Contrasting Cold War Terms
advertisement

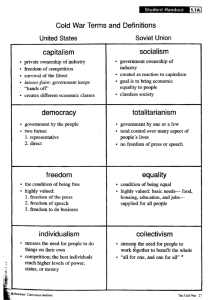
How did America become a superpower? You will learn eight key Cold War terms to help you understand how contrasting valued led to tension between the United States and the Soviet Union during the Cold War? You will finally be able to answer the question of “who cares if they want to be Communist over in Russia?” TODAY’S GOAL… CAN YOU LEARN EACH OF THE 8 COLD WAR TERMS AND CONNECT THEM TO ONE OF THE SUPERPOWERS, USA OR RUSSIA? 1. With your group, review the Cold War Terms and their definitions using the textbook. 2. Examine the worksheets, with their illustrations, written information, and quotations at your station. 3. Discuss which term fits best with your card. Record the number A.1-A.8 next to the term you select Write a brief explanation next to your choice Identify the quote you believe best represented the term and copy it on to your handout. 4. CHECK with my to make sure you are correct before moving to the next station! 1. You and your group will explain ONE of the key terms to the class. As I put up that visual, you can stand at your seats and explain the connection. 2. Decide where your term fits on the spectrum of MOST LIKELY TO PRODUCE A HAPPY AND PRODUCTIVE SOCIETY. Condition of being equal Meeting basic needs, such as food, housing, education, and jobs. Everyone gets one! American Perspective Soviet Perspective Equality of opportunity and Equality of condition was essential equality before the law are both needed for a happy and healthy society Giving necessities without working for it would undermine the quality of a work ethic US moved towards equality and opportunity before the law during the Cold War for a healthy society Society MUST share material wealth No one should have an unfair advantage During the Cold War, Soviets provided education, health care, and other basic necessities Never fully achieved in Russia Governing by the people through voting Two forms: Representative Direct American Perspective Soviet Perspective Best system of Cannot promote democracy and government American makes decision by majority rule capitalism at the same time Democracy = economic system that rewards equality Few take advantage of the many Misery and poverty stem from this Poverty rate in the US during the Cold War was an example as it rose Private ownership of industry Freedom of competition Survival of the fittest Laissez-faire government Various economic and socioeconomic classes American Perspective Soviet Perspective Offers people the opportunity Flawed economic society to better themselves through hard work Incentives Better products and production rates Better work ethic Goods at a lower price Brings out the best in people Emphasis on competition breeds selfishness and undermines cooperation and community Argued poverty and oppression in the world were the result of capitalism! People working together to benefit the whole The greater common good “all for one, and one for all” American Perspective Soviet Perspective Violates human nature Shared ownership of all Doomed to failure Violated the individuals right to own property property is only way to create fair society In USSR, society owned every factory, business, and farm COLLECTIVELY Fruits of society’s labor is fairly distributed Individual pursuits and achievements are highly valued and sought after People working in their own best interest to reach their highest level of achievement which will in turn benefit society American Perspective Soviet Perspective Peoples lives are determined Produces winners by inner fortitude Human nature is to be Individualistic Competitive Society benefits more when each individual is reaching their highest potential Competition is a positive thing and losers Results in a society full of inequality Government ownership of industry End Goal is economic equality for all people Classless society American Perspective Soviet Perspective Threatens one of America’s Response to the inequalities of most basic rights, the individual right to own and control property Inhibits individuals desire and ability to achieve for the betterment of society US Constitution provides for protection of private ownership of business enterprises the Capitalist system Government ownership provided a means by which wealth in society could be evenly spread Only shared ownership can prevent the abuses of capitalism The condition of being free at all times Freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and freedom of business and work is a highly valued entity American Perspective Soviet Perspective At the core of a happy and People are not free unless they productive society is freedom Fought for freedom in the American Revolution, Civil War, World War 1, and World War II share of the countries wealth can cover their basic needs Redistribution of wealth was essential and government must control the press and industry to prohibit anyone from exploiting and denying freedom to the working class Government by one or a few people Total control over many aspects of people’s everyday lives No Freedom of speech or press American Perspective Soviet Perspective Unacceptable in America, Required to transform an threatens out basic human needs such as freedom of the press, freedom of assembly, etc A healthy and productive society can only be achieved when people are able to express their views unequal society into one in which wealth is evenly distributed Protecting the interests of society against a few selfish people’s desires requires governmental powers to silence dissent Tell me another example of a word that means something to you, but something totally different to someone else. Please write your answer on the back of your paper.