Rate of Reaction

Write your homework – leave it to be stamped (INCLUDE THE DATES!)
Update your Table of Contents for today
Review Endothermic Vs. Exothermic with your table partner!
Date Session
#
11/4 -
11/5
4
Activity
Rate of Reaction Note/Lab Guide
Study Guide for Chemistry Test 3
Page
#
6
7
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O + energy --> 6O
2
+ C
6
H
12
O
6
◦ Anybody know what this the chemical equation for?
◦ Photosynthesis
6O
2
+ C
6
H
12
O
6
--> 6H
2
O + 6CO
2
+ energy
◦ Anybody know what this the chemical equation for?
◦ Cellular Respiration
The last few classes we focused on the Law of Conservation of
Mass/Matter, or the idea of “What
Goes In, Must Come Out,”
BUT
the
Law of Conservation of Mass does not tell us anything about
why
a reaction occurs in the first place or the
rate/speed
at which they occur…
With your group, brainstorm things that you think affect the rate, or speed, of a chemical reaction!
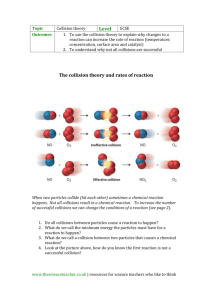
COLLISIONS BETWEEN
MOLECULES ARE WHAT
MAKE CHEMICAL
REACTIONS OCCUR!
Collisions are a factor in ALL reactions, but the other 5 factors below affect the speed/rate at which these collisions and therefore the reactions occur:
◦ Concentration
◦ Temperature
◦ Pressure
◦ Surface Area
◦ Catalysts
Collision Theory – molecules bumping into each other lead to chemical reactions
How does this affect the Rate of Reaction?
◦ More collisions = more reactions
◦ Less collisions = less reactions
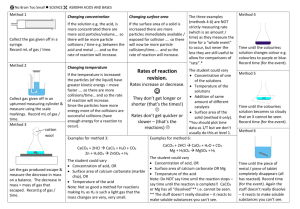
Concentration – the amount or strength of the chemical
How does this affect the Rate of Reaction?
Higher Concentration (concentrated) = more collisions = increased reaction rates
Lower Concentration (dilute) = less collisions = decreased reaction rates
Temperature – how hot/cold a substance is due to movement of particles
◦ What happens to particle movement when the temperature increases or decreases?
How does this affect the Rate of Reaction?
Higher Temperature = more collisions = increased reaction rates
Lower Temperature = less collisions = decreased reaction rates
Pressure – a force on particles depending on the amount of space they have to move
◦ How do objects under pressure react?
(Hint: think of open vs. closed reactions)
How does this affect the Rate of Reaction?
Higher Pressure = more collisions = increased reaction rates
Lower Pressure = less collisions = decreased reaction rates
Surface Area – the area that an object occupies (the sum of all the surfaces of that object)
How can you increase an objects surface area?
How does this affect the Rate of Reaction?
Increased surface area = more collisions = increased reaction rates
Decreased surface area = less collisions = decreased reaction rates
CHEMICAL REACTIONS NEED
ENERGY TO OCCUR!
Catalysts – a substance that acts as a
“matchmaker” to jump start a reaction or make it faster
◦ Reduces the amount of energy needed to make the reaction occur
Catalysts are not affected or used during the reaction – they are still left over
Inhibitors are the opposite of catalysts – how would you describe/define them?
Group Leader – manages the group, reads the directions, makes sure everyone records data
Supply Manager – responsible for getting, returning and clean-up of supplies
Data Technician – Records your group’s data on the class data table on the board as soon as you have it!
Timekeeper – someone with a timer/stopwatch on their phone to time the reaction
Send your supply manager to get 2 test tubes - some of you will receive solutions B1 & C and some of you will receive solutions B2 & C
Pour one of the solutions into the other so all of the liquid is in one test tube…START YOUR TIMER
IMMEDIATELY!
You must watch your experiment until you see the color change. If you are not paying attention, you will miss it!
STOP YOUR TIMER AS SOON AS YOU SEE THE REACTION
BEGIN!
Record the reaction times on your data table & decide as a group which factor affected the reaction rate!
Send your supply manager to get your glue/water mixture, Borax and a popsicle stick.
Mix the Borax into the glue/water mixture and stir with the popsicle stick.
The borax DOES NOT BOND with the glue….it bonds the water with the glue, but is not part of the reaction….it is the leftover liquid in the bottom of your cup
What role does the Borax play in this reaction?
Independent
Variable
Powdered
AlkaSeltzer Tablet
Broken AlkaSeltzer
Tablet
Whole Alka Seltzer
Tablet
Alka Seltzer in Hot
Water
Alka Seltzer in
Room Temp Water
Alka Seltzer in
Cold Water
Alka-Seltzer in
Film Canister 1
Alka-Seltzer in
Film Canister 2
What is Affecting the Reaction Rate?
Temperature Time for Reaction to
Complete
N/A
N/A
N/A
HOT
Room Temp
COLD
N/A
N/A
Complete the Study Guide by
NEXT CLASS!
Start reviewing for Chemistry
Test 3 in 2 classes!
Write your homework – leave it to be stamped!
Update your Table of Contents for today!
Get your Study Guide out to be checked
Review with your Table Partners while
I’m checking the homework
Date Session
#
11/6 -
11/9
5
Review & Wrap Up
Activity Page
#
8
HgO + Cl
2
HgCl + O
2
PbBr
2
+ HCl HBr + PbCl
2
Na
3
P + CaF
2
NaF + Ca
3
P
2
Energy is a reactant
Temperature decreases, so it feels cool/cold
Example:
Photosynthesis
Energy is a product
Temperature increases, so it feels warm/hot
Example: Cellular
Respiration
Have one person read the directions & one person in charge of supplies.
◦ Send your supply manager to get the bin
◦ All students must wear goggles
◦ Perform the experiment with your group, but write the explanation ON YOUR OWN.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OttRV5y kP7A
Collision Theory = all reactions take place due to collisions between molecules, but some things are able to increase or decrease the amount of collisions:
◦ Concentration = amount or strength
◦ Temperature = is due to particle movement
◦ Surface Area = break things into pieces to increase the surface area
◦ Pressure = the amount of space the particles have to move in (open vs. closed container)
◦ Catalyst = makes reactions go faster (reduces energy needed)
◦ Inhibitor = makes reactions go slower
Log in to www.zondle.com
You should have already set up an account, so click on the “google login” button
Your class code is: ____________________
There are 2 games that have been shared with you:
◦ Law of Conservation of Mass
◦ Rate of Reaction
Write your homework – leave it to be stamped!
Update your Table of Contents for today…we are starting a mini Energy unit next, but you can just use the same table of contents!
Grab a Vocab List off the front counter to use for the review game…go through it…which words do you want to go over?
Date Session
#
11/10 -
11/12
6
Energy Pros & Cons
Activity Page
#
9
You need a piece of notebook paper
Number 1-10 5 times for each of the
5 rounds
Please clear your desk of everything but your pencil and calculator
Please put the folders up between you and your table partners.
WHEN YOU FINISH:
◦ Put your test in the basket and make sure your name is on it!
◦ Start the Energy Pros and Cons…you will have time next class to finish it.