards gravity (+); stem & shoots grow away from gravity (-) Thigmatropism- Leaf or flower sensitive to touch; Grow quickly on one side to open or close. Examples: Venus Fly Trap, Sensitivity Fern, Morning Glory, Touch-Me-Not