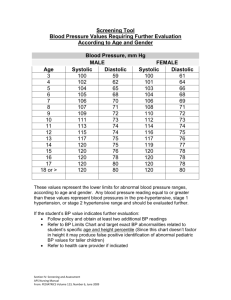
VITAL SIGNS BLOOD PRESSURE Learning Objective: : After completing this lesson, the students will be able to; BLOOD PRESSURE The force produced by the volume of blood pressing on the resisting walls of the arteries Systole – the working period of the heart The heart contracts and pumps blood out into the circulation. Diastole – the resting period of the heart The time when the heart is filling with blood, which will be pumped out during the next systole. Blood pressure Force exerted by blood against arterial walls Work of the heart reflected in periphery via BP Blood Pressure Systolic Peak pressure exerted against arterial walls as the ventricles contract and eject blood Diastolic Minimum pressure exerted against arterial walls between contraction when the heart is at rest Blood pressure Measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) Recorded as systolic over diastolic Pulse pressure Difference between systolic and diastolic BP Regulation The body constantly adjusts arterial pressure to supply blood to body tissues Influenced by three factors Cardiac function Peripheral vascular resistance BP Regulation Blood volume Normal = 5000 ml Volume increases=BP increases Volume decreases= BP decreases Viscosity= reaction same as volume BP Regulation Elasticity Less elasticity creates greater resistance to blood flow= > systolic BP Decreased in smokers and increased cholesterol Additional considerations for BP Palpation Errors Used when BP is too weak to hear Wrong size cuff, deflating too rapidly, incorrect placement Thigh Measures 30-40 mm HG less than normal FACTORS INFLUENCING BLOOD PRESSURE 1. Age – blood pressure rises with age. Arteries lose their elasticity and become more rigid (arteriosclerosis) resulting in even greater resistance to heart’s effort to fill the arteries with blood or arteries may fill with fat deposits (atherosclerosis) that interferes with the amount of blood that can be contained within the arteries. Thus blood pressure is increased. FACTORS INFLUENCING BLOOD PRESSURE 2. Time of day – BP tends to be lowest in morning than later during the day 3. Women have lower blood pressure than men FACTORS INFLUENCING BLOOD PRESSURE 4. Exercise and activity – increases during periods of activity or exercise through regular exercise helps maintain blood pressure within normal FACTORS INFLUENCING BLOOD PRESSURE 5. Emotions and pain tends to make BP rise FACTORS INFLUENCING BLOOD PRESSURE 6. Other factors: A person has lower BP when lying down than when sitting or standing BP rises when urinary bladder is full and when legs are crossed BP rises when a person uses tobacco, drinks caffeinated beverage or is cold Variations in BP Values The Joint National Committee BP ClassificationAdult older than 18 years. Normal: less than120/80 mm Hg Hypotension: less than100mm HG Pre hypertension: more 120/80 mm Hg Hypertension: 140/90= Stage 1; 160/100= Stage 2 Values For the Department of health and Philippine heart Association - Normal BP will fall under 120/80mmHg (the ideal BP for people with lower risk of heart disease or stroke) - Due to Asian ethnicity, Caucasian physical profile is different- bigger build. Variations in BP Persistant increase in BP Damage to vessels; loss of elasticity; decrease in blood flow to vital organs Measurement of BP Indirect Most common, accurate estimate Equipment Sphygomanometer and stethescope Measurement of BP Direct In patient setting only Catheter is threaded into an artery under sterile conditions Attached to tubing that is connected to monitoring system Displayed as waveform on monitoring screen Other BP issues Orthostatic or postural hypotension Sudden drop in BP on moving from lying to sitting or standing position Primary or essential hypertension Diagnosed when no known cause for increase Accounts for at least 90% of all cases of hypertension Remember the following for accuracy of your readings Instruct your patients to avoid coffee, smoking or any other unprescribed drug with sympathomimetic activity on the day of the measurement What Abnormal Results Mean Blood pressure The minimal SBP required to maintain perfusion varies with the individual. Interpretation of low values must take into account the clinical situation. Blood pressure for adult Physician will want to see multiple blood pressure measurements over several days or weeks before making a diagnosis of hypertension and initiating treatment. What Abnormal Results Mean Pre-high blood pressure: systolic pressure consistently 120 to 139, or diastolic 80 to 89 Stage 1 high blood pressure: systolic pressure consistently 140 to 159, or diastolic 90 to 99 What Abnormal Results Mean Stage 2 high blood pressure: systolic pressure consistently 160 or over, or diastolic 100 or over What Abnormal Results Mean Hypotension (blood pressure below normal): may be indicated by a systolic pressure lower than 90, or a pressure 25 mmHg lower than usual Hypertension High blood pressure greater than 139-89.. Blood pressure may be affected by many different conditions Blood pressure may be affected by many different conditions Cardiovascular disorders Neurological conditions Kidney and urological disorders Blood pressure may be affected by many different conditions Pre eclampsia in pregnant women Psychological factors such as stress, anger, or fear Eclampsia END OF SLIDE