2. - s3.amazonaws.com
advertisement

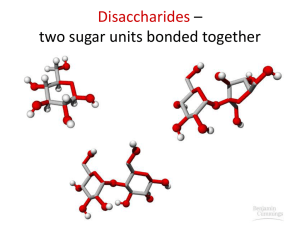
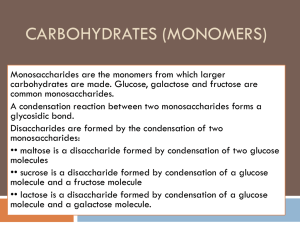
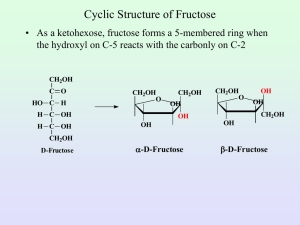
Objectives 1.To know the chemical formulas for the monosaccharides (monomers) Glucose, Fructose and Galactose. 2. To be able to identify the following disaccharides: Maltose, Sucrose and Lactose. 3. To be know the difference between CONDENSATION and HYDROLYSIS reactions. Carbohydrates Carbohydrates contain 3 elements: 1. Carbon (C) 2. Hydrogen (H) 3. Oxygen (O) Carbohydrates are found in one of three forms: 1. Monosaccharides eg. Glucose, Fructose 2. Disaccharides (both sugars) eg. Maltose, Sucrose 3. Polysaccharides eg. Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen C Carbon prefers to have covalent four bonds The most common and important MONOSACHARIDE is Glucose. Its formula is C6H12O6 The molecule is also known as a monomer Glucose forms a 6 sided ring structure DISACCHARIDES are formed when two monosacccharides are joined together by a GLYCOSIDIC BOND Glucose + Glucose = Maltose (disaccharide) + Water Condensation Reaction to produce Maltose Condensation reaction to produce sucrose This is the GALACTOSE MOLECULE. Draw the structural formula for LACTOSE Here are the answers….what were the questions? Monomer Lactose Disaccharide Condensation Reaction Disaccharides On the whiteboards provided draw: A glucose molecule Maltose Glucose comes in two forms alpha and beta This is maltose. It is joined between Carbons 1 and 4. We say therefore that it has a 1-4 GLYCOSIDIC bond Disaccharides can be broken down back into monosaccharides by the addition of water. These reactions are often catalysed by enzymes such as MALTASE. These are HYDROLYSIS reactions. Task Test your partner’s biomolecular knowledge and vocabulary by writing a “gap” passage For example, a sentence in your passage could be… disaccharide Sucrose is an example of a ___________ that is formed from a combination of the fructose monomers glucose and ________. Objectives 1.To know the chemical formulas for the monosaccharides (monomers) Glucose, Fructose and Galactose. 2. To be able to identify the following disaccharides: Maltose, Sucrose and Lactose. 3. To be know the difference between CONDENSATION and HYDROLYSIS reactions.