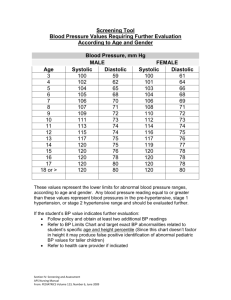
PEDIATRIC NORMALS BLOOD PRESSURE Newborn – 96 hrs: Infants: Toddlers: Preschooler: School-aged: Adolescents: Systolic = 60-90 Diastolic = 20-60 Systolic = 74-100 Diastolic = 50-70 Systolic = 80-112 Diastolic = 50-80 Systolic = 82-112 Diastolic = 50-78 Systolic = 84-112 Diastolic = 54-80 Systolic = 94-140 Diastolic = 62-88 RESPIRATORY RATE <3months: 3 to <12 months: 1year to < 4 years: 4 years to 12 years: > 12 years: 30-60 rpm 24-50 rpm 20-40 rpm 20-30 rpm 12–15 rpm CALORIC NEEDS High-risk neonate: Neonate: 1-2 years 2-6 years 7-9 years 10+ 120-150 cal/kg/day 100-120 cal/kg/day 90-100 cal/kg/day 80-90 cal/kg/day 70-80 cal/kg/day 50-60 cal/kg/day HEART RATE <3 mo: 3 mos to <1 yr: 1 yr to <4 yrs: 4 yrs to 12 yrs: >12 yrs: 110-150 100-150 90-120 70-110 60-100 CALCULATING FLUID MAINTENANCE For the first 10 kg of weight For the second 10 kg of weight For the remaining kg of weight x 4mL/hr x 2mL/hr x 1mL/hr Example: The child’s weight is 24.8 kg. 10 X 4 = 10 X 2 = 4.8 X 1 = 40 20 4.8 64.8mL/hour Compare the hourly and daily intake needs with what the child is actually receiving. Review the TRENDS of the I & O and assess the expected, desired and actual responses of the patient. Consider fluid via IV, PO, NG, OG to ensure the maintenance fluid volume is achieved. CORRELATE hydration with vital signs, neuron status, wound healing, pulmonary and cardiovascular status, renal function and electrolyte balance. URINE OUTPUT ASSESSMENT Minimum urine output is 1 mL/kg/hour. The minimum urine output preference is 1-2 mL/kg/hour. Example: 6 kg infant 6 kg X 1 mL = 6 mL/hour X 24 hours = 144 mL in 24 hours